Abstract
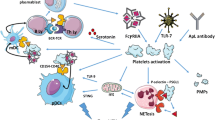
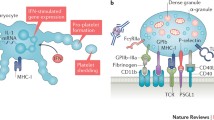
Cytokines, lymphocytes, platelets and several biomolecules have long been implicated in the pathology of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and the influences of antibody production and tagging, and cytokine, chemokine and enzyme production at specific rheumatoid joints were thought to be exclusive to the advancement of disease parameters. Another role player in RA is red blood cells (RBCs) which, of late, have been found to be involved in RA pathobiology, as there is a positive correlation between RBC counts and joint pathology, as well as with inflammatory biomarkers in the disease. There is also an association between RBC distribution width and the incidence of myocardial infarction amongst RA patients, and there is a change in the lipid distribution within RBC membranes. Of late, certain RBC-associated factors with previously obscure roles and cell-derived particles thought to be inconsequential to the other constituents of plasma were found to be active biomolecular players. Several of these have been discovered to be present in or originating from RBCs. Their influences have been shown to involve in membrane dynamics that cause structural and functional changes in both platelets and RBCs. RBC-derived microparticles are emerging entities found to play direct roles in immunomodulation via interactions with other plasma cells. These correlations highlight the direct influences of RBCs on exacerbating RA pathology. This review will attempt to shed more light on how RBCs, in the true inflammatory milieu of RA, are playing an even greater role than previously assumed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Scott DL, Wolfe F, Huizinga TWJ (2010) Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 376(9746):1094–1108
Tobón GJ, Youinou P, Saraux A (2010) The environment, geo-epidemiology, and autoimmune disease: rheumatoid arthritis. J Autoimmun 35(1):10–14
Scott IC, Seegobin SD, Steer S, Tan R, Forabosco P, Hinks A, Eyre S, Morgan AW, Wilson AG, Hocking LJ et al (2013) Predicting the risk of rheumatoid arthritis and its age of onset through modelling genetic risk variants with smoking. PLoS Genet 9(9):e1003808
Bergström U, Jacobsson L, Nilsson J-Å, Wirfält E, Turesson C (2013) Smoking, low formal level of education, alcohol consumption, and the risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol 42(2):123–130
Cooles FA, Isaacs JD (2011) Pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 23(3):233–240. doi:10.1097/BOR.1090b1013e32834518a32834513
van Beers JJBC, Pruijn GJ (2010) The role of synovial citrullinated proteins in the pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Protein Deimination in Human Health and Disease, pp 41–68
Seven A, Güzel S, Aslan M, Hamuryudan V (2008) Lipid, protein, DNA oxidation and antioxidant status in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Biochem 41(7):538–543
Charles-Schoeman C, Lee YY, Grijalva V, Amjadi S, FitzGerald J, Ranganath VK et al (2012) Cholesterol efflux by high density lipoproteins is impaired in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 71:1157–1162
Gasparyan AY, Stavropoulos-Kalinoglou A, Mikhailidis DP, Toms TE, Douglas KMJ, Kitas GD (2011) Platelet function in rheumatoid arthritis: arthritic and cardiovascular implications. Rheumatol Int 31:153–164
Luquita A, Uril L, Svetaz MJ, Gennaro AM, Volpintesta R, Palatnik S et al (2009) Erythrocyte aggregation in rheumatoid arthritis: cell and plasma factor’s role. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc 41:49–56
