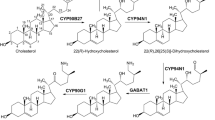
Abstract
Genistein, 4′,5,7-trihydroxyisoflavone, is an isoflavonoid compound predominantly restricted to legumes and known to possess phyto-oestrogenic and antioxidative activities. The key enzyme that redirects phenylpropanoid pathway intermediates from flavonoids to isoflavonoids is the isoflavone synthase (IFS). Brassica napus is a non-legume oilseed crop with vegetative tissues producing phenylpropanoids and flavonoids, but does not naturally accumulate isoflavones due to the absence of IFS. To demonstrate whether exogenous IFS is able to use endogenous substrate to produce isoflavone genistein in oilseed crop, the soybean IFS gene (GmIFS2) was incorporated into B. napus plants. The presence of GmIFS2 in B. napus was shown to direct the synthesis and accumulation of genistein derivatives in leaves up to 0.72 mg g−1 DW. In addition, expression levels for most B. napus genes in the phenylpropanoid pathway were altered. These results suggest that the heterologous GmIFS2 enzyme is functionally active at using the B. napus naringenin as a substrate to produce genistein in oilseed rape.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GmIFS2:
-
Glycine max isoflavone synthase 2
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- MALDI-TOF-MS:
-
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry
References
Akashi T, Aoki T, Ayabe S (2005) Molecular and biochemical characterization of 2-hydroxyisoflavanone dehydratase. Involvement of carboxylesterase-like proteins in leguminous isoflavone biosynthesis. Plant Physiol 137:882–891
Bolanos R, Del Castillo A, Francia J (2010) Soy isoflavones versus placebo in the treatment of climacteric vasomotor symptoms: systematic review and meta-analysis. Menopause 17:660–666
Gao MJ, Lydiate DJ, Li X, Lui H, Gjetvaj B, Hegedus DD, Rozwadowski K (2009) Repression of seed maturation genes by a trihelix transcriptional repressor in Arabidopsis seedlings. Plant Cell 21:54–71
Gullett NP, Ruhul Amin AR, Bayraktar S, Pezzuto JM, Shin DM, Khuri FR, Aggarwal BB, Surh YJ, Kucuk O (2010) Cancer prevention with natural compounds. Semin Oncol 37:258–281
Hashim MF, Hakamatsuka T, Ebizuka Y, Sankawa U (1990) Reaction mechanism of oxidative rearrangement of flavanone in isoflavone biosynthesis. FEBS Lett 271:219–222
Helferich WG, Andrade JE, Hoagland MS (2008) Phytoestrogens and breast cancer: a complex story. Inflammopharmacology 16:219–226
Jung W, Yu O, Lau CSM, O’Keefe DP, Odell J, Fader G, McGonigle B (2000) Identification and expression of isoflavone synthase, the key enzyme for biosynthesis of isoflavones in legumes. Nat Biotechnol 18:208–212
Li Y, Sarkar FH (2002) Gene expression profiles of genistein-treated PC3 prostate cancer cells. J Nutr 132:3623–3631
Li X, Gao MJ, Pan HY, Cui DJ, Gruber MY (2010) Purple canola: Arabidopsis PAP1 increases antioxidants and phenolics in Brassica napus leaves. J Agric Food Chem 58:1639–1645
Li X, Gao P, Wu LM, Cui DJ, Parkin I, Saberianfar R, Menassa R, Pan HY, Westcott N, Gruber MY (2011) The Arabidopsis tt19-4 mutant differentially accumulates flavonoids, proanthocyanidins and anthocyanin through a 3′ amino acid substitution in glutathione S-transferase. Plant Cell Environ 34:374–388
Liu CJ, Blount JW, Steele CL, Dixon RA (2002) Bottlenecks for metabolic engineering of isoflavone glycoconjugates in Arabidopsis. PNAS 99:14578–14583
Moloney MM, Walker JM, Sharma KK (1989) High efficiency transformation of Brassica napus, using Agrobacterium vectors. Plant Cell Rep 8:238–242
