Abstract
Key message
MeCIPK23 interacts with MeCBL1/9, and they confer improved defense response, providing potential genes for further genetic breeding in cassava.
Abstract
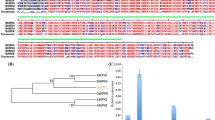
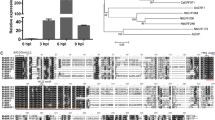
Cassava (Manihot esculenta) is an important food crop in tropical area, but its production is largely affected by cassava bacterial blight. However, the information of defense-related genes in cassava is very limited. Calcium ions play essential roles in plant development and stress signaling pathways. Calcineurin B-like proteins (CBLs) and CBL-interacting protein kinases (CIPKs) are crucial components of calcium signals. In this study, systematic expression profile of 25MeCIPKs in response to Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis (Xam) infection was examined, by which seven candidate MeCIPKs were chosen for functional investigation. Through transient expression in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves, we found that six MeCIPKs (MeCIPK5, MeCIPK8, MeCIPK12, MeCIPK22, MeCIPK23 and MeCIPK24) conferred improved defense response, via regulating the transcripts of several defense-related genes. Notably, we found that MeCIPK23 interacted with MeCBL1 and MeCBL9, and overexpression of these genes conferred improved defense response. On the contrary, virus-induced gene silencing of either MeCIPK23 or MeCBL1/9 or both genes resulted in disease sensitive in cassava. To our knowledge, this is the first study identifying MeCIPK23 as well as MeCBL1 and MeCBL9 that confer enhanced defense response against Xam.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- BiFC:
-
Biomolecular fluorescence complementation
- CaM:
-
Calmodulin
- CBL:
-
Calcineurin B-like protein
- CIPK:
-
CBL-interacting protein kinase
- CML:
-
Calmodulin-like protein
- CPK:
-
Calcium-dependent protein kinase
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole
- dpi:
-
Day post infiltration
- EL:
-
Electrolyte leakage
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- H+ :
-
Hydrogen ion
- H2O2 :
-
Hydrogen peroxide
- MAMPs/PAMPs:
-
Microbe/pathogen-associated molecular patterns
- NOX:
-
NADPH oxidase
- NPR1:
-
Nonexpresser of PR genes 1
- O2 ·− :
-
Superoxide radical
- PM:
-
Plasma membrane
- PP2C:
-
2C-type protein phosphatase
- PPI:
-
Protein–phosphatase interaction
- PR:
-
Pathogensis-related gene
- Rboh:
-
Respiratory burst oxidase homologues
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- VIGS:
-
Virus-induced gene silencing
- Xam :
-
Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis
References
Albrecht V, Ritz O, Linder S, Harter K, Kudla J (2001) The NAF domain defines a novel protein-protein interaction module conserved in Ca2+-regulated kinases. EMBO J 20:1051–1063
Batistic O, Rehers M, Akerman A et al (2012) S-acylation-dependent association of the calcium sensor CBL2 with the vacuolar membrane is essential for proper abscisic acid responses. Cell Res 22:1155–1168
Camilo L, Soto M, Restrepo S (2005) Gene expression profile in response to Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis infection in cassava using a cDNA microarray. Plant Mol Biol 57:393–410
Chaves-Sanjuan A, Sanchez-Barrena MJ, Gonzalez-Rubio JM et al (2014) Structural basis of the regulatory mechanism of the plant CIPK family of protein kinases controlling ion homeostasis and abiotic stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:4532–4541
Chen X, Gu Z, Xin D et al (2011) Identification and characterization of putative CIPK genes in maize. J Genet Genom 38:77–87
Chen L, Ren F, Zhou L, Wang QQ, Zhong H, Li XB (2012) The Brassica napus Calcineurin B-Like 1/CBL-interacting protein kinase 6 (CBL1/CIPK6) component is involved in the plant response to abiotic stress and ABA signaling. J Exp Bot 63:6211–6222
Cutler SR, Ehrhardt DW, Griffitts JS, Somerville CR (2000) Random GFP::cDNA fusions enable visualization of subcellular structures in cells of Arabidopsis at a high frequency. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:3718–3723
de la Torre F, Gutiérrez-Beltrán E, Pareja-Jaime Y, Chakravarthy S, Marti GB, del Pozo O (2013) The tomato calcium sensor Cbl10 and its interacting protein kinase Cipk6 define a signaling pathway in plant immunity. Plant Cell 25:2748–2764
Drerup MM, Schlucking K, Hashimoto K et al (2013) The calcineurin B-like calcium sensors CBL1 and CBL9 together with their interacting protein kinase CIPK26 regulate the Arabidopsis NADPH oxidase RBOHF. Mol Plant 6:559–569
Eckert C, Offenborn JN, Heinz T et al (2014) The vacuolar calcium sensors CBL2 and CBL3 affect seed size and embryonic development in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 78:146–156
Evans NH, McAinsh MR, Hetherington AM (2001) Calcium oscillations in higher plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4:415–420