Lu A (2009) Correlations among cartilage erosion, IgA level, red blood cell and platelet counts in 436 rheumatoid arthritis patients with path analysis. In: Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, Beijing: ICBBE, pp 1–3
Gasparyan AY, Ayvazyan L, Blackmore H, Kitas GD (2011) Writing a narrative biomedical review: considerations for authors, peer reviewers, and editors. Rheumatol Int 31(11):1409–1417
Verma N, Misra R, Singh R, Agarwal S, Naik S (2002) Serological correlates of inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis: usefulness of acute phase reactants in monitoring disease activity. J Indian Rheumatol Assoc 10:1–4
Bunescu A, Seideman P, Lenkei R, Levin K, Egberg N (2004) Enhanced Fcgamma receptor I, alphaMbeta2 integrin receptor expression by monocytes and neutrophils in rheumatoid arthritis: interaction with platelets. J Rheumatol 31(12):2347–2355
Xu J, Lupu F, Esmon CT (2010) Inflammation, innate immunity and blood coagulation. Hamostaseologie 30(1):5–6, 8–9
Maradit-Kremers H, Nicola PJ, Crowson CS, Ballman KV, Jacobsen SJ, Roger VL, Gabriel SE (2007) Raised erythrocyte sedimentation rate signals heart failure in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 66(1):76–80
Vijayakumar D, Suresh K, Manoharan S (2005) Altered pattern of lipids in plasma and erythrocyte membranes of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Indian J Clin Biochem 20(1):52–55
Taubert D, Lazar A, Grimberg G, Jung N, Rubbert A, Delank KS, Perniok A, Erdmann E, Schomig E (2006) Association of rheumatoid arthritis with ergothioneine levels in red blood cells: a case control study. J Rheumatol 33(11):2139–2145
Papadaki HA, Kritikos HD, Valatas V, Boumpas DT, Eliopoulos GD (2002) Anemia of chronic disease in rheumatoid arthritis is associated with increased apoptosis of bone marrow erythroid cells: improvement following anti–tumor necrosis factor-α antibody therapy. J Am Soc Hematol 100:474–482
Wilson A, Yu H, Goodnough LT, Nissenson AR (2004) Prevalence and outcomes of anemia in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review of the literature. Am J Med 116:50S–57S
Nikolaisen C, Figenschau Y, Nossent JC (2008) Anemia in early rheumatoid arthritis is associated with interleukin 6-mediated bone marrow suppression, but has no effect on disease course or mortality. J Rheumatol 35:380–386
Lee WS, Kim T-Y (2010) Relation between red blood cell distribution width and inflammatory biomarkers in rheumatoid arthritis. Arch Pathol Lab Med 134:505–506
Zhou Y, Zhang Q, Yan L, Li Y, Hua L (2015) Association between red cell distribution width and myocardial infarction in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Chem Lab Med 53(7):e153–e155
Goodman SR, Daescu O, Kakhniashvili DG, Zivanic M (2013) The proteomics and interactomics of human erythrocytes. Exp Biol Med 238(5):509–518
Iwaki-Egawa S, Matsuno H, Yudoh K, Nakazawa F, Miyazaki K, Ochiai A et al (2004) High diagnostic value of anticalpastatin autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis detected by ELISA using human erythrocyte calpastatin as antigen. J Rheumatol 31:17–22
Kontos S, Kourtis IC, Dane KY, Hubbell JA (2013) Engineering antigens for in situ erythrocyte binding induces T-cell deletion. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110(1):E60–E68
Meyer PWA, Hodkinson B, Ally M, Musenge E, Wadee AA, Fickl H, et al (2011) Circulating cytokine profiles and their relationships with autoantibodies, acute phase reactants, and disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mediators of inflammation 2010
Staroń A, Mąkosa G, Koter-Michalak M (2012) Oxidative stress in erythrocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 32(2):331–334
