Abstract
Key message
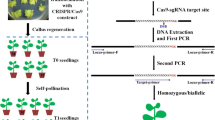
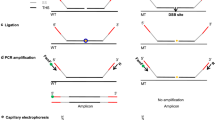
A method based on DNA single-strand conformation polymorphism is demonstrated for effective genotyping of CRISPR/Cas9-induced mutants in rice.
Abstract
Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)/CRISPR-associated 9 (Cas9) has been widely adopted for genome editing in many organisms. A large proportion of mutations generated by CRISPR/Cas9 are very small insertions and deletions (indels), presumably because Cas9 generates blunt-ended double-strand breaks which are subsequently repaired without extensive end-processing. CRISPR/Cas9 is highly effective for targeted mutagenesis in the important crop, rice. For example, homozygous mutant seedlings are commonly recovered from CRISPR/Cas9-treated calli. However, many current mutation detection methods are not very suitable for screening homozygous mutants that typically carry small indels. In this study, we tested a mutation detection method based on single-strand conformational polymorphism (SSCP). We found it can effectively detect small indels in pilot experiments. By applying the SSCP method for CRISRP-Cas9-mediated targeted mutagenesis in rice, we successfully identified multiple mutants of OsROC5 and OsDEP1. In conclusion, the SSCP analysis will be a useful genotyping method for rapid identification of CRISPR/Cas9-induced mutants, including the most desirable homozygous mutants. The method also has high potential for similar applications in other plant species.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carroll D (2011) Genome engineering with zinc-finger nucleases. Genetics 188:773–782
Cermak T, Doyle EL, Christian M, Wang L, Zhang Y, Schmidt C, Baller JA, Somia NV, Bogdanove AJ, Voytas DF (2011) Efficient design and assembly of custom TALEN and other TAL effector-based constructs for DNA targeting. Nucleic Acids Res 39:e82
Christian M, Cermak T, Doyle EL, Schmidt C, Zhang F, Hummel A, Bogdanove AJ, Voytas DF (2010) Targeting DNA double-strand breaks with TAL effector nucleases. Genetics 186:757–761
Christian M, Qi Y, Zhang Y, Voytas DF (2013) Targeted mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana using engineered TAL effector nucleases. G3 3:1697–1705
Cong L, Ran FA, Cox D, Lin S, Barretto R, Habib N, Hsu PD, Wu X, Jiang W, Marraffini LA, Zhang F (2013) Multiplex genome engineering using CRISPR/Cas systems. Science 339:819–823
Dahlem TJ, Hoshijima K, Jurynec MJ, Gunther D, Starker CG, Locke AS, Weis AM, Voytas DF, Grunwald DJ (2012) Simple methods for generating and detecting locus-specific mutations induced with TALENs in the zebrafish genome. PLoS Genet 8:e1002861
Doudna JA, Charpentier E (2014) Genome editing. The new frontier of genome engineering with CRISPR-Cas9. Science 346:1258096
Endo M, Mikami M, Toki S (2015) Multigene knockout utilizing off-target mutations of the CRISPR/Cas9 system in rice. Plant Cell Physiol 56:41–47
Esvelt KM, Mali P, Braff JL, Moosburner M, Yaung SJ, Church GM (2013) Orthogonal Cas9 proteins for RNA-guided gene regulation and editing. Nat Methods 10:1116–1121
Fauser F, Schiml S, Puchta H (2014) Both CRISPR/Cas-based nucleases and nickases can be used efficiently for genome engineering in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 79:348–359
Feng Z, Zhang B, Ding W, Liu X, Yang DL, Wei P, Cao F, Zhu S, Zhang F, Mao Y, Zhu JK (2013) Efficient genome editing in plants using a CRISPR/Cas system. Cell Res 23:1229–1232
