Abstract
Key message
Site-directed mutagenesis of nitrate reductase genes using direct delivery of purified Cas9 protein preassembled with guide RNA produces mutations efficiently in Petunia × hybrida protoplast system.
Abstract
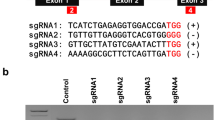
The clustered, regularly interspaced, short palindromic repeat (CRISPR)-CRISPR associated endonuclease 9 (CRISPR/Cas9) system has been recently announced as a powerful molecular breeding tool for site-directed mutagenesis in higher plants. Here, we report a site-directed mutagenesis method targeting Petunia nitrate reductase (NR) gene locus. This method could create mutations efficiently using direct delivery of purified Cas9 protein and single guide RNA (sgRNA) into protoplast cells. After transient introduction of RNA-guided endonuclease (RGEN) ribonucleoproteins (RNPs) with different sgRNAs targeting NR genes, mutagenesis at the targeted loci was detected by T7E1 assay and confirmed by targeted deep sequencing. T7E1 assay showed that RGEN RNPs induced site-specific mutations at frequencies ranging from 2.4 to 21 % at four different sites (NR1, 2, 4 and 6) in the PhNR gene locus with average mutation efficiency of 14.9 ± 2.2 %. Targeted deep DNA sequencing revealed mutation rates of 5.3–17.8 % with average mutation rate of 11.5 ± 2 % at the same NR gene target sites in DNA fragments of analyzed protoplast transfectants. Further analysis from targeted deep sequencing showed that the average ratio of deletion to insertion produced collectively by the four NR-RGEN target sites (NR1, 2, 4, and 6) was about 63:37. Our results demonstrated that direct delivery of RGEN RNPs into protoplast cells of Petunia can be exploited as an efficient tool for site-directed mutagenesis of genes or genome editing in plant systems.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aida T, Chiyo K, Usami T, Ishikubo H, Imahashi R, Wada Y, Tanaka KF, Sakuma T, Yamamoto T, Tanaka K (2015) Cloning-free CRISPR/Cas system facilitates functional cassette knock-in in mice. Genome Biol 16:87. doi:10.1186/s13059-015-0653-x
Bae S, Kweon J, Kim HS, Kim JS (2014a) Microhomology-based choice of Cas9 nuclease target sites. Nat Methods 11:705–706
Bae S, Park J, Kim JS (2014b) Cas-OFFinder: a fast and versatile algorithm that searches for potential off-target sites of Cas9 RNA-guided endonucleases. Bioinformatics 30:1473–1475
Beerli RR, Barbas CF (2002) engineering polydactyl zinc finger transcription factors. Nat Biotechnol 20:135–141
Bitinaite J, Wah DA, Aggarwal AK, Schildkraut I (1998) FokI dimerization is required for DNA cleavage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:10570–10575
Chen K, Gao C (2013) TALENs: customizable molecular DNA scissors for genome engineering of plants. J Genet Genom 40:271–279
Cho SW, Kim S, Kim JM, Kim JS (2013) Targeted genome engineering in human cells with the Cas9 RNA-guided endonuclease. Nat Biotechnol 31:230–232
Cho SW, Kim S, Kim Y, Kweon J, Kim HS, Bae S, Kim JS (2014) Analysis of off-target effects of CRISPR/Cas-derived RNA-guided endonucleases and nickases. Genome Res 24:132–141
Cocking EC, Peberdy JF (1974) The use protoplasts from fungi and higher plants as genetic systems—a practical handbook. Department of Botany, University of Nottingham, Nottingham
Conner AJ, Albert NW, Deroles, SC (2009) Transfection and regeneration of Petunia. In: Gerats T, Strommer J (eds) Petunia: evolutionary, developmental and physiological genetics, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, pp 395–416
Dicarlo JE, Norville JE, Mali P, Rios X, Aach J, Church GM (2013) Genome engineering in Saccharomyces cerevisiae using CRISPR–Cas systems. Nucleic Acids Res 41:4336–4343
Dubois V, Botton E, Meyer C, Rieu A, Bedu M, Maisonneuve B, Mazier M (2005) Systematic silencing of a tobacco nitrate reductase transgene in lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.). J Exp Bot 56:2379–2388
Feng Z, Zhang B, Ding W, Liu X, Yang DL, Wei P, Cao F, Zhu S, Zhang F, Mao Y, Zhu JK (2013) Efficient genome editing in plants using a CRISPR/Cas system. Cell Res 23:1229–1232
