Abstract
Key message
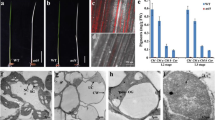
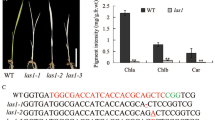
An albinic rice is caused by mutation of threonyl-tRNA synthetase, which is essential for plant development by stabilizing of NEP and PEP gene expressions and chloroplast protein synthesis.
Abstract
Chloroplast biogenesis and development depend on complex genetic mechanisms. Apart from their function in translation, aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (aaRSs) play additional role in gene expression regulation, RNA splicing, and cytokine activity. However, their detailed functions in plant development are still poorly understood. We isolated a lethal albinic seedling (las) mutant in rice. Physiological and ultrastructural analysis of las mutant plants revealed weak chlorophyll fluorescence, negligible chlorophyll accumulation, and defective thylakoid membrane development. By map based cloning we determined that the LAS allele gene encodes threonyl-tRNA synthetase (ThrRS). LAS was constitutively expressed with relatively high level in leaves. NEP-dependent gene transcripts accumulated in the developing chloroplasts, while PEP-dependent transcripts were reduced in the las mutant. This result indicated that PEP activity was impaired. Chloroplast-encoded protein levels were sharply reduced in the las mutant. Biogenesis of chloroplast rRNAs (16S and 23S rRNA) was arrested, leading to impaired translation and protein synthesis. Together, our findings indicated that LAS is essential not only for chloroplast development by stabilizing the NEP and PEP gene expression, but also for protein synthesis and construction of the ribosome system in rice chloroplasts.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- aaRSs:
-
Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases
- Chl:
-
Chlorophyll
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- RNAi:
-
RNA interference
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeat
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscopy
- PEP:
-
Plastid-encoded RNA polymerase
- NEP:
-
Nuclear-encoded RNA polymerase
- RBCL:
-
Rubisco large subunits
- AtpB:
-
ATP synthase CF1βsubunit
- RBCS:
-
Rubisco small subunit
- rpl2:
-
Ribosome large subunit 2
- psaA1:
-
PS I P700 apoprotein A1
- psaA2:
-
PS I P700 apoprotein A2
- psbC:
-
PS II CP43-protein
- cytf:
-
Cytochrome b6f complex
- Hsp90:
-
Heat-shock protein 90
- CBB:
-
Coomassie blue
References
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts: polyphenol oxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24:1–15
Asakura Y, Galarneau E, Watkins KP, Barkan A, van Wijk KJ (2012) Chloroplast RH3 DEAD box RNA helicases in maize and Arabidopsis function in splicing of specific group II introns and affect chloroplast ribosome biogenesis. Plant Physiol 159:961–974
Berg M, Rogers R, Muralla R, Meinke D (2005) Requirement of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases for gametogenesis and embryo development in Arabidopsis. Plant J 44:866–878
Börner T, Aleynikova AY, Zubo YO, Kusnetsov VV (2015) Chloroplast RNA polymerases: role in chloroplast biogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1847:761–769
Cahoon AB, Harris SM, Stern DB (2004) Analysis of developing maize plastids reveals two mRNA stability classes correlating with RNA polymerase type. EMBO Rep 5:801–806
Chen S, Tao L, Zeng L, Vega-Sanchez ME, Umemura K, Wang GL (2006) A highly efficient transient protoplast system for analyzing defence gene expression and protein–protein interactions in rice. Mol Plant Pathol 7:417–427
Chi W, He B, Mao J, Li Q, Ma J, Ji D, Zou M, Zhang L (2012) The function of RH22, a DEAD RNA helicase, in the biogenesis of the 50S ribosomal subunits of Arabidopsis chloroplasts. Plant Physiol 158:693–707