Wolfe F, Sharp JT (1998) Radiographic outcome of recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis: a 19-year study of radiographic progression. Arthritis Rheum 41(9):1571–1582
De Oliveira S, De Almeida VV, Calado A, Rosário HS, Saldanha C (2012) Integrin-associated protein (CD47) is a putative mediator for soluble fibrinogen interaction with human red blood cells membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta 1818(3):481–490
Saldanha C, Freitas T, Almeida JP (2012) Fibrinogen effects on erythrocyte nitric oxide mobilization in presence of acetylcholine. Life Sci 91(21–22):1017–1022
Saldanha C, Freitas T, Lopez de Almeida JP, Silva-Herdade A (2014) Signal transduction pathways in erythrocyte nitric oxide metabolism under high fibrinogen levels. Korea-Aust Rheol J 26(2):217–223
Glasmästar K, Larsson C, Höök F, Kasemo B (2002) Protein adsorption on supported phospholipid bilayers. J Colloid Interface Sci 246(1):40–47
Mbamala EC, Ben-Shaul A, May S (2005) Domain formation induced by the adsorption of charged proteins on mixed lipid membranes. Biophys J 88(3):1702–1714
Jewell SA, Petrov PG, Winlove CP (2013) The effect of oxidative stress on the membrane dipole potential of human red blood cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1828(4):1250–1258
Hilliquin P, Borderie D, Hernvann A, Menkes CJ, Ekindjian OG (1997) Nitric oxide as s-nitrosoproteins in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 40(8):1512–1517
Aryaeian N, Djalali M, Shahram F, Jazayeri S, Chamari M, Nazari S (2011) Beta-Carotene, Vitamin E, MDA, glutathione reductase and arylesterase activity levels in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Iranian J Public Health 40(2):102–109
Mohr S, Hallak H, de Boitte A, Lapetina EG, Brüne B (1999) Nitric oxide-induced S-glutathionylation and inactivation of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem 274(14):9427–9430
Toms TE, Symmons DP, Kitas DG (2010) Dyslipidaemia in rheumatoid arthritis: the role of inflammation, drugs, lifestyle and genetic factors. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 8:301–326
Myasoedova E, Crowson CS, Kremers HM, Roger VL, Fitz-Gibbon PD, Therneau TM et al (2011) Lipid paradox in rheumatoid arthritis: the impact of serum lipid measures and systemic inflammation on the risk of cardiovascular disease. Ann Rheum Dis 70(3):482–487
van Zwieten R, Bochem AE, Hilarius PM, vanBruggen R, Bergkamp F, Hovingh GK, Verhoeven AJ (2012) The cholesterol content of the erythrocyte membrane is an important determinant of phosphatidylserine exposure. Biochim Biophys Acta 182(12):1493–1500
Rubin O, Canellini G, Delobel J, Lion N, Tissot J-D (2012) Red blood cell microparticles: clinical relevance. Transfus Med Hemother 39(5):342
Bosman GJ, Lasonder E, Groenen-Döpp YAM, Willekens FLA, Werre JM (2012) The proteome of erythrocyte-derived microparticles from plasma: new clues for erythrocyte aging and vesiculation. J Proteom 76:203–210
Mouro-Chanteloup I, Delaunay J, Gane P, Nicolas V, Johansen M, Brown EJ, Peters LL, Le Van Kim C, Cartron JP, Colin Y (2003) Evidence that the red cell skeleton protein 4.2 interacts with the Rh membrane complex member CD47 vol 101
Leventis PA, Grinstein S (2010) The distribution and function of phosphatidylserine in cellular membranes. Annu Rev Biophys 39:407–427
Miyabe Y, Miyabe C, Iwai Y, Yokoyama W, Sekine C, Sugimoto K, Harigai M, Miyasaka M, Miyasaka N, Nanki T (2014) Activation of fibroblast-like synoviocytes derived from rheumatoid arthritis via lysophosphatidic acid–lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 cascade. Arthritis Res Ther 16(5):461
