Abstract
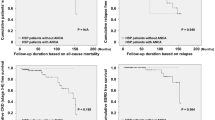
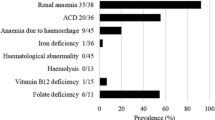
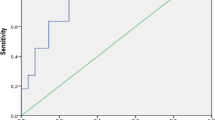
Protein-losing enteropathy (PLE) has been reported to be associated with various systemic autoimmune diseases. However, reports regarding PLE in ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) patients are limited. We herein aimed to describe the clinical characteristics of AAV with PLE. We conducted a retrospective chart review of patients who were diagnosed with AAV and who began treatment at the University of Tokyo Hospital between June 2003 and June 2020. Among 68 AAV patients, there were four patients (5.9%) with PLE, consisting of two patients with MPA, one patient with GPA, and one patient with EGPA. Clinical courses were described, and their data were compared with AAV patients without PLE. Demographic characteristics, disease activity, and the pattern of organ involvement were similar between patients with PLE and without PLE. Patients with PLE had hypocomplementemia more frequently than the patients without PLE (CH50 75.0% vs 1.8%, p < 0.001, C3 50.0% vs 1.8%, p = 0.01, C4 75.0% vs 3.5%, p = 0.001). Although hypoalbuminemia improved with immunosuppressive therapy for AAV, the improvement in hypoalbuminemia was slow in most cases. We also performed a systematic review on PLE associated with vasculitis. Thirteen reports were included, and Henoch–Schonlein Purpura patients with PLE also tended to have hypocomplementemia. In conclusion, PLE is a rare complication of AAV and complement system may associate with the mechanism of PLE.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levitt DG, Levitt MD (2017) Protein losing enteropathy: comprehensive review of the mechanistic association with clinical and subclinical disease states. Clin Exp Gastroenterol 10:147–168. https://doi.org/10.2147/CEG.S136803
Law ST, Ma KM, Li KK (2012) Protein-losing enteropathy associated with or without systemic autoimmune disease: what are the differences? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 24:294–302. https://doi.org/10.1097/MEG.0b013e32834f3ea0
Zheng WJ, Tian XP, Li L, Jing HL, Li F, Zeng XF, Tang FL (2007) Protein-losing enteropathy in systemic lupus erythematosus: analysis of the clinical features of fifteen patients. J Clin Rheumatol 13:313–316. https://doi.org/10.1097/RHU.0b013e31815bf9c6
Nagashima T, Hoshino M, Shimoji S, Morino N, Kamimura T, Okazaki H, Minota S (2009) Protein-losing gastroenteropathy associated with primary Sjögren’s syndrome: a characteristic oriental variant. Rheumatol Int 29:817–820. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-008-0794-2
Weiser MM, Andres GA, Brentjens JR, Evans JT, Reichlin M (1981) Systemic lupus erythematosus and intestinal venulitis. Gastroenterology 81:570–579. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-5085(81)90612-0
Watts R, Lane S, Hanslik T, Hauser T, Hellmich B, Koldingsnes W, Mahr A, Segelmark M, Cohen-Tervaert JW, Scott D (2007) Development and validation of a consensus methodology for the classification of the ANCA-associated vasculitides and polyarteritis nodosa for epidemiological studies. Ann Rheum Dis 66:222–227. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2006.054593
Mukhtyar C, Lee R, Brown D, Carruthers D, Dasgupta B, Dubey S, Flossmann O, Hall C, Hollywood J, Jayne D, Jones R, Lanyon P, Muir A, Scott D, Young L, Luqmani RA (2009) Modification and validation of the Birmingham Vasculitis Activity Score (version 3). Ann Rheum Dis 68:1827–1832. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2008.101279
Khalesi M, Nakhaei AA, Seyed AJ, Treglia G, Zakavi SR, Sadeghi R, Kianifar HR (2013) Diagnostic accuracy of nuclear medicine imaging in protein losing enteropathy: systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. Acta Gastroenterol Belg 76:413–422
Suzuki C, Higaki S, Nishiaki M, Mitani N, Yanai H, Tada M, Okita K (1997) 99mTc-HSA-D scintigraphy in the diagnosis of protein-losing gastroenteropathy due to secondary amyloidosis. J Gastroenterol 32:78–82. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01213300