Chiu W, Niwa Y, Zeng W, Hirano T, Kobayashi H, Sheen J (1996) Engineered GFP as a vital reporter in plants. Curr Biol 6:325–330
Clark RL, Neidhardt FC (1990) Role of the two lysyl-tRNA synthetases of Escherichia coli: analysis of nucleotide sequences and mutant behavior. J Bacteriol 172:3237–3243
Duchêne AM, Giritch A, Hoffmann B, Cognat V, Lancelin D, Peeters NM, Zaepfel M, Marechal-Drouard L, Small ID (2005) Dual targeting is the rule for organellar aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:16484–16489
Fristedt R, Scharff LB, Clarke CA, Wang Q, Lin C, Merchant SS, Bock R (2014) RBF1, a plant homolog of the bacterial ribosome-binding factor RbfA, acts in processing of the chloroplast 16S ribosomal RNA. Plant Physiol 164:201–215
Gong XD, Jiang Q, Xu XL, Zhang JH, Teng S, Lin DZ, Dong YJ (2013) Disruption of the rice plastid ribosomal protein S20 leads to chloroplast developmental defects and seedling lethality. G3 (Bethesda) 10:1769–1777
Hajdukiewicz PT, Allison LA, Maliga P (1997) The two RNA polymerases encoded by the nuclear and the plastid compartments transcribe distinct groups of genes in tobacco plastids. EMBO J 16:4041–4048
Han CD, Coe EH Jr, Martienssen RA (1992) Molecular cloning and characterization of iojap (ij), a pattern striping gene of maize. EMBO J 11:4037–4046
Hanaoka M, Kanamaru K, Takahsashi H, Tanaka K (2003) Molecular genetic analysis of chloroplast gene promoters dependent on SIG2, a nucleus-encoded sigma factor for the plastid-encoded RNA polymerase, in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids Res 31:7090–7098
Hotto AM, Castandet B, Gilet L, Higdon A, Condon C, Sterna DB (2015) Arabidopsis chloroplast mini-ribonuclease III participates in rRNA maturation and intron recycling. Plant Cell 27:724–740
Hu Z, Xu F, Guan L, Qian P, Liu Y, Zhang H, Huang Y, Hou S (2014) The tetratricopeptide repeat-containing protein slow green1 is required for chloroplast development in Arabidopsis. J Exp Bot 65:1111–1123
Jarvis P, Lopez-Juez E (2013) Biogenesis and homeostasis of chloroplasts and other plastids. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 14:787–802
Jefferson RA (1987) Assaying chimeric genes in plants: the GUS gene fusion system. Plant Mol Biol Rep 5:387–405
Jeon JS, Lee S, Jung KH, Jun SH, Jeong DH, Lee J, Kim C, Jang S, Yang K, Nam J, An K, Han MJ, Sung RJ, Choi HS, Yu JH, Choi JH, Cho SY, Cha SS, Kim SI, An G (2002) T-DNA insertional mutagenesis for functional genomics in rice. Plant J 22:561–570
Jiang L, Wang S, Li HJ, Zhang GX (2012) EMBRYONIC FACTOR 31 encodes a tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase that is essential for seed development. Mol Biol Rep 39:8297–8305
Kim YK, Lee JY, Cho HS, Lee SS, Ha HJ, Kim S, Choi D, Pai HS (2005) Inactivation of organellar glutamyl- and seryl-tRNA synthetases leads to developmental arrest of chloroplasts and mitochondria in higher plants. J Biol Chem 280:37098–37106
Kremnev D, Strand à (2014) Plastid encoded RNA polymerase activity and expression of photosynthesis genes required for embryo and seed development in Arabidopsis. Front Plant Sci 5:385
Kusumi K, Iba K (2014) Establishment of the chloroplast genetic system in rice during early leaf development and at low temperatures. Front Plant Sci 5:386. doi:10.3389/fpls.2014.00386
Kusumi K, Mizutani A, Nishimura M, Iba K (1997) A virescent gene V1 determines the expression timing of plastid genes for transcription/translation apparatus during early leaf development in rice. Plant J 12:1241–1250
Kusumi K, Hirotsuka S, Shimada H, Chono Y, Matsuda O, Iba K (2010) Contribution of chloroplast biogenesis to carbon–nitrogen balance during early leaf development in rice. J Plant Res 123:617–622
Leelavathi S, Bhardwaj A, Kumar S, Dass A, Pathak R, Pandey SS, Tripathy BC, Padmalatha KV, Dhandapani G, Kanakachari M, Solanke AU, Kumar PA, Cella R, Siva Reddy V (2011) Genome-wide transcriptome and proteome analyses of tobacco psaA and psbA deletion mutants. Plant Mol Biol 76:407–423