Neidlinger NA, Larkin SK, Bhagat A, Victorino GP, Kuypers FA (2006) Hydrolysis of phosphatidylserine-exposing red blood cells by secretory phospholipase A2 generates lysophosphatidic acid and results in vascular dysfunction. J Biol Chem 281(2):775–781
Aoki J (2004) Mechanisms of lysophosphatidic acid production. In: Seminars in cell & developmental biology: 2004. Elsevier, pp 477–489
Yang L, Andrews DA, Low PS (2000) Lysophosphatidic acid opens a Ca++ channel in human erythrocytes. Blood 95(7):2420–2425
Khorchid A, Ikura M (2002) How calpain is activated by calcium. Nat Struct Mol Biol 9(4):239–241
Muravyov A, Tikhomirova I (2012) Role Ca2 + in mechanisms of the red blood cells microrheological changes. In: Calcium signaling. Springer, pp 1017–1038
Chung S-M, Bae O-N, Lim K-M, Noh J-Y, Lee M-Y, Jung Y-S, Chung J-H (2007) Lysophosphatidic acid induces thrombogenic activity through phosphatidylserine exposure and procoagulant microvesicle generation in human erythrocytes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27(2):414–421
Weerheim A, Kolb A, Sturk A, Nieuwland R (2002) Phospholipid composition of cell-derived microparticles determined by one-dimensional high-performance thin-layer chromatography. Anal Biochem 302(2):191–198
Butikofer P, Kuypers F, Xu C, Chiu D, Lubin B (1989) Enrichment of two glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins, acetylcholinesterase and decay accelerating factor, in vesicles released from human red blood cells. Blood 74(5):1481–1485
An X, Guo X, Sum H, Morrow J, Gratzer W, Mohandas N (2004) Phosphatidylserine binding sites in erythroid spectrin: location and implications for membrane stability. Biochemistry 43(2):310–315
Arosa FA, Pereira CF, Fonseca AM (2004) Red blood cells as modulators of T cell growth and survival. Curr Pharm Des 10(2):191–201
Profumo E, Buttari B, Petrone L, Straface E, Gambardella L, Pietraforte D, Genuini I, Capoano R, Salvati B, Malorni W (2011) Redox imbalance of red blood cells impacts T lymphocyte homeostasis: implication in carotid atherosclerosis. Thromb Haemost 106(6):1117
Antunes RF, Brandão C, Maia M, Arosa FA (2011) Red blood cells release factors with growth and survival bioactivities for normal and leukemic T cells. Immunol Cell Biol 89(1):111–121
Rubin O, Delobel J, Prudent M, Lion N, Kohl K, Tucker EI, Tissot JD, Angelillo-Scherrer A (2013) Red blood cell–derived microparticles isolated from blood units initiate and propagate thrombin generation. Transfusion 53(8):1744–1754
Kabouridis PS, Jury EC (2008) Lipid rafts and T-lymphocyte function: implications for autoimmunity. FEBS Lett 582(27):3711–3718
Hutchinson RM, Davis P, Jayson MI (1976) Thrombocytosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 35(2):138–142
Farr MSD, Constable TJ, Hawker RJ, Hawkins CF, Stuart J (1983) Thrombocytosis of active rheumatoid disease. Ann Rheum Dis 42:545–549
Yazici S, Yazici M, Erer B, Erer B, Calik Y, Ozhan H et al (2010) The platelet indices in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: mean platelet volume reflects disease activity. Platelets 21:122–125
Gasparyan AY, Stavropoulos-Kalinoglou A, Toms TE, Douglas KMJ, Kitas GD (2010) Association of mean platelet volume with hypertension in rheumatoid arthritis. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets 9:45–50
Habets KL, Huizinga TW, Toes RE (2013) Platelets and autoimmunity. Eur J Clin Invest 43:746–757
Boilard E, Blanco P, Nigrovic PA (2012) Platelets: active players in the pathogenesis of arthritis and SLE. Nat Rev Rheumatol 8:534–542
Senzel L, Gnatenko DV, Bahou WF (2009) The platelet proteome. Curr Opin Hematol 16(5):329–333
