Abstract
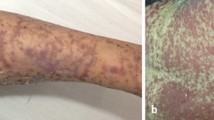
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) are life-threatening dermatological conditions that are characterized by mucosal erosions, epidermal detachments and erosions. The most common causes of SJS and TEN are drugs; other causes such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), vaccinations and infections have been rarely implicated. We present the case of a 14-year-old female patient with acute pancreatitis as an initial manifestation of systemic lupus erythematosus, complicated by the toxic epidermal necrolysis with a fatal outcome. She initially presented with abdominal pain, fever, vomiting, and intolerance to oral intake and elevated pancreatic enzyme levels. Systemic lupus erythematosus was diagnosed secondary when her condition has been already complicated by the toxic epidermal necrolysis. The administration of corticosteroids and high doses of intravenous immunoglobulin did not lead to positive effects in the treatment of our patient.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cetin GY, Sayar H, Ozkan F et al (2013) A case of toxic epidermal necrolysis-like skin lesions with systemic lupus erythematosus and review of the literature. Lupus 22(8):839–846. doi:10.1177/0961203313492242
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40(9):1725. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(199709)40:9&It;1725::AID-ART29>3.0CO;2-Y
Richer O, Ulinski T, Lemelle I et al (2007) Abdominal manifestations in childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 66(2):174–178. doi:10.1136/ard.2005.050070
Obermoser G, Sontheimer RD, Zelger B (2010) Overview of common, rare and atypical manifestations of cutaneous lupus erythematosus and histopathological correlates. Lupus 19(9):1050–1070. doi:10.1177/0961203310370048
Campos LM, Omori CH, Lotito AP et al (2010) Acute pancreatitis in juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus: a manifestation of macrophage activation syndrome? Lupus 19(14):1654–1658. doi:10.1177/0961203310378863
Paradela S, Martinez-Gomez W, Fernandez-Jorge B et al (2007) Toxic epidermal necrolysis-like acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Lupus 16(9):741–745. doi:10.1177/0961203307079498
Ting W, Stone MS, Racila D et al (2004) Toxic epidermal necrolysis-like acute cutaneous lupus erythematosus and the spectrum of the acute syndrome of apoptotic pan-epidermolysis (ASAP): a case report, concept review and proposal for new classification of lupus erythematosus vesiculobullous skin lesions. Lupus 13(12):941–950
Auquier-Dunant A, Mockenhaupt M, Naldi L et al (2002) Correlations between clinical patterns and causes of erythema multiforme majus, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Arch Dermatol 138(8):1019–1024
Yu J, Brandling-Bennett H, Co DO et al (2016) Toxic epidermal necrolysis-like cutaneous lupus in pediatric patients: a case series and review. Pediatrics 137(6):e20154497. doi:10.1542/peds.2015-4497
Torchia D, Romanelli P, Kardel FA (2012) Erythema multiforme and Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with lupus erythematosus. J Am Acad Dermatol 67(3):417–421. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2011
Moallem HJ, Baqi N, Taningco G et al (2002) Systemic lupus erythematosus presenting as toxic epidermal necrolysis in an adolescent. Int Pediatr 17:31–33
Miralles ES, Nunez M, del Olmo N et al (1995) Ranitidine-related toxic epidermal necrolysis in a patient with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Am Acad Dermatol 32:133–134
Velez A, Moreno JC (2000) Second case of ranitidine-related toxic epidermal necrolysis in a patient with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. J Am Acad Dermatol 42:305
Reifenstein EC, Reifenstein GH (1939) A variable symptom complex of undetermined aetiology with fatal termination. Arch Intern Med 63:552–574
Mockenhaupt M, Viboud C, Dunant A et al (2008) Stevens-Jonson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: assessment of medication risk with emphasis on recently marketed drugs. The EuroSKAR study. J Investig Dermatol 128(1):35–44. doi:10.1038/sj.jid.5701033
DeBanto JR, Goday PS, Pedroso MR et al (2002) Acute pancreatitis in children. Am J Gastroenterol 97(7):1726–1731. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.05833.x
Lawson M, Dalzell AM, Couriel JM (2006) A rare cause of massive pleural effusion. Eur J Pediatr 165(1):73–75. doi:10.1007/s00431-005-1744-6
Ziemer M, Kardaun SH, Liss Y et al (2012) Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in patients with lupus erythematosus: a descriptive study of 17 cases from a national registry and review of the literature. Br J Dermatol 166(3):575–600. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2133.2011.10705.x
Worwick S, Cotliar J (2011) Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: a review of treatment options. Dermatol Ther 24(2):207–218. doi:10.1111/j.1529-8019.2011.01396.x
Law EH, Leung M (2015) Corticosteroids in Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis: current evidence and implications for future research. Ann Pharmacother 49(3):335–342. doi:10.1177/1060028014560012
Wang AS, Armstrong EJ, Armstrong AW (2013) Corticosteroids and wound healing: clinical considerations in the perioperative period. Am J Surg 206(3):410–417. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg
Aihara M, Kano Y, Fujita H et al (2015) Efficacy of additional i.v.immunoglobulinto steroid therapy in Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Dermatol 42(8):768–777. doi:10.1111/1346-8138
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Funding
This manuscript was not funded.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from the father.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marija, S., Ivana, B., Nina, R. et al. Toxic epidermal necrolysis in a child with lupus-associated pancreatitis. Rheumatol Int 37, 1221–1226 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-017-3677-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-017-3677-6