Feng Z, Mao Y, Xu N, Zhang B, Wei P, Yang DL, Wang Z, Zhang Z, Zheng R, Yang L, Zeng L, Liu X, Zhu JK (2014) Multigeneration analysis reveals the inheritance, specificity, and patterns of CRISPR/Cas-induced gene modifications in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:4632–4637
Gaj T, Gersbach CA, Barbas CF 3rd (2013) ZFN, TALEN, and CRISPR/Cas-based methods for genome engineering. Trends Biotechnol 31:397–405
Hiei Y, Ohta S, Komari T, Kumashiro T (1994) Efficient transformation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) mediated by Agrobacterium and sequence analysis of the boundaries of the T-DNA. Plant J 6:271–282
Hou Z, Zhang Y, Propson NE, Howden SE, Chu LF, Sontheimer EJ, Thomson JA (2013) Efficient genome engineering in human pluripotent stem cells using Cas9 from Neisseria meningitidis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:15644–15649
Hsu PD, Lander ES, Zhang F (2014) Development and applications of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome engineering. Cell 157:1262–1278
Huang X, Qian Q, Liu Z, Sun H, He S, Luo D, Xia G, Chu C, Li J, Fu X (2009) Natural variation at the DEP1 locus enhances grain yield in rice. Nat Genet 41:494–497
Ikeda T, Tanaka W, Mikami M, Endo M, Hirano HY (2015) Generation of artificial drooping leaf mutants by CRISPR-Cas9 technology in rice. Genes Genet Syst 90:231–235
Jiang W, Zhou H, Bi H, Fromm M, Yang B, Weeks DP (2013) Demonstration of CRISPR/Cas9/sgRNA-mediated targeted gene modification in Arabidopsis, tobacco, sorghum and rice. Nucleic Acids Res 41:e188
Jinek M, Chylinski K, Fonfara I, Hauer M, Doudna JA, Charpentier E (2012) A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science 337:816–821
Kakavas VK, Plageras P, Vlachos TA, Papaioannou A, Noulas VA (2008) PCR-SSCP: a method for the molecular analysis of genetic diseases. Mol Biotechnol 38:155–163
Kim YG, Cha J, Chandrasegaran S (1996) Hybrid restriction enzymes: zinc finger fusions to Fok I cleavage domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:1156–1160
Li T, Huang S, Jiang WZ, Wright D, Spalding MH, Weeks DP, Yang B (2011) TAL nucleases (TALNs): hybrid proteins composed of TAL effectors and FokI DNA-cleavage domain. Nucleic Acids Res 39:359–372
Lowder LG, Zhang D, Baltes NJ, Paul JW, Tang X, Zheng X, Voytas DF, Hsieh TF, Zhang Y, Qi Y (2015) A CRISPR/Cas9 toolbox for multiplexed plant genome editing and transcriptional regulation. Plant Physiol 169:1–15
Ma X, Zhang Q, Zhu Q, Liu W, Chen Y, Qiu R, Wang B, Yang Z, Li H, Lin Y, Xie Y, Shen R, Chen S, Wang Z, Chen Y, Guo J, Chen L, Zhao X, Dong Z, Liu YG (2015) A robust CRISPR/Cas9 system for convenient, high-efficiency multiplex genome editing in monocot and dicot plants. Mol Plant 8:1274–1284
Mali P, Yang L, Esvelt KM, Aach J, Guell M, DiCarlo JE, Norville JE, Church GM (2013) RNA-guided human genome engineering via Cas9. Science 339:823–826
Mashal RD, Koontz J, Sklar J (1995) Detection of mutations by cleavage of DNA heteroduplexes with bacteriophage resolvases. Nat Genet 9:177–183
Miao J, Guo D, Zhang J, Huang Q, Qin G, Zhang X, Wan J, Gu H, Qu LJ (2013) Targeted mutagenesis in rice using CRISPR-Cas system. Cell Res 23:1233–1236
Mikami M, Toki S, Endo M (2015) Comparison of CRISPR/Cas9 expression constructs for efficient targeted mutagenesis in rice. Plant Mol Biol 88:561–572