Hauck P, Thilmony R, He SY (2003) A Pseudomonas syringae type III effector suppresses cell wall-based extracellular defence in susceptible Arabidopsis plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:8577–8582
Hu HC, Wang YY, Tsay YF (2009) AtCIPK8, a CBL-interacting protein kinase, regulates the low-affinity phase of the primary nitrate response. Plant J 57:264–278
Hu Y, Jiang L, Wang F, Yu D (2013) Jasmonate regulates the inducer of cbf expression-C-repeat binding factor/DRE binding factor1 cascade and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 25:2907–2924
Hu W, Wei Y, Xia Z et al (2015a) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the NAC transcription factor family in cassava. PLoS ONE 10:e0136993
Hu W, Xia Z, Yan Y et al (2015b) Genome-wide gene phylogeny of CIPK family in cassava and expression analysis of partial drought-induced genes. Front Plant Sci 6:187
Hu DG, Ma QJ, Sun CH, Sun MH, You CX, Hao YJ (2016) Overexpression of MdSOS2L1, a CIPK protein kinase, increases the antioxidant metabolites to enhance salt tolerance in apple and tomato. Physiol Plant 156:201–214
Kim KN, Cheong YH, Grant JJ, Pandey GK, Luan S (2003) CIPK3, a calcium sensor-associated protein kinase that regulates abscisic acid and cold signal transduction in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 15:411–423
Kleist TJ, Luan S (2016) Constant change: dynamic regulation of membrane transport by calcium signalling networks keeps plants in tune with their environment. Plant Cell Environ 39:467–481
Kolukisaoglu U, Weinl S, Blazevic D, Batistic O, Kudla J (2004) Calcium sensors and their interacting protein kinases: genomics of the Arabidopsis and rice CBL-CIPK signaling networks. Plant Physiol 134:43–58
Kudla J, Batistic O, Hashimoto K (2010) Calcium signals: the lead currency of plant information processing. Plant Cell 22:541–563
Kurusu T, Hamada J, Hamada H, Hanamata S, Kuchitsu K (2010) Roles of calcineurin B-like protein-interacting protein kinases in innate immunity in rice. Plant Signal Behav 5:1045–1047
Lan WZ, Lee SC, Che YF, Jiang YQ, Luan S (2011) Mechanistic analysis of AKT1 regulation by the CBL-CIPK-PP2CA interactions. Mol Plant 4:527–536
Li L, Kim BG, Cheong YH, Pandey GK, Luan S (2006) A Ca2+ signaling pathway regulates a K+ channel for low-K response in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:12625–12630
Li ZY, Xu ZS, He GY et al (2012) Overexpression of soybean GmCBL1 enhances abiotic stress tolerance and promotes hypocotyl elongation in Arabidopsis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 427:731–736
Liu J, Zhu JK (1998) A calcium sensor homolog required for plant salt tolerance. Science 280:1943–1945
Liu Y, Schiff M, Dinesh-Kumar SP (2002) Virus-induced gene silencing in tomato. Plant J 31:777–786
Liu J, Liu L, Li Y et al (2015) Role for the banana AGAMOUS-like gene MaMADS7 in regulation of fruit ripening and quality. Physiol Plant 155:217–231
Luan S, Lan W, Chul-Lee S (2009) Potassium nutrition, sodium toxicity, and calcium signaling: connections through the CBL-CIPK network. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:339–346
Lyzenga WJ, Liu H, Schofield A, Muise-Hennessey A, Stone SL (2013) Arabidopsis CIPK26 interacts with KEG, components of the ABA signalling network and is degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome system. J Exp Bot 64:2779–2791
Mähs A, Steinhorst L, Han JP, Shen LK, Wang Y, Kudla J (2013) The calcineurin B-like Ca2 + sensors CBL1 and CBL9 function in pollen germination and pollen tube growth in Arabidopsis. Mol Plant 6:1149–1162
Manik SM, Shi S, Mao J et al (2015) The calcium sensor CBL-CIPK is involved in plant's response to abiotic stresses. Int J Genomics 2015:493191
Meena MK, Ghawana S, Dwivedi V, Roy A, Chattopadhyay D (2015) Expression of chickpea CIPK25 enhances root growth and tolerance to dehydration and salt stress in transgenic tobacco. Front Plant Sci 6:683
Muñoz-Bodnar A, Perez-Quintero AL, Gomez-Cano F et al (2014) RNAseq analysis of cassava reveals similar plant responses upon infection with pathogenic and non-pathogenic strains of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis. Plant Cell Rep 33:1901 – 1112
Pandey GK, Kanwar P, Singh A et al (2015) CBL-interacting protein kinase, CIPK21, regulates osmotic and salt stress responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 169:780–792
Qiu QS, Guo Y, Dietrich MA, Schumaker KS, Zhu JK (2002) Regulation of SOS1, a plasma membrane Na+/H+ exchanger in Arabidopsis thaliana, by SOS2 and SOS3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:8436–8441
Quan R, Lin H, Mendoza I et al (2007) SCABP8/CBL10, a putative calcium sensor, interacts with the protein kinase SOS2 to protect Arabidopsis shoots from salt stress. Plant Cell 19:1415–1431
Sanchez-Barrena MJ, Fujii H, Angulo I, Martinez-Ripoll M, Zhu JK, Albert A (2007) The structure of the C-terminal domain of the protein kinase AtSOS2 bound to the calcium sensor AtSOS3. Mol Cell 26:427–435