Gaj T, Gersbach CA, Barbas CF III (2013) ZFN, TALEN, and CRISPR/Cas-based methods for genome engineering. Trends Biotechnol 31:397–405
Gao J, Wang G, Ma S, Xie X, Wu X, Zhang X, Wu Y, Zhao P, Xia Q (2015) CRISPR/Cas9-mediated targeted mutagenesis in Nicotiana tabacum. Plant Mol Biol 87:99–110
Gerats T, Vandenbussche M (2005) A model system for comparative research: Petunia. Trends Plant Sci 10:251–256
Gübitz T, Hoballah ME, Dell’Olivo A, Kuhlemeier C (2009) Petunia as a model system for the genetics and evolution of pollination syndromes. In: Gerats T, Strommer J (eds) Petunia: evolutionary, developmental and physiological genetics, 2nd edn. Springer, New York, pp 29–49
Hsu PD, Lander ES, Zhang F (2014) Development and applications of CRISPR-Cas9 for genome engineering. Cell 157:1262–1278
Hwang WY, Fu Y, Reyon D, Maeder ML, Tsai SQ, Sander JD, Peterson RT, Yeh JR, Joung JK (2013) Efficient genome editing in zebrafish using a CRISPR-Cas system. Nat Biotechnol 31:227–229
Hyun Y, Kim J, Cho SW, Choi Y, Kim JS, Coupland G (2015) Site-directed mutagenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana using dividing tissue-targeted RGEN of the CRISPR/Cas system to generate heritable null alleles. Planta 241:271–284
Jiang W, Zhou H, Bi H, Fromm M, Yang B, Weeks DP (2013) Demonstration of CRISPR/Cas9/sgRNA-mediated targeted gene modification in Arabidopsis, tobacco, sorghum and rice. Nucleic Acids Res 41:e188
Jiang W, Yang B, Weeks DP (2014) Efficient CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene editing in Arabidopsis thaliana and inheritance of modified genes in the T2 and T3 generations. PLoS One 9:e99225
Jinek M, Chylinski K, Fonfara I, Hauer M, Doudna JA, Charpentier E (2012) A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science 6096:816–821
Kanchiswamy CN, Malnoy M, Velasco R, Kim JS, Viola R (2015) Non-GMO genetically edited crop plants. Trends Biotechnol 33:489–491
Kim H, Kim JS (2014) A guide to genome engineering with programmable nucleases. Nat Rev Genet 15:321–334
Kim HJ, Lee HJ, Kim H, Cho SW, Kim JS (2009) Targeted genome editing in human cells with zinc finger nucleases constructed via modular assembly. Genome Res 19:1279–1288
Kim Y, Kweon J, Kim JS (2013) TALENs and ZFNs are associated with different mutation signatures. Nat Methods 10:185
Kim S, Kim D, Cho SW, Kim J, Kim JS (2014) Highly efficient RNA-guided genome editing in human cells via delivery of purified Cas9 ribonucleoproteins. Genome Res 24:1012–1019
Li T, Liu B, Spalding MH, Weeks DP, Yang B (2012) High-efficiency TALEN based gene editing produces disease-resistant rice. Nat Biotechnol 30:390–392
Li JF, Norville JE, Aach J, McCormack M, Zhang D, Bush J, Church GM, Sheen J (2013) Multiplex and homologous recombination mediated genome editing in Arabidopsis and Nicotiana benthamiana using guide RNA and Cas9. Nat Biotechnol 31:688–691
Liang Z, Zhang K, Chen K, Gao C (2014) Targeted mutagenesis in Zea mays using TALENs and the CRISPR/Cas system. J Genet Genom 41:63–68
Luo S, Li J, Stoddard TJ, Baltes NJ, Demorest ZL, Clasen BM, Coffman A, Retterath A, Mathis L, Voytas DF, Zhang F (2015) Non-transgenic plant genome editing using purified sequence-specific nucleases. Mol Plant 8:1425–1427
Meyer P (2001) Chromatin remodelling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 4:457–462
Meyer L, Serek M, Winkelmann T (2009) Protoplast isolation and plant regeneration of different genotypes of Petunia and Calibrachoa. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 99:27–34
Miao J, Guo D, Zhang J, Huang Q, Qin G, Zhang X, Wan J, Gu H, Qu LJ (2013) Targeted mutagenesis in rice using CRISPR-Cas system. Cell Res 23:1233–1236
Miller JC, Holmes MC, Wang J, Guschin DY, Lee YL, Rupniewski I, Beausejour CM, Waite AJ, Wang NS, Kim KA, Gregory PD, Pabo CO, Rebar EJ (2007) An improved zinc-finger nuclease architecture for highly specific genome editing. Nature Biotech 25:778–785
Morton J, Davis MW, Jorgensen EM, Carroll D (2006) Induction and repair of zinc-finger nuclease-targeted double-strand breaks in Caenorhabditis elegans somatic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci 103:16370–16375