Miller JC, Holmes MC, Wang J, Guschin DY, Lee YL, Rupniewski I, Beausejour CM, Waite AJ, Wang NS, Kim KA, Gregory PD, Pabo CO, Rebar EJ (2007) An improved zinc-finger nuclease architecture for highly specific genome editing. Nat Biotechnol 25:778–785
Miller JC, Tan S, Qiao G, Barlow KA, Wang J, Xia DF, Meng X, Paschon DE, Leung E, Hinkley SJ, Dulay GP, Hua KL, Ankoudinova I, Cost GJ, Urnov FD, Zhang HS, Holmes MC, Zhang L, Gregory PD, Rebar EJ (2011) A TALE nuclease architecture for efficient genome editing. Nat Biotechnol 29:143–148
Oleykowski CA, Bronson Mullins CR, Godwin AK, Yeung AT (1998) Mutation detection using a novel plant endonuclease. Nucleic Acids Res 26:4597–4602
Orita M, Iwahana H, Kanazawa H, Hayashi K, Sekiya T (1989a) Detection of polymorphisms of human DNA by gel electrophoresis as single-strand conformation polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:2766–2770
Orita M, Suzuki Y, Sekiya T, Hayashi K (1989b) Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutations and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics 5:874–879
Ota S, Hisano Y, Muraki M, Hoshijima K, Dahlem TJ, Grunwald DJ, Okada Y, Kawahara A (2013) Efficient identification of TALEN-mediated genome modifications using heteroduplex mobility assays. Genes Cells: Devot Mol Cell Mech 18:450–458
Paques F, Duchateau P (2007) Meganucleases and DNA double-strand break-induced recombination: perspectives for gene therapy. Curr Gene Ther 7:49–66
Qi Y, Li X, Zhang Y, Starker CG, Baltes NJ, Zhang F, Sander JD, Reyon D, Joung JK, Voytas DF (2013a) Targeted deletion and inversion of tandemly arrayed genes in Arabidopsis thaliana using zinc finger nucleases. G3 3:1707–1715
Qi Y, Zhang Y, Zhang F, Baller JA, Cleland SC, Ryu Y, Starker CG, Voytas DF (2013b) Increasing frequencies of site-specific mutagenesis and gene targeting in Arabidopsis by manipulating DNA repair pathways. Genome Res 23:547–554
Qi Y, Starker CG, Zhang F, Baltes NJ, Voytas DF (2014) Tailor-made mutations in Arabidopsis using zinc finger nucleases. Methods Mol Biol 1062:193–209
Ran FA, Cong L, Yan WX, Scott DA, Gootenberg JS, Kriz AJ, Zetsche B, Shalem O, Wu X, Makarova KS, Koonin EV, Sharp PA, Zhang F (2015) In vivo genome editing using Staphylococcus aureus Cas9. Nature 520:186–191
Sander JD, Joung JK (2014) CRISPR-Cas systems for editing, regulating and targeting genomes. Nat Biotechnol 32:347–355
Sekiya T (1996) Single-strand conformation polymorphism (SSCP) analysis: a convenient, rapid method for detection of single-base changes in DNA. Tanpakushitsu kakusan koso Protein, nucleic acid, enzyme 41:539–545
Shan Q, Wang Y, Li J, Zhang Y, Chen K, Liang Z, Zhang K, Liu J, Xi JJ, Qiu JL, Gao C (2013) Targeted genome modification of crop plants using a CRISPR-Cas system. Nat Biotechnol 31:686–688
Shirasawa K, Monna L, Kishitani S, Nishio T (2004) Single nucleotide polymorphisms in randomly selected genes among japonica rice (Oryza sativa L.) varieties identified by PCR-RF-SSCP. DNA Res: Int J Rapid Publ Rep Genes Genomes 11:275–283
Smith J, Grizot S, Arnould S, Duclert A, Epinat JC, Chames P, Prieto J, Redondo P, Blanco FJ, Bravo J, Montoya G, Paques F, Duchateau P (2006) A combinatorial approach to create artificial homing endonucleases cleaving chosen sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 34:e149
Sternberg SH, Redding S, Jinek M, Greene EC, Doudna JA (2014) DNA interrogation by the CRISPR RNA-guided endonuclease Cas9. Nature 507:62–67
