Abstract
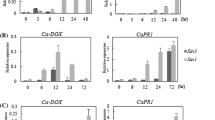
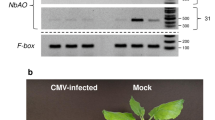
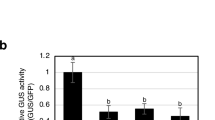
An 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid (ACC) oxidase, NbACO1, was cloned from cDNA of Nicotiana benthamiana leaves infected with the hemibiotrophic fungal pathogen, Colletotrichum orbiculare. Expression of NbACO1 increased approximately 3-fold by 24 h after inoculation and then continued to increase reaching a maximum that was 6-folds greater than that in healthy plants by 96 h after inoculation. A portion of NbACO1 was cloned into a PVX vector for virus-induced gene silencing, and the silencing resulted in a reduction in its expression to 7–9% of that found in the controls for fungal-infected leaf tissue. Silencing of NbACO1 also resulted in significant reductions in transcript levels of genes encoding an ethylene responsive transcription factor and two glutathione S-transferases, but not for a basic pathogenesis-related protein gene, indicating that at least some genes associated with ethylene signaling were affected by the silencing treatment. Inoculated NbACO1-silenced plants developed more lesions more quickly as a result of an accelerated switch from the symptomless, biotrophic phase to the symptomatic necrotrophic phase of infection compared to inoculated control plants. This indicates that manipulation of ACC oxidase can affect the length of the biotrophic phase of infection in this interaction.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- cDNA:
-
Complimentary DNA;
- RACE:
-
Rapid amplification of cDNA ends;
- HR:
-
Hypersensitive response;
- RT-PCR:
-
Reverse transcriptase PCR;
- SYAS:
-
Sodium chloride-yeast extract-sucrose agar;
- VIGS:
-
Virus-induced gene silencing
References
Arshad M, Frakenberger WT (2002) Ethylene. Kluwer Academic Press, Dordrecht, NL
Baulcombe D (1999) Fast forward genetics based on virus-induced gene silencing. Curr Opin Plant Biol 2:109–133
Ben-Amor M, Flores B, Latche A, Bouzayen M, Pech JC, Romojaro F (1999) Inhibition of ethylene biosynthesis by antisense ACC oxidase RNA prevents chilling injury in Charentais cantaloupe melons. Plant Cell Environ 22:1579–1586
Chen GYJ, Jin S, Goodwin PH (2002) An improved method for the isolation of total RNA from Malva pusilla tissues infected with Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. J Phytopathol 148:57–60
Chen N, Goodwin PH, Hsiang T (2003a) The role of ethylene during the infection of Nicotiana tabacum by Colletotrichum destructivum. J Exp Bot 54:2449–2456
Chen N, Hsiang T, Goodwin PH (2003b) Use of green fluorescent protein to quantify the growth of Colletotrichum during infection of tobacco. J Microbiol Methods 53:113–122
Cooper W, Bouzayen M, Hamilton A, Barry C, Rossall S, Grierson D (1998) Use of transgenic plants to study the role of ethylene and polygalacturonase during infection of tomato fruit by Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. Plant Pathol 47:308–316
Dean JD, Goodwin PH, Hsiang T (2002) Comparison of relative RT-PCR and Northern blot analyses to measure expression of β-l,3-glucanase in Nicotianabenthamiana infected with Colletotrichum destructivum. Plant Mol Biol Rep 20:347–356
Dean JD, Goodwin PH, Hsiang T (2005) Induction of glutathione S-transferase genes of Nicotiana benthamiana following infection by Colletotrichum destructivum and C. orbiculare and involvement of one in resistance. J Exp Bot 56:1525–1533
Esquerré-Tugayé MT, Bottin A, Rickauer M, Sancan JP, Fournier J, Pouenat ML (1993) Ethylene in early signalling phenomena at the plant-microorganism interaction. In: Pech JC, Latché A, Balagué C (eds) Cellular and molecular aspects of the plant hormone ethylene. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, NL, pp 217–222
Ge L, Liu JZ, Wong WS, Hsiao WLW, Chong K, Xu K, Yang SF, Kung SD, Li N (2000) Identification of a novel multiple environmental factor-responsive 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase gene, NT-ACS2, from tobacco. Plant Cell Environ 23:1169–1182
Geraats BPJ, Bakker PAHM, Lawrence CB, Achuo EA, Hofte M, van Loon LC (2003) Ethylene-insensitive tobacco shows differentially altered susceptibility to different pathogens. Phytopathology 93:813–821
Henzi MX, Christey MC, McNeil DL (2000) Morphological characterisation and gronomic evaluation of transgenic broccoli (Brassica oleracea L. var. italica) containing an antisense ACC oxidase gene. Euphytica 113:9–8
Hoffman T, Schmidt JS, Zheng X, Bent AF (1999) Isolation of ethylene-insensitive soybean mutants that are altered in pathogen susceptibility and gene-for-gene disease resistance. Plant Physiol 3:935–950
Itzhaki H, Maxson JM, Woodson WR (1994) An ethylene-responsive enhancer element is involved in the senescene-related expression of the carnation glutathione S-transferase (GSTI) gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:8925–8929
Johnson PR, Ecker JR (1998) The ethylene gas signal transduction pathway: a molecular perspective. Annu Rev Genet 32:227–254
