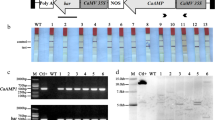
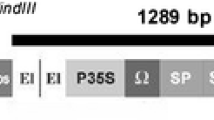
Abstract
Black rot of sweet potato caused by pathogenic fungus Ceratocystis fimbriata severely deteriorates both growth of plants and post-harvest storage. Antimicrobial peptides from various organisms have broad range activities of killing bacteria, mycobacteria, and fungi. Plant thionin peptide exhibited anti-fungal activity against C. fimbriata. A gene for barley α-hordothionin (αHT) was placed downstream of a strong constitutive promoter of E12Ω or the promoter of a sweet potato gene for β-amylase of storage roots, and introduced into sweet potato commercial cultivar Kokei No. 14. Transgenic E12Ω:αHT plants showed high-level expression of αHT mRNA in both leaves and storage roots. Transgenic β-Amy:αHT plants showed sucrose-inducible expression of αHT mRNA in leaves, in addition to expression in storage roots. Leaves of E12Ω:αHT plants exhibited reduced yellowing upon infection by C. fimbriata compared to leaves of non-transgenic Kokei No. 14, although the level of resistance was weaker than resistance cultivar Tamayutaka. Storage roots of both E12Ω:αHT and β-Amy:αHT plants exhibited reduced lesion areas around the site inoculated with C. fimbriata spores compared to Kokei No. 14, and some of the transgenic lines showed resistance level similar to Tamayutaka. Growth of plants and production of storage roots of these transgenic plants were not significantly different from non-transgenic plants. These results highlight the usefulness of transgenic sweet potato expressing antimicrobial peptide to reduce damages of sweet potato from the black rot disease and to reduce the use of agricultural chemicals.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akazawa T, Uritani I (1962) Pattern of carbohydrate breakdown in sweet potato roots infected with Ceratocystis fimbriata. Plant Physiol 37:662–670
Allefs SJHM, De Jong ER, Florack DEA, Hoogendoorn C, Stiekema WJ (1996) Erwinia soft rot resistance of potato cultivars expressing antimicrobial peptide tachyplesin I. Mol Breed 2:97–105
Bohlmann H, Apel K (1991) Thionins. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 42:227–240
Carmona MJ, Molina A, Fernandez JA, Lopez-Fando JJ, Garcia-Olmedo F (1993) Expression of the alpha-thionin gene from barley in tobacco confers enhanced resistance to bacterial pathogens. Plant J 3:457–462
Chan YL, Prasad V, Sanjaya, Chen KH, Liu PC, Chan MT, Cheng CP (2005) Transgenic tomato plants expressing an Arabidopsis thionin (Thi2.1) driven by fruit-inactive promoter battle against phytopathogenic attack. Planta 221:386–393
Clark CA, La Bonte DR (1992) Disease factors in breeding and biotechnology for sweet potato. In: Hill WA, Bonsi CK, Loretan PA (eds) Sweet potato technology for the 21st century. Tuskegee University Press, Tuskegee, pp 484–494
Epple P, Apel K, Bohlmann H (1997) Overexpression of an endogenous thionin enhances resistance of Arabidopsis against Fusarium oxysporum. Plant Cell 9:509–520
Estruch JJ, Estruch JJ, Carozzi NB, Desai N, Duck NB, Warren GW, Koziel MG (1997) Transgenic plants: an emerging approach to pest control. Nat Biotechnol 15:137–141
Florack DE, Stiekema WJ (1994) Thionins: properties, possible biological roles and mechanisms of action. Plant Mol Biol 26:25–37
Florack DE, Visser B, Vries PMD, Van Vuurde JWL, Stiekema WJ (1993) Analysis of the toxicity of purothionins and hordothionins for plant pathogenic bacteria. Neth J P1ant Path 99:259–268
Florack DE, Dirkse WG, Visser B, Heidekamp F, Stiekema WJ (1994) Expression of biologically active hordothionins in tobacco. Effects of pre- and pro-sequences at the amino and carboxyl termini of the hordothionin precursor on mature protein expression and sorting. Plant Mol Biol 24:83–96
Gao AG, Hakimi SM, Mittanck CA, Wu Y, Woerner BM, Stark DM, Shah DM, Liang J, Rommens CM (2000) Fungal pathogen protection in potato by expression of a plant defensin peptide. Nat Biotechnol 18:1307–1310
Holland PM, Abramson RD, Watson R, Gelfand DH (1991) Detection of specific polymerase chain-reaction product by utilizing the 5′3′ exonuclease activity of thermus aquaticus DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:7276–7280
Iwai T, Kaku H, Honkura R, Nakamura S, Ochiai H, Sasaki T, Ohashi Y (2002) Enhanced resistance to seed-transmitted bacterial diseases in transgenic rice plants overproducing an oat cell-wall-bound thionin. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15:515–521
James WC, Teng PS, Nutter FW (1990) Estimated losses of crops from pathogens. In: Pimentel D (ed) Handbook of pest management in agriculture, vol I, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 15–52
Kahl G, Winter P (1995) Plant genetic engineering for crop improvement. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 11:449–460