Kanda Y (2013) Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software “EZR” for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transpl 48:452–458. https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2012.244
Masi AT, Hunder GG, Lie JT, Michel BA, Bloch DA, Arend WP, Calabrese LH, Edworthy SM, Fauci AS, Leavitt RY et al (1990) The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of Churg–Strauss syndrome (allergic granulomatosis and angiitis). Arthritis Rheum 33:1094–1100. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780330806
Reif S, Jain A, Santiago J, Rossi T (1991) Protein losing enteropathy as a manifestation of Henoch-Schönlein purpura. Acta Paediatr Scand 80:482–485. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1651-2227.1991.tb11888.x
Cho CS, Min JK, Park SH, Yang HI, Lee SH, Choi YJ, Kim BS, Kim HY (1996) Protein losing enteropathy associated with Henoch-Schönlein purpura in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol 25:334–336. https://doi.org/10.3109/03009749609104068
Kano K, Ozawa T, Kuwashima S, Ito S (1998) Uncommon multisystemic involvement in a case of Henoch-Schönlein purpura. Acta Paediatr Jpn 40:159–161. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-200x.1998.tb01903.x
Jarasvaraparn C, Lertudomphonwanit C, Pirojsakul K, Worawichawong S, Angkathunyakul N, Treepongkaruna S (2016) Henoch-Schönlein without purpura: a case report and review literature. J Med Assoc Thai 99:441–445
Jafri FM, Mendelow H, Shadduck RK, Sekas G (1990) Jejunal vasculitis with protein-losing enteropathy after bone marrow transplantation. Gastroenterology 98:1689–1692. https://doi.org/10.1016/0016-5085(90)91108-i
Ferrante M, Penninckx F, De Hertogh G, Geboes K, D’Hoore A, Noman M, Vermeire S, Rutgeerts P, Van Assche G (2006) Protein-losing enteropathy in Crohn’s disease. Acta Gastroenterol Belg 69:384–389
Oh DC, Ng TM, Ho J, Leong KP (2006) Systemic lupus erythematosus with concurrent protein-losing enteropathy and primary sclerosing cholangitis: a unique association. Lupus 15:102–104. https://doi.org/10.1191/0961203306lu2251cr
Jauhola O, Ronkainen J, Koskimies O, Ala-Houhala M, Arikoski P, Hölttä T, Jahnukainen T, Rajantie J, Ormälä T, Nuutinen M (2010) Clinical course of extrarenal symptoms in Henoch-Schonlein purpura: a 6-month prospective study. Arch Dis Child 95:871–876. https://doi.org/10.1136/adc.2009.167874
Hernstadt HM, Bartlett M, Kausman JY, Macgregor D, Akikusa JD (2015) Complicated Henoch-Schönlein purpura. J Paediatr Child Health 51:639–642. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpc.12786
Cherqaoui B, Chausset A, Stephan JL, Merlin E (2016) Intravenous immunoglobulins for severe gastrointestinal involvement in pediatric Henoch-Schönlein purpura: a French retrospective study. Arch Pediatr 23:584–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcped.2016.03.018
Pattnaik SA, Mitra S, Mishra TS, Purkait S, Kumar P, Naik S (2019) A vasculitis-associated neuromuscular and vascular hamartoma presenting as a fatal form of abdominal cocoon. Int J Surg Pathol 27:108–115. https://doi.org/10.1177/1066896918786582
Mok CC, Ying KY, Mak A, To CH, Szeto ML (2006) Outcome of protein-losing gastroenteropathy in systemic lupus erythematosus treated with prednisolone and azathioprine. Rheumatology (Oxford) 45:425–429. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kei164
Nanjo S, Nishikawa J, Miwa S, Mihara H, Fujinami H, Yoshita H, Ueda A, Kajiura S, Hasumoto Y, Ando T, Hosokawa A, Sugiyama T (2014) Immune-mediated protein-losing enteropathy with Down syndrome. Intern Med 53:2301–2305. https://doi.org/10.2169/internalmedicine.53.1980
Lin Q, Min Y, Li Y, Zhu Y, Song X, Xu Q, Wang L, Cheng J, Feng Q, Li X (2012) Henoch-Schönlein purpura with hypocomplementemia. Pediatr Nephrol 27:801–806. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-011-2070-z
Tsutsumi A, Sugiyama T, Matsumura R, Sueishi M, Takabayashi K, Koike T, Tomioka H, Yoshida S (1991) Protein losing enteropathy associated with collagen diseases. Ann Rheum Dis 50:178–181. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.50.3.178