Legen J, Kemp S, Krause K, Profanter B, Herrmann RG, Maier RM (2002) Comparative analysis of plastid transcription profiles of entire plastid chromosomes from tobacco attributed to wild-type and PEP-deficient transcription machineries. Plant J 31:171–188
Leister D, Kleine T (2016) Definition of a core module for the nuclear retrograde response to altered organellar gene expression identifies GLK overexpressors as gun mutants. Physiol Plant 3:297–309
Liere K, Weihe A, Börner T (2011) The transcription machineries of plant mitochondria and chloroplasts: composition, function, and regulation. Plant Physiol 168:1345–1360
Liu CH, Zhu HT, Xing Y, Tan JJ, Chen XH, Zhang JJ, Peng HF, Xie QJ, Zhang ZM (2016) Albino Leaf 2 is involved in the splicing of chloroplast group I and II introns in rice. J Exp Bot 18:5339–5347
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−∆∆CT method. Methods 25:402–408
Millar AH, Whelan J, Small I (2006) Recent surprises in protein targeting to mitochondria and plastids. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9:610–615
Min B, Pelaschier JT, Graham DE, Tumbula-Hansen D, SÖll D (2002) Transfer RNA-dependent amino acid biosynthesis: an essential route to asparagine formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:2678–2683
Motohashi R, Yamazaki T, Myouga F, Ito T, Ito K, Satou M, Kobayashi M, Nagata N, Yoshida S, Nagashima A, Tanaka K, Takahashi S, Shinozaki K (2007) Chloroplast ribosome release factor 1 (AtcpRF1) is essential for chloroplast development. Plant Mol Biol 64:61481–61497
Nishimura K, Ashida H, Ogawa T, Yokota A (2010) A DEAD box protein is required for formation of a hidden break in Arabidopsis chloroplast 23 S rRNA. Plant J 63:766–777
Park SG, Ewalt KL, Kim S (2005) Functional expansion of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases and their interacting factors: new perspectives on housekeepers. Trends Biochem Sci 30:569–574
Pesaresi P, Masiero S, Eubel H, Braun HP, Bhushan S, Glaser E, Salamini F, Leister D (2006) Nuclear photosynthetic gene expression is synergistically modulated by rates of protein synthesis in chloroplasts and mitochondria. Plant Cell 8:970–991
Pogson BJ, Albrecht V (2011) Genetic dissection of chloroplast biogenesis and development: an overview. Plant Physiol 155:1545–1551
Puthiyaveetil S, Kavanagh TA, Cain P, Sullivan JA, Newell CA, Gray JC, Robinson C, van der PutarjunanA, Liu XY, Nolan T, Yu F, Rodermel S (2013) Understanding chloroplast biogenesis using second-site suppressors of immutans and var2. Photosynth Res 116:437–453
Qiao J, Li J, Chu W, Luo M (2013) PRDA1, a novel chloroplast nucleoid protein, is required for early chloroplast development and is involved in the regulation of plastid gene expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol 54:2071–2084
Schön A, Kannangara CG, Gough S, Söll D (1988) Protein biosynthesis in organelles requires misaminoacylation of tRNA. Nature 331:187–190
Serino G, Aligna P (1998) RNA polymerase subunits encoded by the plastid rpo genes are not shared with the nucleus-encoded plastid enzyme. Plant Physiol 117:1165–1170
Souciet G, Menand B, Ovesna J, Cosset A, Dietrich A, Wintz H (1999) Characterization of two bifunctional Arabdopsis thaliana genes coding for mitochondrial and cytosolic forms of valyl-tRNA synthetase and threonyl-tRNA synthetase by alternative use of two in-frame AUGs. Eur J Biochem 266:848–854
Surpin M, Larkin RM, Chory J (2002) Signal transduction between the chloroplasts and the nucleus. Plant Cell 14:S327–S338
Swiatecka-Hagenbruch M, Emanuel C, Hedtke B, Liere K, Börner T (2008) Impaired function of the phage-type RNA polymerase RpoTp in transcription of chloroplast genes is compensated by a second phage-type RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res 36:785–792