Komarek M, Cadkova E, Chrastny V, Bordas F, Bollinger JC (2010) Contamination of vineyard soils with fungicides: a review of environmental and toxicological aspects. Environ Int 36:138–151
Kummerer K (2004) Resistance in the environment. J Antimicrob Chemother 54:311–320
Linsmaier EM, Skoog F (1965) Organic growth factor requirement of tobacco tissue culture. Physiol Plant 18:100–127
Maeo K, Tomiya T, Hayashi K, Akaike M, Morikami A, Ishiguro S, Nakamura K (2001) Sugar-responsible elements in the promoter of a gene for β-amylase of sweet potato. Plant Mol Biol 46:627–637
Matsuzaki K (1999) Why and how are peptide-lipid interactions utilized for self-defense? Magainins and tachyplesins as archetypes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1462:1–10
Mita S, Suzuki-Fujii K, Nakamura K (1995) Sugar-inducible expression of a gene for β-amylase in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 107:895–904
Mitsuhara I, Ugaki M, Hirochika H, Ohshima M, Murakami T, Gotoh Y, Katayose Y, Nakamura S, Honkura R, Nishimiya S, Ueno K, Mochizuki A, Tanimoto H, Tsugawa H, Otsuki Y, Ohashi Y (1996) Efficient promoter cassettes for enhanced expression of foreign genes in dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous plants. Plant Cell Physiol 37:49–59
Moran R, Garcia R, Lopez A, Zaldua Z, Mena J, Garcia M, Armas R, Somonte D, Rodriguez J, Gomez M, Pimentel E (1998) Transgenic sweet potato plants carrying the delta-endotoxin gene from Bacillus thuringiensis var. tenebrionis. Plant Sci 139:175–184
Nakamura K, Ohto MA, Yoshida N (1991) Sucrose-induced accumulation of β-amylase occurs concomitant with the accumulation of starch and sporamin in leaf-petiole cuttings of sweet potato. Plant Physiol 96:902–909
Ohta S, Mita S, Hattori T, Nakamura K (1990) Construction and expression in tobacco of a β-glucuronidase (GUS) reporter gene containing an intron within the coding sequence. Plant Cell Physiol 31:805–813
Osusky M, Zhou G, Osuska L, Hancock RE, Kay WW, Misra S (2000) Transgenic plants expressing cationic peptide chimeras exhibit broad-spectrum resistance to phytopathogens. Nat Biotechnol 18:1162–1166
Otani M, Shimada T, Kimura T, Saito A (1998) Transgenic plant production from embryogenic callus of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.) using Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Biotechnol 15:11–16
Ovard SV, Enright FM (2006) Expression of the antimicrobial peptides in plants to control phytopathogenic bacteria and fungi. Plant Cell Rep 25:561–572
Peters BM, Shirtliff ME, Jabra-Rizk MA (2010) Antimicrobial peptides: primeval molecules or future drugs? PLoS Pathog 6:e1001067
Ponti D, Mangoni ML, Mignogna G, Simmaco M, Barra D (2003) An amphibian antimicrobial peptide variant expressed in Nicotiana tabacum confers resistance to phytopathogens. Biochem J 370:121–127
Ponz F, Paz-Ares J, Hernandez-Lucas C, Carbonero P, Garcia-Olmedo F (1983) Synthesis and processing of thionin precursors in developing endosperm from barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). EMBO J 2:1035–1040
Shai Y (1999) Mechanism of the binding, insertion and destabilization of phospholipid bilayer membranes by α-helical antimicrobial and cell non-selective membrane-lytic peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta 1462:55–70
Stec B (2006) Plant thionins; the structural perspective. Cell Mol Life Sci 63:1370–1385
Takeda S, Mano S, Ohto M, Nakamura K (1994) Inhibitors of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A block the sugar-inducible gene expression in plants. Plant Physiol 106:567–574
Uritani I, Stahmann MA (1961) Changes in nitrogen metabolism in sweet potato with black rot. Plant Physiol 36:770–782
Yang L, Weiss TM, Lehrer RI, Huang HW (2000) Crystallization of antimicrobial pores in membranes: magainin and protegrin. Biophys J 79:2002–2009
Yoshida N, Hayashi K, Nakamura K (1992) A nuclear gene encoding β-amylase of sweet potato. Gene 120:255–259
Zasloff M (2002) Antimicrobial peptides of multicellular organisms. Nature 415:389–395
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported in part by a grant from the New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization, Japan (NEDO), and the Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry, Japan (METI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by F. Sato.
This paper is dedicated to Professor Emeritus Ikuzo Uritani of Nagoya University, who passed away on 25th September 2010 at the age of 91.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muramoto, N., Tanaka, T., Shimamura, T. et al. Transgenic sweet potato expressing thionin from barley gives resistance to black rot disease caused by Ceratocystis fimbriata in leaves and storage roots. Plant Cell Rep 31, 987–997 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1217-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1217-5