Abstract
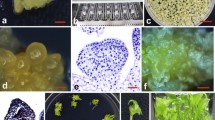
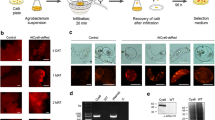
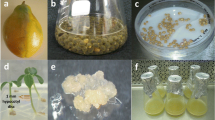
A protocol was developed for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of embryogenic suspension cultures of cassava. The bacterial strain ABI containing the binary vector pMON977 with the nptII gene as selectable marker and an intron-interrupted uidA gene (encoding β-glucuronidase) as visible marker was used for the experiments. Selection of transformed tissue with paromomycin resulted in the establishment of antibiotic-resistant, β-glucuronidase-expressing lines of friable embryogenic callus, from which embryos and subsequently plants were regenerated. Southern blot analysis demonstrated stable integration of the uidA gene into the cassava genome in five lines of transformed embryogenic suspension cultures and in two plant lines.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
González, A., Schöpke, C., Taylor, N. et al. Regeneration of transgenic cassava plants (Manihot esculenta Crantz) through Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of embryogenic suspension cultures. Plant Cell Reports 17, 827–831 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990050492
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990050492