Abstract
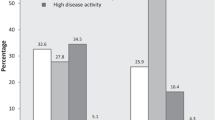
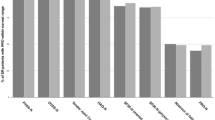
Management of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in many Latin-American countries is impaired by fragmentation and scarce healthcare provision, resulting in obstacles to access, diagnosis, and treatment, and consequently in poor health outcomes. The aim of this study is to propose a comprehensive care program as a model to provide healthcare to RA patients receiving synthetic DMARDs in a Colombian setting by describing the model and its results. Health outcomes were prospectively collected in all patients entering the program. By protocol, patients are followed up during 24 months using a treat-to-target strategy with a patient-centered care (PCC) model, meaning that a patient should be seen by rheumatologist, physical and occupational therapist, physiatrist, nutritionist and psychologist, at least three times a year according to disease activity by DAS28. Otherwise, patients receive standard therapy. The incidence of remission and low disease activity (LDA) was calculated by periods of follow-up. A total of 968 patients entered the program from January 2015 to December 2016; 80.2% were women. At baseline, 41% of patients were in remission, 17% in LDA and 42% in MDS/SDA. At 24 months of follow-up, 66% were in remission, 18% in LDA and only 16% in MDS/SDA. Regarding DAS28, the mean at the beginning of the time analysis was 3.1 (SD 1.0) and after 24 months it was 2.4 (SD 0.7), showing a statistically significant improvement (p < 0.001). In all patients, the reduction of disease activity was 65% (95% CI, 58–71). Patients entering the PCC program benefited from a global improvement in disease activity in terms of DAS28.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alamanos Y, Drosos AA (2005) Epidemiology of adult rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmun Rev 4:130–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2004.09.002
Epstein FH, Choy EHS, Panayi GS (2001) Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 344:907–916. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM200103223441207
Barreto SM, Miranda JJ, Figueroa JP et al (2012) Epidemiology in Latin America and the Caribbean: current situation and challenges. Int J Epidemiol 41:557–571
Santos-Moreno P, Galarza-Maldonado C, Caballero-Uribe CV et al (2015) REAL-PANLAR project for the implementation and accreditation of centers of excellence in rheumatoid arthritis throughout Latin America. JCR J Clin Rheumatol 21:175–180. https://doi.org/10.1097/RHU.0000000000000247
Al Maini M, Adelowo F, Al Saleh J et al (2015) The global challenges and opportunities in the practice of rheumatology: white paper by the world forum on rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases. Clin Rheumatol 34:819–829
Fondo Colombiano de Enfermendades de Alto Costo-Cuenta de Alto Costo [CAC] (2017) Situación de la artritis reumatoide en Colombia 2016. Bogotá D.C. https://cuentadealtocosto.org/site/index.php. Accessed 24 Oct 2017
Kumar K, Peters S, Barton A (2016) Rheumatoid arthritis patient perceptions on the value of predictive testing for treatments: a qualitative study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 17(1):460
Organización Panamericana de la Salud-OPS (2012) Redes integradas de servicios de salud. http://www.paho.org/%0Ahq/index.php?option=com_content&view=category&layout=%0Ablog&id=3184&Itemid=3553&lang=es. Accessed 30 ene 2017
Santos-Moreno P, Castañeda O, Garro B et al (2015) From the model of integral attention to the creation of centers of excellence in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 34(Suppl 1):S71–S77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-015-3017-8
Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Bijlsma JWJ et al (2012) Treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: recommendations of an international task force. Ann Rheum Dis 69:631–637. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.123919
Smolen. JS, Breedveld. FC, Burmester GR et al (2015) Treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: 2014 update of the recommendations of an international task force. Ann Rheum Dis 0:1–13
Ministerio de Salud y Protección Social Resolución 1393 de 2015. https://cuentadealtocosto.org/site/images/Resolucion1393 de 2015-ARTRITIS.pdf. Accessed 25 Oct 2017
Ministerio de Salud y Protección Social—Ministerio de Hacienda y Crédito Público Cuenta de Alto Costo. https://cuentadealtocosto.org/site/index.php. Accessed 25 Oct 2017
Ministerio de Salud y Protección Social (2014) Guía de Práctica Clínica para la detección temprana, diagnóstico y tratamiento de la artritis reumatoide. https://cuentadealtocosto.org/site/index.php. Accessed 24 Oct 2017
Fransen J, Van Riel P (2005) The disease activity score and the EULAR response criteria. Clin Exp Rheumatol 23:S93
Szklo M, Nieto FJ (2014) Epidemiology: beyond the basics. Jones & Bartlett Learning, Burlington, VT
Ministerio de Salud y Protección Social Resolución Número 8430 de 1993. https://www.minsalud.gov.co/sites/rid/Lists/BibliotecaDigital/RIDE/DE/DIJ/RESOLUCION-8430-DE-1993.PDF. Accessed 25 Oct 2017
Tan BE, Lim AL, Kan SL et al (2017) Management of rheumatoid arthritis in clinical practice using treat-to-target strategy: Where do we stand in the multi-ethnic Malaysia population? Rheumatol Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-017-3705-6