Cloutier N, Tan S, Boudreau LH, Cramb C, Subbaiah R, Lahey L, Albert A, Shnayder R, Gobezie R, Nigrovic PA et al (2013) The exposure of autoantigens by microparticles underlies the formation of potent inflammatory components: the microparticle-associated immune complexes. EMBO Mol Med 5:235–249
Cloutier N, Pare A, Farndale RW, Schumacher HR, Nigrovic PA, Lacroix S et al (2012) Platelets can enhance vascular permeability. J Am Soc Hematol 120:1334–1343
Gitz E, Pollitt AY, Gitz-Francois JJ, Alshehri O, Mori J, Montague S, Nash GB, Douglas MR, Gardiner EE, Andrews RK et al (2014) CLEC-2 expression is maintained on activated platelets and on platelet microparticles. Blood 124:2262
Pietraforte D, Vona R, Marchesi A, de Jacobis IT, Villani A, Del Principe D, Straface E (2014) Redox control of platelet functions in physiology and pathophysiology. Antioxid Redox Signal 21(1):177–193
Knijff-Dutmer EAJ, Koerts J, Nieuwland R, Kalsbeek-Batenburg EM, Van De Laar MAFJ (2002) Elevated levels of platelet microparticles are associated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 46:1498–1503
Nurden AT (2011) Platelets, inflammation and tissue regeneration. Thromb Haemost 105(Suppl 1):S13–S33
Almasry SM, Soliman HM, El-Tarhouny SA, Algaidi SA, Ragab EM (2015) Platelet rich plasma enhances the immunohistochemical expression of platelet derived growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor in the synovium of the meniscectomized rat models of osteoarthritis. Ann Anat 197:38–49
Vallés J, Santos MT, Aznar J, Martínez M, Moscardó A, Piñón M, Broekman MJ, Marcus AJ (2002) Platelet-erythrocyte interactions enhance αIIbβ3 integrin receptor activation and P-selectin expression during platelet recruitment: down-regulation by aspirin ex vivo. Blood 99(11):3978–3984
Valles J, Santos M, Aznar J, Marcus A, Martinez-Sales V, Portoles M, Broekman M, Safier L (1991) Erythrocytes metabolically enhance collagen-induced platelet responsiveness via increased thromboxane production, adenosine diphosphate release, and recruitment. Blood 78:154–162
Berckmans RJ, Nieuwland R, Tak PP, Böing AN, Romijn FP, Kraan MC, Breedveld FC, Hack CE, Sturk A (2002) Cell-derived microparticles in synovial fluid from inflamed arthritic joints support coagulation exclusively via a factor VII–dependent mechanism. Arthritis Rheum 46(11):2857–2866
Danesh A, Inglis HC, Jackman RP, Wu S, Deng X, Muench MO, Heitman JW, Norris PJ (2014) Exosomes from red blood cell units bind to monocytes and induce proinflammatory cytokines, boosting T-cell responses in vitro. Blood 123:687–696
Biró É, Nieuwland R, Tak PP, Pronk LM, Schaap MC, Sturk A, Hack CE (2007) Activated complement components and complement activator molecules on the surface of cell-derived microparticles in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and healthy individuals. Ann Rheum Dis 66(8):1085–1092
Beyer C, Pisetsky DS (2010) The role of microparticles in the pathogenesis of rheumatic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol 6(1):21–29
Jy W, Johansen ME, Bidot C, Horstman LL, Ahn YS (2013) Red cell-derived microparticles (RMP) as haemostatic agent. Thromb Haemost 110(4):751–760
Horne MK, Cullinane AM, Merryman PK, Hoddeson EK (2006) The effect of red blood cells on thrombin generation. Br J Haematol 133(4):403–408
Whelihan MF, Mann KG (2013) The role of the red cell membrane in thrombin generation. Thromb Res 131(5):377–382
Bonomini M, Sirolli V, Merciaro G, Antidormi T, Di Liberato L, Brummer U, Papponetti M, Cappelli P, Di Gregorio P, Arduini A (2005) Red blood cells may contribute to hypercoagulability in uraemia via enhanced surface exposure of phosphatidylserine. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20(2):361–366