Jones L, Hamilton AJ, Voinnet O, Thomas CL, Maule AJ, Baulcombe D (1999) RNA-DNA interactions and DNA methylation in post-transcriptional gene silencing. Plant Cell 11:2291–2301
Kitajima S, Koyama T, Ohme-Takagi M, Shinshi H, Sato F (2000) Characterization of gene expression of NsERFs, transcription factors of basic PR genes from Nicotiana sylvestris. Plant Cell Physiol 41:817–824
Kim YS, Choi D, Lee MM, Lee SH, Kim WT (1998) Biotic and abiotic stress-related expression of 1-aminocyclopropane-l-carboxylate oxidase gene family in Nicotiana glutinosa L. Plant Cell Physiol 6:565–573
Knoester M, Bol JF, van Loon LC, Linthorst HJ (1995) Virus-induced gene expression for enzymes of ethylene biosynthesis in hypersensitively reacting tobacco. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 8:177–180
Knoester M, Linthorst HJM, Bol JF, van Loon LC (1997) Modulation of stress-inducible ethylene biosynthesis by sense and antisense gene expression in tobacco. Plant Sci 126:173–183
Knoester M, Linthorst HJM, Bol JF, van Loon LC (2001) Involvement of ethylene in lesion development and systemic acquired resistance in tobacco during the hypersensitive reaction to tobacco mosaic virus. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 59:45–57
Knoester M, van Loon LC, van den Heuvel J, Hennig J, Bol JF, Linthorst HJM (1998) Ethylene-insensitive tobacco lacks nonhost resistance against soil-borne fungi. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 4:1933–1937
Lahey KA, Yuan RC, Burns JK, Ueng PP, Timmer LW, Chung KR (2004) Induction of phytohormones and differential gene expression in citrus flowers infected by the fungus Colletotrichum acutatum. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 17:1394–1401
Lieberherr D, Wagner U, Dubuis PH, Metraux JP, Mauch F (2003) The rapid induction of glutathione S-transferases AtGSTF2 and AtGSTF6 by avirulent Pseudomonas syringae is the result of combined salicylic acid and ethylene signaling. Plant Cell Physiol 44:750–757
Lu R, Martin-Hernandez AM, Peart JR, Malcuit L, Baulcombe DC (2003) Virus-induced gene silencing in plants. Methods 30:296–303
Lund ST, Stall RE, Klee HJ (1998) Ethylene regulates the susceptible response to pathogen infection in tomato. Plant Cell 3:371–382
Mandanhar J, Hartman G, Sinclair J (1986) Colletotrichum destructivum, the anamorph of Glomerella glycines. Phytopathology 76:282–285
Narusaka Y, Narusaka M, Park P, Kubo Y, Hirayama T, Seki M, Shiraishi T, Ishida J, Nakashima M, Enju A, Sakurai T, Satou M, Kobayashi M (2004) RCH1, a locus in arabidopsis that confers resistance to the hemibiotrophic fungal pathogen Colletotrichum higginsianum. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 17:749–762
Ohme-Takagi M, Suzuki K, Shinshi H (2000) Regulation of ethylene-induced transcription of defense genes. Plant Cell Physiol 41:1187–1192
Ohtsubo N, Mitsuhara I, Koga M, Seo S, Ohashi Y (1999) Ethylene promotes the necrotic lesion formation and basic PR gene expression in TMV-infected tobacco. Plant Cell Physiol 40:808–817
Robertson D (2004) VIGS vectors for gene silencing: many targets, many tools. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:495–519
Ruiz MT, Voinnet O, Baulcombe DC (1998) Initiation and maintenance of virus-induced gene silencing. Plant Cell 10:937–946
Schlagnhaufer CD, Arteca RN, Pell EJ (1997) Sequential expression of two 1-aminocyclopropane-l-carboxylate synthase genes in response to biotic and abiotic stresses in potato (Solarium tuberosum L.) leaves. Plant Mol Biol 6:683–688
Shen S, Goodwin PH, Hsiang T (2001) Infection of Nicotiana species by the anthracnose fungus, Colletotrichum orbiculare. Eur J Plant Pathol 107:763–773
Thomma BP, Eggermont K, Tierens KF, Broekaert WF (1999) Requirement of functional ethylene-insensitive 2 gene for efficient resistance of arabidopsis to infection by Botrytis cinerea. Plant Physiol 121:1093–1102
Tsuchisaka A, Theologis A (2004) Unique and overlapping expression patterns among the arabidopsis 1-amino-cyclopropane-l-carboxylate synthase gene family members. Plant Physiol 136:2982–3000
Wi SJ, Park KY (2002) Antisense expression of carnation cDNA encoding ACC synthase or ACC oxidase enhances polyamine content and abiotic stress tolerance in transgenic tobacco plants. Mol Cells 13:209–222
Wubben MJE, Su H, Rodermel SR, Baum TJ (2001) Susceptibility to the sugar beet cyst nematode is modulated by ethylene signal transduction in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 14:1206–1212
Acknowledgment
Funding for this study was provided by the Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H.S. Judelson
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shan, X.C., Goodwin, P.H. Silencing an ACC oxidase gene affects the susceptible host response of Nicotiana benthamiana to infection by Colletotrichum orbiculare . Plant Cell Rep 25, 241–247 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-005-0063-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-005-0063-8