Szymanski M, Deniziak M, Barciszewski J (2000) The new aspects of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Acta Biochim Pol 47:821–834
Uwer U, Willmitzer L, Altmann T (1998) Inactivation of a glycyl-tRNA synthetase leads to an arrest in plant embryo development. Plant Cell 10:1277–1294
Wang YL, Wang CM, Zheng M, Lyu J, Xu Y, Li XH, Niu M, Long WH, Wang D, Wang HY, Terzaghi W, Wang YH, Wan JM (2016) WHITE PANICLE1, a val-tRNA synthetase regulating chloroplast ribosome biogenesis in rice, is essential for early chloroplast development. Plant Physiol 170:2110–2123
Yagi Y, Shiina T (2014) Recent advances in the study of chloroplast gene expression and its evolution. Front Plant Sci 5:61
Yu F, Liu X, Alsheikh M, Park S, Rodermel S (2008) Mutations in SUPPRESSOR OF VARIEGATION1, a factor required for normal chloroplast translation, suppress var2-mediated leaf variegation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 20:1786–1804
Zhang JZ, Somerville CR (1997) Suspensor-derived polyembryony caused by altered expression of valyl-tRNA synthetase in the twn2 mutant of Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:7349–7355
Zhang ZM, Tan JJ, Shi ZY, Xie QJ, Xing Y, Liu CH, Chen QL, Zhu HT, Wang J, Zhang JL, Zhang GQ (2016) Albino Leaf1 that encodes the sole octotricopeptide repeat protein is responsible for chloroplast development. Plant Physiol 171:1182–1191
Zhelyazkova P, Sharma CM, Förstner KU, Liere K, Vogel J, Börner T (2012) The primary transcriptome of barley chloroplasts: numerous noncoding RNAs and the dominating role of the plastid-encoded RNA polymerase. Plant Cell 24:123–136
Zhou WB, Cheng YX, Yap A, Chateigner-Boutin AL, Delannoy E, Hammani K, Small I, Huang JR (2009) The Arabidopsis gene YS1 encoding a DYW protein is required for editing of rpoB transcripts and the rapid development of chloroplasts during early growth. Plant J 58:82–96
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Key Laboratory of Biology, Genetics and Breeding of Japonica Rice in the Mid-lower Yangtze River, Ministry of Agriculture, P.R. China; Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Center for Modern Crop Production; the Yangtze River Valley Hybrid Rice Collaboration Innovation Center; grants from the National 863 Program (2014AA10A 600), National Transformation Science and Technology Program (2014ZX08001004-002), National Science and Technology Support Program of China (2013BAD01B02-16), And Jiangsu Science and Technology Development Program (BE2014394, BE2015363).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Kang Chong.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
299_2017_2136_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Fig. S1 Phenotypes of RNAi and complementation of transgenic plants of LAS. A, wt, wild type; las, mutant plant; RNAi, RNA interference transgenic T0 plant, las/1390:LAS, complementation transgenic T0 plant. B, Complementation transgenic T0 lines of las (TIF 9100 KB)
299_2017_2136_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Fig. S2 Transcript analyses of chlorophyll synthesis genes in wild type and las. Genes upregulated by more than two times compared to the mutant include HEML, HEMC, HEME, URO-D, HEMF, CHLI, CHLM, POR, CHLG, PS and FLU. Genes down-regulated in the mutant include CAO, HO, GUN4, PIF4 (TIF 1006 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, YY., Hao, YY., Wang, YH. et al. Lethal albinic seedling, encoding a threonyl-tRNA synthetase, is involved in development of plastid protein synthesis system in rice. Plant Cell Rep 36, 1053–1064 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-017-2136-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-017-2136-x