Spoerke NJ, Van PY, Differding JA, Zink KA, Cho SD, Muller PJ, Karahan ZA, Sondeen JL, Holcomb JB, Schreiber MA (2010) Red blood cells accelerate the onset of clot formation in polytrauma and hemorrhagic shock. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 69(5):1054–1061
Goldschmidt N, Spectre G, Brill A, Zelig O, Goldfarb A, Rachmilewitz E, Varon D (2008) Increased platelet adhesion under flow conditions is induced by both thalassemic platelets and red blood cells. Thromb Haemost 100(5):864–870
Perez V, Johansen ME, Jy W, Horstman L, Ahn YS (2013) Interaction of platelets with red cell-derived microparticles (RMP): RMP increase platelet aggregate size in a shear-dependent manner. Blood 122(21):3580
Xiong Z, Cavaretta J, Qu L, Stolz DB, Triulzi D, Lee JS (2011) Red blood cell microparticles show altered inflammatory chemokine binding and release ligand upon interaction with platelets. Transfusion 51(3):610–621
Hakala M, Risteli L, Manelius J, Nieminen P, Risteli J (1993) Increased type I collagen degradation correlates with disease severity in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 52(12):866–869
King KL, Cidlowski JA (1995) Cell cycle and apoptosis: common pathways to life and death. J Cell Biochem 58(2):175–180
Zwaal RFA, Comfurius P, Bevers EM (2005) Surface exposure of phosphatidylserine in pathological cells. CMLS, Cell Mol Life Sci 62(9):971–988
Abed M, Towhid ST, Mia S, Pakladok T, Alesutan I, Borst O, Gawaz M, Gulbins E, Lang F (2012) Sphingomyelinase-induced adhesion of eryptotic erythrocytes to endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 303(9):C991–C999
Walker B, Towhid ST, Schmid E, Hoffmann SM, Abed M, Münzer P, Vogel S, Neis F, Brucker S, Gawaz M et al (2014) Dynamic adhesion of eryptotic erythrocytes to immobilized platelets via platelet phosphatidylserine receptors. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 306:C291–C297
Hermand P, Gane P, Huet M, Jallu V, Kaplan C, Sonneborn HH, Cartron J-P, Bailly P (2003) Red cell ICAM-4 is a novel ligand for platelet-activated αIIbβ3 integrin. J Biol Chem 278(7):4892–4898
Du VX, Huskens D, Maas C, Al Dieri R, de Groot PG, de Laat B (2014) New insights into the role of erythrocytes in thrombus formation. Semin Thromb Hemost 40(1):72–80
Hernández-Hernández A, Rodríguez MC, López-Revuelta A, Sánchez-Gallego JI, Shnyrov V, Llanillo M, Sánchez-Yagüe J (2006) Alterations in erythrocyte membrane protein composition in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Blood Cells Mol Dis 36(3):355–363
Gupta P, Vijayan VK, Bansal SK (2012) Changes in protein profile of erythrocyte membrane in bronchial asthma. J Asthma 49(2):129–133
De Castro J, Hernández-Hernández A, Rodríguez MC, Sardina JL, Llanillo M, Sánchez-Yagüe J (2007) Comparison of changes in erythrocyte and platelet phospholipid and fatty acid composition and protein oxidation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma. Platelets 18(1):43–51
Bochsen L, Johansson PI, Kristensen AT, Daugaard G, Ostrowski SR (2011) The influence of platelets, plasma and red blood cells on functional haemostatic assays. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 22(3):167–175
Santos M, Valles J, Lago A, Tembl J, Sanchez E, Moscardo A, Cosin J (2008) Residual platelet thromboxane A2 and prothrombotic effects of erythrocytes are important determinants of aspirin resistance in patients with vascular disease. J Thromb Haemost 6(4):615–621
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olumuyiwa-Akeredolu, Oo.O., Pretorius, E. Platelet and red blood cell interactions and their role in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 35, 1955–1964 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-015-3300-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-015-3300-7