Sanyal SK, Pandey A, Pandey GK (2016) The CBL-CIPK signaling module in plants: a mechanistic perspective. Physiol Plant 155:89–108
Sardar A, Nandi AK, Chattopadhyay D (2017) CBL-interacting protein kinase 6 negatively regulates immune response to Pseudomonas syringae in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 13:3573–3584
Shi H, Ishitani M, Kim C, Zhu JK (2000) The Arabidopsis thaliana salt tolerance gene SOS1 encodes a putative Na+/H+ antiporter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6896–6901
Shi H, Wang X, Ye T et al (2014) The cysteine2/histidine2-type transcription factor ZINC FINGER OF ARABIDOPSIS THALIANA 6 modulates biotic and abiotic stress responses by activating salicylic acid-related genes and C-REPEAT-BINDING FACTOR genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 165:1367–1379
Sparkes IA, Runions J, Kearns A, Hawes C (2006) Rapid, transient expression of fluorescent fusion proteins in tobacco plants and generation of stably transformed plants. Nat Protoc 1:2019–2025
Steinhorst L, Mähs A, Ischebeck T et al (2015) Vacuolar CBL-CIPK12 Ca2+-sensor-kinase complexes are required for polarized pollen tube growth. Curr Biol 25:1475–1482
Sun T, Wang Y, Wang M et al (2015) Identification and comprehensive analyses of the CBL and CIPK gene families in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Plant Biol 15:1–17
Tang RJ, Liu H, Yang Y et al (2012) Tonoplast calcium sensors CBL2 and CBL3 control plant growth and ion homeostasis through regulating V-ATPase activity in Arabidopsis. Cell Res 22:1650–1665
Tang RJ, Zhao F, Garcia VJ et al (2015) Tonoplast CBL–CIPK calcium signaling network regulates magnesium homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:3134–3139
Thapa G, Dey M, Sahoo L, Panda SK (2011) An insight into the drought stress induced alterations in plants. Biol Plant 5:603–613
Tian Q, Zhang X, Yang A, Wang T, Zhang WH (2016) CIPK23 is involved in iron acquisition of Arabidopsis by affecting ferric chelate reductase activity. Plant Sci 246:70–79
Tsou PL, Lee SY, Allen NS, Winter-Sederoff H, Robertson D (2012) An ER-targeted calcium-binding peptide confers salt and drought tolerance mediated by CIPK6 in Arabidopsis. Planta 235:539–552
Wang RK, Li LL, Cao ZH et al (2012) Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a novel apple MdCIPK6L gene reveals its involvement in multiple abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic plants. Plant Mol Biol 79:123–135
Wang XP, Chen LM, Liu WX et al (2016) AtKC1 and CIPK23 synergistically modulate AKT1-mediated low potassium stress responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 170:2264–2277
Weinl S, Kudla J (2009) The CBL-CIPK Ca2+-decoding signaling network: function and perspectives. New Phytol 184:517–528
Xiang Y, Huang Y, Xiong L (2007) Characterization of stress-responsive CIPK genes in rice for stress tolerance improvement. Plant Physiol 144:1416–1428
Xu J, Li HD, Chen LQ et al (2006) A protein kinase, interacting with two calcineurin B-like proteins, regulates K+ transporter AKT1 in Arabidopsis. Cell 125:1347–1360
Yan J, Niu F, Liu WZ et al (2014) Arabidopsis CIPK14 positively regulates glucose response. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 450:1679–1683
Yang W, Kong Z, Omo-Ikerodah E, Xu W, Li Q, Xue Y (2008) Calcineurin B-like interacting protein kinase OsCIPK23 functions in pollination and drought stress responses in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Genet Genom 35:531–543
Yu Y, Xia X, Yin W, Zhang H (2007) Comparative genomic analysis of CIPK gene family in Arabidopsis and Populus. Plant Growth Regul 52:101–110
Yu Q, An L, Li W (2014) The CBL-CIPK network mediates different signaling pathways inplants. Plant Cell Rep 33:203–214
Zhang H, Yang B, Liu WZ, Li H, Wang L, Wang B et al (2014) Identification and characterization of CBL and CIPK gene families in canola (Brassica napus L.). BMC Plant Biol 14:1–24
Zhou J, Wang J, Bi Y et al (2014) Overexpression of PtSOS2 enhances salt tolerance in transgenic poplars. Plant Mol Biol 32:185–197
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Chris R. Somerville, Dr. Jie Zhou, Dr. Yanru Hu, and Dr. Jiang Tian for sharing their vector plasmids. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31760067), the startup funding and the scientific research foundation of Hainan University (No. kyqd1531) to Haitao Shi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Ying-Tang Lu.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, Y., He, X., Hu, W. et al. Functional analysis of MeCIPK23 and MeCBL1/9 in cassava defense response against Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis. Plant Cell Rep 37, 887–900 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-018-2276-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-018-2276-7