Abstract
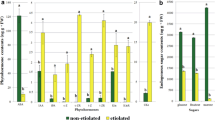
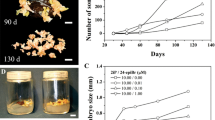
Endogenous indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), abscisic acid (ABA) and cytokinins [zeatin (Z) zeatin riboside, dihydrozeatin, dihydrozeatin riboside, N6-isopentenyl adenine (iP) and N6-isopentenyladenine riboside] were evaluated in hazelnut (Corylus avellana L.) cotyledons of different developmental stage and genetic source for their somatic embryogenic capacity. There was an inverse correlation between the embryogenic potential of cotyledons and the degree of maturity of zygotic embryos, the first characteristic being associated with iP-type cytokinins and the second with Z-type cytokinins. Although the differences in total cytokinin, ABA and IAA contents between the cotyledons were small, the IAA/ABA and, mainly, the iP-type/Z-type cytokinin ratios were found to be two good indexes of the embryogenic competence of explants, suggesting that the endogenous hormonal balance is a very important factor defining the in vitro potential of hazelnut cotyledons.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 6 January 1997 / Revision received: 3 March 1997 / Accepted 1 April 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Centeno, M., Rodríguez, R., Berros, B. et al. Endogenous hormonal content and somatic embryogenic capacity of Corylus avellana L. cotyledons. Plant Cell Reports 17, 139–144 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990050367
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002990050367