Negrutiu I, Shillito R, Potrykus I, Biasini G, Sala F (1987) Hybrid genes in the analysis of transformation conditions I. Setting up a simple method for direct gene transfer in plant protoplasts. Plant Mol Biol 8:363–373
Nekrasov V, Staskawicz B, Weigel D, Jones JD, Kamoun S (2013) Targeted mutagenesis in the model plant Nicotiana benthamiana using Cas9 RNA-guided endonuclease. Nat Biotechnol 31:691–693
Oh MH, Kim SG (1994) Plant regeneration from petal protoplast culture of Petunia hybrida. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 36:275–283
Park J, Bae S, Kim JS (2015) Cas-Designer: a web-based tool for choice of CRISPR-Cas9 target sites. Bioinformatics 31:4014–4016
Perez EE, Wang J, Miller JC, Jouvenot Y, Kim KA, Liu O, Wang N, Lee G, Bartsevich VV, Lee YL et al (2008) Establishment of HIV-1 resistance in CD4 + T cells by genome editing using zinc-finger nucleases. Nat Biotechnol 26:808–816
Salanoubat M, Ha DBD (1993) Analysis of the Petunia nitrate reductase apoenzyme-encoding gene: a first step for sequence modification analysis. Gene 128:147–154
Sander JD, Joung JK (2014) CRISPR-Cas systems for editing, regulating and targeting genomes. Nat Biotechnol 32:347–355
Shan Q, Wang Y, Li J, Zhang Y, Chen K, Liang Z, Zhang K, Liu J, Xi JJ, Qiu JL, Gao C (2013) Targeted genome modification of crop plants using a CRISPR-Cas system. Nat Biotechnol 31:686–688
Svitashev S, Young JK, Schwartz C, Gao H, Falco SC, Cigan AM (2015) Targeted mutagenesis, precise gene editing, and site-specific gene insertion in maize using Cas9 and guide RNA. Plant Physiol 169:931–945
van Houwelingen A, Souer E, Mol J, Koes R (1999) Epigenetic interactions among three dTph1 transposons in two homologous chromosomes activate a new excision-repair mechanism in petunia. Plant Cell 11:1319–1336
Vandenbussche M, Zethof J, Royaert S, Weterings K, Gerats T (2004) The duplicated B-class heterodimer model: whorl-specific effects and complex genetic interactions in Petunia hybrida flower development. Plant Cell 16:741–754
Vaucheret H, Palauqui JC, Mourrain P, Elmayan T (1997) Nitrate reductase and nitrite reductase as targets to study gene silencing phenomena in transgenic plants. Euphytica 00:195–200
Wang Y, Cheng X, Shan Q, Zhang Y, Liu J, Gao C, Qiu JL (2014) Simultaneous editing of three homoeoalleles in hexaploid bread wheat confers heritable resistance to powdery mildew. Nat Biotechnol 32:947–951
Wilkinson JQ, Crawford NM (1993) Identification and characterization of a chlorate-resistant mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana with mutations in both nitrate reductase structural genes NIA1 and NIA2. Mol Gen Genet 239:289–297
Woo JW, Kim J, Kwon S, Corvalán C, Cho SW, Kim H, Kim SG, Kim ST, Choe S, Kim JS (2015) DNA-free genome editing in plants with preassembled CRISPR-Cas9 ribonucleoproteins. Nat Biotechnol 33:1162–1164
Wyman C, Kanaar R (2006) DNA double-strand break repair: all’s well that ends well. Annu Rev Genet 40:363–383
Xie K, Yang Y (2013) RNA-guided genome editing in plants using A CRISPRCas system. Mol Plant 6:1975–1983
Zhao XQ, Nie XL, Xiao XG (2013) Over-Expression of a Tobacco Nitrate Reductase gene in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) increases seed protein content and weight without augmenting nitrogen supplying. Plos One 8:e74678
Acknowledgments
This work was carried out with the support of “Plant Molecular Breeding Center of Next Generation Biogreen 21 Program” (Project No. PJ01119203 to G. -J. L., PJ01119201 to S. B.) funded by Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea. S. B. was supported by a research fund of Hanyang University (HY-2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Additional information
Communicated by T. Cardi.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Subburaj, S., Chung, S.J., Lee, C. et al. Site-directed mutagenesis in Petunia × hybrida protoplast system using direct delivery of purified recombinant Cas9 ribonucleoproteins. Plant Cell Rep 35, 1535–1544 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-016-1937-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-016-1937-7