Stewart CN Jr, Via LE (1993) A rapid CTAB DNA isolation technique useful for RAPD fingerprinting and other PCR applications. Biotechniques 14:748–750
Urnov FD, Miller JC, Lee YL, Beausejour CM, Rock JM, Augustus S, Jamieson AC, Porteus MH, Gregory PD, Holmes MC (2005) Highly efficient endogenous human gene correction using designed zinc-finger nucleases. Nature 435:646–651
Urnov FD, Rebar EJ, Holmes MC, Zhang HS, Gregory PD (2010) Genome editing with engineered zinc finger nucleases. Nat Rev Genet 11:636–646
Vouillot L, Thelie A, Pollet N (2015) Comparison of T7E1 and surveyor mismatch cleavage assays to detect mutations triggered by engineered nucleases. G3 5:407–415
Xie K, Minkenberg B, Yang Y (2015) Boosting CRISPR/Cas9 multiplex editing capability with the endogenous tRNA-processing system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:3570–3575
Xu RF, Li H, Qin RY, Li J, Qiu CH, Yang YC, Ma H, Li L, Wei PC, Yang JB (2015) Generation of inheritable and “transgene clean” targeted genome-modified rice in later generations using the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Sci Rep 5:11491
Zhang Y, Zhang F, Li X, Baller JA, Qi Y, Starker CG, Bogdanove AJ, Voytas DF (2013) Transcription activator-like effector nucleases enable efficient plant genome engineering. Plant Physiol 161:20–27
Zhang H, Zhang J, Wei P, Zhang B, Gou F, Feng Z, Mao Y, Yang L, Zhang H, Xu N, Zhu JK (2014) The CRISPR/Cas9 system produces specific and homozygous targeted gene editing in rice in one generation. Plant Biotechnol J 12:797–807
Zhou H, Liu B, Weeks DP, Spalding MH, Yang B (2014) Large chromosomal deletions and heritable small genetic changes induced by CRISPR/Cas9 in rice. Nucleic Acids Res 42:10903–10914
Zhu X, Xu Y, Yu S, Lu L, Ding M, Cheng J, Song G, Gao X, Yao L, Fan D, Meng S, Zhang X, Hu S, Tian Y (2014) An efficient genotyping method for genome-modified animals and human cells generated with CRISPR/Cas9 system. Sci Rep 4:6420
Zou LP, Sun XH, Zhang ZG, Liu P, Wu JX, Tian CJ, Qiu JL, Lu TG (2011) Leaf rolling controlled by the homeodomain leucine zipper class IV gene Roc5 in rice. Plant Physiol 156:1589–1602
Acknowledgments
The pBlueScript-derived constructs were kind gifts from Satoshi Ota and Atsuo Kawahara at RIKEN Institute in Japan. This work is supported by Grants including the National Science Foundation of China (31330017, 31271420 and 31371682), the national Transgenic Major Project (2014ZX0801003B-002) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (ZYGX2013J099) to YZ, and startup funds from East Carolina University and a Collaborative Funding Grant (2016-CFG-8003) from North Carolina Biotechnology Center and Syngenta to YQ.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict interests.
Additional information
Communicated by T. Cardi.
X. Zheng, S. Yang and D. Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
299_2016_1967_MOESM2_ESM.pptx
Supplementary material 2 (PPTX 71 kb) Fig. S1 PAGE-based detection of heteroduplex DNA of 1-bp and 2-bp deletions. This method is not as sensitive as SSCP because it failed to detect the 1-bp deletion in this case
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, X., Yang, S., Zhang, D. et al. Effective screen of CRISPR/Cas9-induced mutants in rice by single-strand conformation polymorphism. Plant Cell Rep 35, 1545–1554 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-016-1967-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-016-1967-1