Abstract
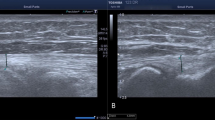
The objective of this study was to investigate the role of real-time sonoelastography (RTSE) in patients with lateral epicondylitis (LE) and whether it is associated with clinical parameters. Seventeen patients with unilateral LE were enrolled in the study. The healthy elbows of the participants constituted the control group. Using B-mode ultrasound, color Doppler ultrasound, and RTSE, we prospectively examined 34 common extensor tendon elbows of 17 patients. Both color scales and strain ratio were used for evaluating RTSE images. Two radiologists evaluated the RTSE images separately. Elbow pain was scored on a 100-mm visual analog scale (VAS). Symptom duration and the presence of nocturnal pain were questioned. Quick disabilities of arm shoulder and hand (DASH) Questionnaire was applied to assess the pain, function, and disability. Nottingham health profile (NHP) was used to determine and quantify perceived health problems. Both color scales and strain ratios of the affected tendon portions were significantly different from that of healthy tendons (p < 0.001). There was no significant association between NHP, VAS, Quick DASH scores, and color scales and strain ratio. Strain ratio of the medial portion of the affected tendon was significantly correlated with symptom duration (rho = −0.61 p = 0.010) and nocturnal pain (rho = 0.522 p = 0.031). Interobserver agreement was substantial for color scales (κ = 0.74, p = 0.001) and strain ratio (ICC = 0.61, p = 0.031). RTSE may facilitate differentiation between healthy and affected elbows as a feasible and practical supplementary method with substantial interobserver agreement. RTSE was superior to B-mode ultrasound and color Doppler ultrasound in discriminating tendons with LE. Strain ratio of the medial portion of the tendon is associated moderately with nocturnal pain and symptom duration. No other associations were present between RTSE findings and clinical or functional parameters.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shiri R, Viikari-Juntura E, Varonen H, Heliövaara M (2006) Prevalence and determinants of lateral and medial epicondylitis: a population study. Am J Epidemiol 164:1065–1074
Field LD, Savoie FH (1998) Common elbow injuries in sport. Sports Med 26:193–205
Tosti R, Jennings J, Sewards JM (2013) Lateral epicondylitis of the elbow. Am J Med. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2012.09.018
Levin D, Nazarian LN, Miller TT, O’Kane PL, Feld RI, Parker L, McShane JM (2005) Lateral epicondylitis of the elbow: US findings. Radiology 237:230–234
Sampath SC, Sampath SC, Bredella M (2013) Magnetic resonance imaging of the elbow: a structured approach. Sports Health. doi:10.1177/1941738112467941
Ooi CC, Malliaras P, Schneider ME, Connell DA (2014) “Soft, hard, or just right?” Applications and limitations of axial-strain sonoelastography and shear-wave elastography in the assessment of tendon injuries. Skelet Radiol 43:1–12
De Zordo T, Lill SR, Fink C, Feuchtner GM, Jaschke W, Bellmann-Weiler R, Klauser A (2009) Real-time sonoelastography of lateral epicondylitis: comparison of findings between patients and healthy volunteers. AJR. doi:10.2214/AJR.08.2020
Ahn KS, Kang CH, Hong SJ, Jeong WK (2014) Ultrasound elastography of lateral epicondylosis: clinical feasibility of quantitative elastographic measurements. AJR Am J Roentgenol. doi:10.2214/AJR.13.11003
Clarke AW, Ahmad M, Curtis M, Connell DA (2010) Lateral elbow tendinopathy: correlation of ultrasound findings with pain and functional disability. Am J Sports Med. doi:10.1177/0363546509359066
Gummesson C, Ward MM, Atroshi I (2006) The shortened disabilities of the arm, shoulder and hand questionnaire (Quick DASH): validity and reliability based on responses within the full-length DASH. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 44:1–7
Imaeda T, Toh S, Wada T, Uchiyama S, Okinaga S, Kusunose K, Sawaizumi T (2006) Reliability of a visual analog version of the Quick DASH. J Bone Jt Surg Am 88:1782–1787
Koldas S, Ay S, Evcik D, Baser O (2011) Adaptation of Turkish version of the questionnaire quick disability of the arm, shoulder, and hand (Quick DASH) in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome. Clin Rheumatol. doi:10.1007/s10067-010-1470-y