de Andrade NPB, da Silva Chakr RM, Xavier RM et al (2017) Long-term outcomes of treat-to-target strategy in established rheumatoid arthritis: a daily practice prospective cohort study. Rheumatol Int. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-017-3695-4
Wabe N, Wiese MD (2016) Treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: physician and patient adherence issues in contemporary rheumatoid arthritis therapy. J Eval Clin Pract. https://doi.org/10.1111/jep.12620
BRAND C, HUNTER D, HINMAN R et al (2011) Improving care for people with osteoarthritis of the hip and knee: how has national policy for osteoarthritis been translated into service models in Australia? Int J Rheum Dis 14:181–190. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1756-185X.2011.01613.x
Puchner R, Hochreiter R, Pieringer H, Vavrovsky A (2017) Improving patient flow of people with rheumatoid arthritis has the potential to simultaneously improve health outcomes and reduce direct costs. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 18:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-016-1362-7
Fagnani F, Pham T, Claudepierre P et al (2016) Modeling of the clinical and economic impact of a risk-sharing agreement supporting a treat-to-target strategy in the management of patients with rheumatoid arthritis in France. J Med Econ 19:812–821. https://doi.org/10.1080/13696998.2016.1176576
Speerin R, Slater H, Li L et al (2014) Moving from evidence to practice: models of care for the prevention and management of musculoskeletal conditions. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 28:479–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.berh.2014.07.001
Gunnarsson C, Chen J, Rizzo JA et al (2015) The employee absenteeism costs of rheumatoid arthritis. J Occup Environ Med 57:635–642. https://doi.org/10.1097/JOM.0000000000000461
Voshaar MJH, Nota I, van de Laar MAFJ., van den Bemt BJF (2015) Patient-centred care in established rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 29:643–663. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.berh.2015.09.007
Weinberg DB, Cooney-Miner D, Perloff JN et al (2011) Building collaborative capacity: promoting interdisciplinary teamwork in the absence of formal teams. Med Care 49:716–723. https://doi.org/10.1097/MLR.0b013e318215da3f
Coulter A, Ellins J (2007) Effectiveness of strategies for informing, educating, and involving patients. BMJ 335:24–27. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.39246.581169.80
Frampton S, Guastello S, Brady C et al (2008) Patient-centered care improvement guide. CT Planetree, Derby
Elwyn G, Laitner S, Coulter A et al (2010) Implementing shared decision making in the NHS. BMJ 341:c5146
Kremer JA, van der Eijk M, Aarts JW, Bloem BR (2015) The individual formerly known as patient. Patient-centered care 99
van der Eijk M, Nijhuis FAP, Faber MJ, Bloem BR (2013) Moving from physician-centered care towards patient-centered care for Parkinson’s disease patients. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 19:923–927
Sevin C, Moore G, Shepherd J et al (2009) Transforming care teams to provide the best possible patient-centered, collaborative care. J Ambul Care Manage 32:24–31. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.JAC.0000343121.07844.e0
Bensing J (2000) Bridging the gap. The separate worlds of evidence-based medicine and patient-centered medicine. Patient Educ Couns 39:17–25
Park DC, Hertzog C, Leventhal H et al (1999) Medication adherence in rheumatoid arthritis patients: older is wiser. J Am Geriatr Soc 47:172–183. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.1999.tb04575.x
Jaillier JCR, Arango AMP, Pérez DAM (2015) Challenges faced in Latin America for the implementation of an ideal health-care model for rheumatoid arthritis patients: are we ready? Clin Rheumatol 34:79–93. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-015-3034-7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PS-M designed the study, collected the data, reviewed the drafted manuscript, and approved the final manuscript for submission. NA-Z and NA-G designed the study, drafted the manuscript, carried out analysis, and approved the final manuscript. MC-S helped carrying out analysis, reviewed the drafted manuscript, and approved the final manuscript. AP-C helped carrying out analysis, reviewed the drafted manuscript, and approved the final manuscript, and LV-P helped collected the data, reviewed the drafted manuscript, and approved the final manuscript. All authors assume the integrity of the content of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Pedro Santos-Moreno, Nelson J. Alvis-Zakzuk, Laura Villarreal-Peralta, Maria Carrasquilla-Sotomayor, Angel Paternina-Caicedo and Nelson Alvis-Guzmán declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
No funding was received.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santos-Moreno, P., Alvis-Zakzuk, N.J., Villarreal-Peralta, L. et al. A comprehensive care program achieves high remission rates in rheumatoid arthritis in a middle-income setting. Experience of a Center of Excellence in Colombia. Rheumatol Int 38, 499–505 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-017-3903-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-017-3903-2