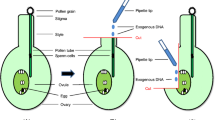
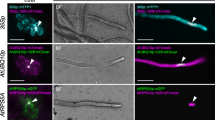
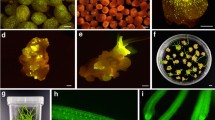
Abstract
We report here a new selectable marker for tobacco immature pollen transformation based on the expression of dihydrofolate reductase (dhfr) gene which confers resistance to methotrexate (Mtx). Two immature pollen transformation approaches, i.e., male germ line transformation and particle bombardment of embryogenic mid-bicellular pollen have been used for the production of stable transgenic tobacco plants. In the first method, two methotrexate-resistant plants were selected from a total of 7161 seeds recovered after transformation experiments. In the second method, four methotrexate-resistant plants were obtained from 29 bombardments using 3.7×105 pollen grains per bombardment. Southern analysis confirmed the transgenic nature of T0 and T1 candidate transgenic plants, and a genetic analysis showed that the transgenes are transmitted to subsequent generations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altpeter F, Vasil V, Srivastava V, Stöger E, Vasil IK (1996) Accelerated production of transgenic wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) plants. Plant Cell Rep 16:12–17. DOI 10.1007/s002990050166
Aziz N, Machray GC (2003) Efficient male germ line transformation for transgenic tobacco production without selection. Plant Mol Biol 51:203–211. DOI 10.1023/A:10211(99)71835-6
Baranyi M, Greilhuber J (1996) Flow cytometric and Feulgen densitometric analysis of genome size variation in Pisum. Theor Appl Genet 92:297–307. DOI 10.1007/s001220050128
Beck E, Ludwig G, Auerswald EA, Reiss B, Schaller H (1982) Nucleotide sequence and exact localization of the neomycin phosphotransferase gene from transposon Tn5. Gene 19:327–336. DOI 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90023-3
Benito-Moreno RM, Macke F, Hauser MT, Alwen A, Heberle-Bors E (1988) Sporophytes and gametophytes from in vitro cultured, immature tobacco pollen. In: Cresti M, Jori P, Paccini E (eds) Sexual reproduction in higher plants. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 137–142
Carlson AR, Letarte J, Chen J, Kasha KJ (2001) Visual screening of microspore-derived transgenic barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) with green-fluorescent protein. Plant Cell Rep 20:331–337. DOI 10.1007/s00299-01-0032-8
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1990) Isolation of plant DNA from fresh tissue. Focus 12:13–15
Eichholtz DA, Rogers SG, Horsch RB, Klee HJ, Hayford M, Hoffman NL, Braford SB, Fink CF, Flick J, O’Connell KM, Fraley RT (1987) Expression of mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene confers methotrexate resistance in transgenic petunia plants. Som Cell Mol Genet 13:67–76
Fukuoka H, Ogawa T, Matsuoka M, Ohkawa Y, Yano H (1998) Direct gene delivery into isolated microspores of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) and production of fertile transgenic plants. Plant Cell Rep 17:323–328. DOI 10.1007/s00299-00-5040-1
Galbraith DW, Harkins KR, Maddox JM, Ayres NM, Sharma DP, Firoozabady E (1983) Rapid flow cytometric analysis of the cell cycle in intact plant tissues. Science 220:1049–1051
Hu TC, Kasha KJ (1999) A cytological study of pretreatments used to improve isolated microspore cultures of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cv. Chris. Genome 42:432–441
Irdani T, Bogani P, Mengoni A, Mastromei G, Buiatti M (1998) Construction of a new vector conferring methotrexate resistance in Nicotiana tabacum plants. Plant Mol Biol 37:1079–1084. DOI 10.1023/A:10060(82)81543-4
Jähne A, Becker D, Brettschneider R, Lörz H (1994) Regeneration of transgenic, microspore-derived, fertile barley. Theor Appl Genet 89:525–533
Kasha KJ, Hu TC, Oro R, Simion E, Shim YS (2001) Nuclear fusion leads to chromosome doubling during mannitol pretreatment of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) microspores. J Exp Bot 52:1227–1238
Kyo M, Harada H (1986) Control of the developmental pathway of tobacco pollen in vitro. Planta 168:427–432
Maliga P, Breznovitz A, Marton L (1973) Streptomycin-resistant plants from callus culture of haploid tobacco. Nat New Biol 244:29–30
Miki B, McHugh S (2004) Selectable marker genes in transgenic plants: application, alternatives, and biosafety. J Biotechnol 107:193–232. DOI 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2003.10.011
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Neuhaus G, Spangenberg G, Mittelsten SO, Schweiger HG (1987) Transgenic rapeseed plants obtained by the microinjection of DNA into microspore-derived embryoids. Theor Appl Genet 75:30–36
Polsoni L, Kott LS, Beversdorf WD (1988) Large-scale microspore culture technique for mutation selection studies in Brassica napus L. Can J Bot 66:1681–1685
Reiss B, Schubert I, Köpchen K, Wendeler E, Schell J, Puchta H. (2000) RecA stimulates sister chromatid exchange and the fidelity of double-strand break repair, but not gene targeting, in plants transformed by Agrobacterium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:3358–3363
Simonsen CC, Levison AD (1983) Isolation and expression of an altered mouse dihydrofolate reductase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:2495–2499
Stöger E, Fink C, Pfosser M, Heberle-Bors E (1995) Plant transformation by particle bombardment of embryogenic pollen. Plant Cell Rep 14:273–278. DOI 10.1007/BF00232027
Swanson EB, Erickson LR (1989) Haploid transformation in Brassica napus using an octopine-producing strain of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Theor Appl Genet 78:831–835
Tupy J, Rihova L, Zarsky V (1991) Production of fertile tobacco pollen from microspores in suspension culture and its storage for in situ pollination. Sex Plant Reprod 4:284–287
Touraev A, Heberle-Bors E (1999) Microspore embryogenesis and in vitro pollen maturation in tobacco. In: Hall R (ed) Plant Cell Culture Protocols 111. Humana, Totowa, NJ, pp 281–291
Touraev A, Stöger E, Voronin V, Heberle-Bors E (1997) Plant male germ line transformation. Plant J 12:949–956. DOI 10.1046/j.1365-313X.1997.12040949.x
Touraev A, Pfosser M, Heberle-Bors E (2001) The microspore: a haploid multipurpose cell. Adv Bot Res 35:53–109
Vain P, McMullen MD, Finer JJ (1993) Osmotic treatment enhances particle bombardment-mediated transient and stable transformation of maize. Plant Cell Rep12:84–88. DOI: 10.1007/BF00241940
Yao QA, Simion E, William M, Krochko J, Kasha KJ (1997) Biolistic transformation of haploid isolated microspores of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Genome 40:570–581
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr J Greilhuber and Dr EM Temsch (Botany Institute, University of Vienna) for technical support and kind help to perform the Flow cytometry analysis. The authors are also very thankful to Dr B Reiss (Max-Planck Institute für Züchtungsforschung, Köln, Germany) for providing the pMN125 plasmid. This study was funded by the grant of the European Union QLK-CT-2000-00365.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by W. Harwood
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aionesei, T., Hosp, J., Voronin, V. et al. Methotrexate is a new selectable marker for tobacco immature pollen transformation. Plant Cell Rep 25, 410–416 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-005-0067-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-005-0067-4