Abstract
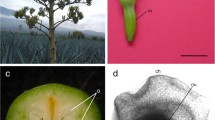
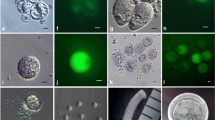
Mature ovules of Dianthus (Caryophyllaceae) were histologically observed by clearing and serial sectioning to characterize the cells of the embryo sac. The results show that the mature embryo sac was located deep inside the hemitropous ovule due to thick nucellar tissue at the micropylar region. For the isolation of the embryo sacs, ovules were collected from ovaries of flowers 1 day after anthesis, and treated with an enzyme solution for digesting cell walls on a gyratory shaker. After 12 h of enzyme treatment, these ovules were dissected using a glass needle under an inverted microscope to release the embryo sacs. The embryo sacs, characterized by their specific size, were successfully released by these successive treatments. The viability of the embryo sacs was more than 80% as assessed with fluorescein diacetate staining. Fluorescent staining with 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole revealed the nuclei of the egg apparatus in the isolated embryo sacs. The procedure for isolating embryo sacs established in this study will offer a new approach to further in vitro studies on fertilization in Dianthus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 20 January 1999 / Revision received: 12 July 1999 / Accepted: 17 August 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoshino, Y., Nishino, E. & Mii, M. Isolation of embryo sacs from Dianthus ovules by enzymatic treatments and microdissection. Plant Cell Reports 19, 443–447 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990050753
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990050753