The European group for quality of life assessment and health measurement (1993) European guide to the Nottingham Health Profile. Brookwood-Surrey Medical Publications, Brookwood, pp 1–16
Küçükdevecı AA, McKenna S, Kutlay S, Gürsel Y, Whalley D, Arasıl T (2000) The development and psychometric assessment of the Turkish version of the Nottingham Health Profile. Int J Rehabil Res 23:31–38
Breidahl WH, Newman JS, Taljanovic MS, Adler RS (1996) Power doppler sonography in the assessment of musculoskeletal fluid collections. AJR 166:1443–1446
Connell D, Burke F, Coombes P, McNealy S, Freeman D, Pryde D, Hoy G (2001) Sonographic examination of lateral epicondylitis. AJR 176:777–782
De Zordo T, Chhem R, Smekal V, Feuchtner G, Reindl M, Fink C, Faschingbauer R, Jaschke W, Klauser AS (2010) Real-time sonoelastography: findings in patients with symptomatic Achilles tendons and comparison to healthy volunteers. Ultraschall Med. doi:10.1055/s-0028-1109809
Koçyiğit F, Koçyiğit A, Karabulut N (2015) Color scaling in sonoelastography. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. doi:10.1097/PHM.0000000000000333
Havre RF, Waage JR, Gilja OH, Odegaard S, Nesje LB (2011) Real-time elastography: strain ratio measurements are influenced by the position of the reference area. Ultraschall Med. doi:10.1055/s-0031-1273247
Karimollah HT (2013) Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis for medical diagnostic test evaluation. Caspian J Intern Med 4:627–635
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Walz DM, Newman JS, Konin GP, Ross G (2010) Epicondylitis: pathogenesis, imaging, and treatment. Radiographics 30:167–184
Kotnis NA, Chiavaras MM, Harish S (2012) Lateral epi-condylitis and beyond: imaging of lateral elbow pain with clinical-radiologic correlation. Skeletal Radiol 41:369–386
Miller TT, Shapiro MA, Schultz E, Kalish PE (2002) Comparison of sonography and MRI for diagnosing epicondylitis. J Clin Ultrasound 30:193–202
Khoury V, Cardinal E (2009) “Tenomalacia”: a new sonographic sign of tendinopathy? Eur Radiol. doi:10.1007/s00330-008-1112-9
Lyshchik A, Higashi T, Asato R, Tanaka S, Ito J, Mai JJ, Pellot-Barakat C, Insana MF, Brill AB, Saga T, Hiraoka M, Togashi K (2005) Thyroid gland tumor diagnosis at US elastography. Radiology 237:202–211
Lyshchik A, Higashi T, Asato R, Tanaka S, Ito J, Hiraoka M, Insana MF, Brill AB, Saga T, Togashi K (2007) Cervical lymph node metastases: diagnosis at sonoelastography—initial experience. Radiology 243:258–267
Drakonaki EE, Allen GM, Wilson DJ (2009) Real-time ultrasound elastography of the normal Achilles tendon: reproducibility and pattern description. Clin Radiol 64:1196–1202
Kocyigit F, Kuyucu E, Kocyigit A, Karabulut N (2015) Sonoelastographic strain index in the early diagnosis of plantar fasciitis. Clin Imaing. doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2015.06.004
Hunter DJ, Guermazi A, Roemer F, Zhang Y, Neogi T (2013) Structural correlates of pain in joints with osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil 21:1170–1178
Steffens D, Hancock MJ, Maher CG, Williams C, Jensen TS, Latimer J (2014) Does magnetic resonance imaging predict future low back pain? A systematic review. Eur J Pain 18:7557–7565
Havre RF, Elde E, Gilja OH, Odegaard S, Eide GE, Matre K, Nesje LB (2008) Freehand realtime elastography: impact of scanning parameters on image quality and in vitro intra- and interobserver validations. Ultrasound Med Biol 34:1638–1650
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
No funding or grant or equipment was provided for the project from any source. The study was approved by Pamukkale University Noninvasive Research Ethical Committee. Study number: 60116787-020/1008. Each participant gave written informed consent.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kocyigit, F., Kuyucu, E., Kocyigit, A. et al. Association of real-time sonoelastography findings with clinical parameters in lateral epicondylitis. Rheumatol Int 36, 91–100 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-015-3356-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-015-3356-4