Ozen A, Comrie WA, Ardy RC, Domínguez Conde C, Dalgic B, Beser ÖF, Morawski AR, Karakoc-Aydiner E, Tutar E, Baris S, Ozcay F, Serwas NK, Zhang Y, Matthews HF, Pittaluga S, Folio LR, Unlusoy Aksu A, McElwee JJ, Krolo A, Kiykim A, Baris Z, Gulsan M, Ogulur I, Snapper SB, Houwen RHJ, Leavis HL, Ertem D, Kain R, Sari S, Erkan T, Su HC, Boztug K, Lenardo MJ (2017) CD55 deficiency, early-onset protein-losing enteropathy, and thrombosis. N Engl J Med 377:52–61. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1615887
Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Bacon PA, Basu N, Cid MC, Ferrario F, Flores-Suarez LF, Gross WL, Guillevin L, Hagen EC, Hoffman GS, Jayne DR, Kallenberg CG, Lamprecht P, Langford CA, Luqmani RA, Mahr AD, Matteson EL, Merkel PA, Ozen S, Pusey CD, Rasmussen N, Rees AJ, Scott DG, Specks U, Stone JH, Takahashi K, Watts RA (2013) 2012 revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides. Arthritis Rheum 65:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.37715
Fukui S, Iwamoto N, Umeda M, Nishino A, Nakashima Y, Koga T, Kawashiri SY, Ichinose K, Hirai Y, Tamai M, Nakamura H, Origuchi T, Sato S, Kawakami A (2016) Antineutrophilic cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis with hypocomplementemia has a higher incidence of serious organ damage and a poor prognosis. Medicine (Baltimore) 95:e4871. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000004871
García L, Pena CE, Maldonado R, Costi C, Mamberti M, Martins E, García MA (2019) Increased renal damage in hypocomplementemic patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis: retrospective cohort study. Clin Rheumatol 38:2819–2824. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04636-9
Acknowledgements
We would like to express our gratitude to the patients at our hospital for their cooperation with this study.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Study design: MG, YT, HS, KF. Data acquisition: MG, YT, KT, HT, YS, TK, YI. Data analysis: MG. Manuscript preparation: MG, YT.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
MG has received speaking fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb and Ono Pharmaceutical. YT has received grants from GlaxoSmithKline and speaking fees from GlaxoSmithKline and Chugai. TK has received speaking fees and/or honoraria from Tanabe Mitsubishi, Kissei, Pfizer, Amgen and received grants and speaking fees from GlaxoSmithKline. HS has received fees from Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Sanofi, AbbVie, GlaxoSmithKline, Gilead, Boehringer Ingelheim, Jansen, Novartis, Chugai, Takeda, Astellas, Eisai, Asahi Kasei and Daiichi-Sankyo, and has received research grants from Novartis. KF has received speaking fees and/or honoraria from Tanabe Mitsubishi, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Chugai, Jansen, Pfizer, Ono, Abbie, Ayumi, Astellas, Sanofi, Novartis, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Asahi Kasei, Japan Blood Products Organization, and Kowa, and has received research grants from Tanabe Mitsubishi, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Chugai, Abbie, Ayumi, Astellas, Sanofi, Eisai, and Asahi Kasei.
Ethics approval
This study was approved by the ethics committee of the University of Tokyo Hospital (2431) on February 20th in 2009.
Consent to participate/consent for publication (include appropriate statements)
The ethics committee at our institution does not require patient consent for retrospective chart studies. Patients were provided chances to opt out of the study.
Data availability of data and material (data transparency)
Not applicable.
Code availability (software application or custom code)
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goto, M., Tsuchida, Y., Terada, K. et al. ANCA-associated vasculitis with protein-losing enteropathy is characterized by hypocomplementemia. Rheumatol Int 42, 1863–1872 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-021-04923-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-021-04923-2