Nesi N, Delourme R, Brégeon M, Falentin C, Renard M (2008) Genetic and molecular approaches to improve nutritional value of Brassica napus L. seed. C R Biol 331:763–771
Owens DK, Crosby KC, Runac J, Howard BA, Winkel BSJ (2008) Biochemical and genetic characterization of Arabidopsis flavanone 3β-hydroxylase. Plant Physiol Biochem 46:833–843
Parniske M, Ahlborn B, Werner D (1991) Isoflavonoid-inducible resistance to the phytoalexin glyceollin in soybean rhizobia. J Bacteriol 173:3432–3439
Pedras MS, Zheng QA, Gadagi RS, Rimmer SR (2008) Phytoalexins and polar metabolites from the oilseeds canola and rapeseed: differential metabolic responses to the biotroph Albugo candida and to abiotic stress. Phytochemistry 69:894–910
Shih CH, Chen Y, Wang M, Chu IK, Lo C (2008) Accumulation of isoflavone genistin in transgenic tomato plants overexpressing a soybean isoflavone synthase gene. J Agri Food Chem 56:5655–5661
Southern EM (1975) Southern, detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98:503–517
Sreevidya VS, Srinivasa Rao C, Sullia SB, Ladha JK, Reddy PM (2006) Metabolic engineering of rice with soybean isoflavone synthase for promoting nodulation gene expression in rhizobia. J Exp Bot 57:1957–1969
Steele CL, Gijzen M, Qutob D, Dixon RA (1999) Molecular characterization of the enzyme catalyzing the aryl migration reaction of isoflavonoid biosynthesis in soybean. Arch Biochem Biophys 367:146–150
Subramanian S, Graham MY, Yu O, Graham TL (2005) RNA interference of soybean isoflavone synthase genes leads to silencing in tissues distal to the transformation site and to enhanced susceptibility to Phytophthora sojae. Plant Physiol 137:1345–1353
Taylor CK, Levy RM, Elliott JC, Burnett BP (2009) The effect of genistein aglycone on cancer and cancer risk: a review of in vitro, preclinical, and clinical studies. Nutr Rev 67:398–415
Tyler BM (2002) Molecular basis of recognition between Phytophthora pathogens and their hosts. Annu Rev Phytopathol 40:137–167
Wei S, Li X, Gruber MY, Li R, Zhou R, Zebarjadi A, Hannoufa A (2009) RNAi-mediated suppression of DET1 alters the levels of carotenoids and sinapate esters in seeds of Brassica napus. J Agric Food Chem 57:5326–5333
Wong MC, Emery PW, Preedy VR, Wiseman H (2008) Health benefits of isoflavones in functional foods? Proteomic and metabonomic advances. Inflammopharmacology 16:235–239
Yu O, Jez JM (2008) Nature’s assembly line: biosynthesis of simple phenylpropanoids and polyketides. Plant J 54:750–762
Yu O, McGonigle B (2005) Metabolic engineering of isoflavone biosynthesis. Adv Agron 86:147–190
Yu O, Shi J, Hession AO, Maxwell CA, McGonigle B, Odell JT (2003) Metabolic engineering to increase isoflavone biosynthesis in soybean seed. Phytochemistry 63:753–763
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (XL, NCET09-0423), Ministry of Education of the People’s Republic of China; National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC-31000149 and NSFC-30971885); and supported by Transgenic Key Project from Agricultural Ministry (2009ZX08009-062B); Basic Research Program (20060544), Science and Technology Department of Jilin Province; International Technology Cooperation Project (06GH07), Changchun, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by J. Zou.
X. Li and J.-C. Qin are joint first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Qin, JC., Wang, QY. et al. Metabolic engineering of isoflavone genistein in Brassica napus with soybean isoflavone synthase. Plant Cell Rep 30, 1435–1442 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1052-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-011-1052-8