Abstract
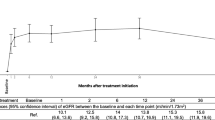
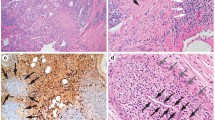
Renal parenchymal lesions in patients with IgG4-related kidney disease (IgG4-RKD) are characterized by tubulointerstitial nephritis with storiform fibrosis and infiltration by high numbers of IgG4-positive plasma cells. The aim of this study was to evaluate the clinical and pathological effects of corticosteroid therapy in patients with IgG4-RKD. Of six patients who were diagnosed with IgG4-RKD, four patients underwent re-biopsy at approximately 30–50 days after corticosteroid therapy was initiated. Based on the classification of Yamaguchi et al., the degree of tubulointerstitial fibrosis was classified before and after therapy. In addition, tubulointerstitial expression patterns of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA), collagen I, III, and IV protein, and connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) mRNA were examined. Histopathological findings before treatment showed α-SMA-positive myofibroblasts in the lesion, and CTGF mRNA-positive cells were found in the cellular infiltrate. Although corticosteroid therapy improved serum creatinine clinically, the stage of fibrosis advanced pathologically as evidenced by increased staining for collagen I and III. However, the number of IgG4-positive plasma cells decreased, and CTGF mRNA expression reduced. In other words, fibrosis had advanced from the time of extensive cell infiltration in patients with IgG4-RKD and inflammation was relieved by corticosteroid. A reduced number of positive CTGF mRNA expression cells in repeat biopsies indicated that the fibrosis process was terminated by corticosteroid therapy. We propose that corticosteroid therapy could terminate the pathway of active fibrosis, thereby inhibiting progression to renal dysfunction.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A et al (2001) High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med 344:732–738
Yamamoto M, Takahashi H, Sugai S, Imai K (2005) Clinical and pathological characteristics of Mikulicz’s disease (IgG4-related plasmacytic exocrinopathy). Autoimmun Rev 4:195–200
Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y et al (2012) Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RKD). Mod Rheumatol 22:21–30. doi:10.1007/s10165-011-0571-z
Hamano H, Kawa S, Ochi Y et al (2002) Hydronephrosis associated with retroperitoneal fibrosis and sclerosing pancreatitis. Lancet 159:1403–1404
Takeda S, Haratake Y, Kasai T, Takeda C, Takazakura E (2004) IgG4-associated idiopathic tubulointerstitial nephritis complicating autoimmune pancreatitis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 19:474–476
Uchiyama-Tanaka Y, Mori Y, Kimura T et al (2004) Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis associated with autoimmune-related pancreatitis. Am J Kidney Dis 43:E18–E25
Kawano M, Saeki T, Nakashima H et al (2011) Proposal for diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol 15:615–626. doi:10.1007/s10157-011-0521-2
Boor P, Ostendorf T, Floege J (2010) Renal fibrosis: novel insights into mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Nephrol 6:643–656
Yokoi H, Mukoyama M, Sugawara A et al (2002) Role of connective tissue growth factor in fibronectin expression and tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 282:F933–F942
Blom IE, van Dijk AJ, Wieten L et al (2001) In vitro evidence for differential involvement of CTGF, TGFβ, and PDGF-BB in mesangial response to injury. Nephrol Dial Transplant 16:1139–1148
Ito Y, Goldschmeding P, Kasuga H et al (2010) Expression patterns of connective tissue growth factor and of TGF-β isoforms during glomerular injury recapitulate glomerulogenesis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 299:F545–F558. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00120.2009
Saeki T, Nishi S, Imai N et al (2010) Clinicopathological characteristics of patients with IgG4-related tuburointerstitial nephritis. Kidney Int 78:1016–1023. doi:10.1038/ki.2010.271
Raissian Y, Nasr SH, Larsen CP et al (2011) Diagnosis of IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:1343–1352. doi:10.1681/ASN.2011010062
Nishi S, Imai N, Yoshida K, Ito Y, Saeki T (2011) Cliniocopathological findings of immunoglobulin G4-related kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol 15:810–819
Mizushima I, Yamada K, Fujii H et al (2012) Clinical and histological changes associated with corticosteroid therapy in IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis. Mod Rheumatol 22:859–870. doi:10.1007/s10165-011-0589-2
Yamaguchi Y, Kanetsuna Y, Honda K et al (2011) Characteristic tubulointerstitial nephritis in IgG4-related disease. Hum Pathol 43:536–549. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2011.06.002
Ito Y, Aten J, Bende RJ et al (1998) Expression of connective tissue growth factor in human renal fibrosis. Kidney Int 53:853–861
Ito Y, Goldschmeding R, Bende RJ et al (2001) Kinetics of connective tissue growth factor expression during experimental proliferative glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:472–484
Risdon RA, Sloper JC, DeWardener HE (1968) Relationship between renal function and histological changes found in specimens from patients with persistent glomerular nephritis. Lancet 2:363–366
Bohle A, Müller GA, Wehrmann M, Mackensen-Hean S, Xiao JC (1996) Pathogenesis of chronic renal failure in the primary glomerulonephritis, renal vasculopathies, and chronic interstitial nephritides. Kidney Int 54:S2–S9
Zaidan M, Cervera-Pierot P, Seigneux S et al (2011) Evidence of follicular T-cell implication in a case of IgG4-related systemic disease with interstitial nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26:2047–2050. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfr097
Topazian M, Witzig TE, Smyrk TC et al (2008) Rituximab therapy for refractory biliary strictures in immunoglobin G4-associated cholangitis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 6:364–366. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2007.12.020
Khosroshahi A, Carruthers MN, Deshpande V, Unizony S, Bloch DB, Stone JH (2012) Rituximab for the treatment of IgG4-related disease: lessons from ten consecutive patients. Medicine 91:57–66. doi:10.1097/MD.0b013e3182431ef6
Khosroshahi A, Bloch DB, Deshpande V, Stone JH (2010) Rituximab therapy leads to rapid decline of serum IgG4 levels and prompt clinical improvement in IgG4-related disease. Arthritis Rheum 62:1755–1762. doi:10.1002/art.27435
Ito K, Yamada K, Mizushima I et al (2013) Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis in a patient with IgG4-related disease: a possible association. Clin Nephrol 79:246–252. doi:10.5414/CN107114
Watson SJ, Jenkins DA, Bellamy CO (2006) Nephrology in IgG4-related systemic disease. Am J Surg Pathol 30:1472–1477
Saeki T, Imai N, Ito T, Yamazaki H, Nishi S (2009) Membranous nephropathy associated with IgG4-related systemic disease and without autoimmune pancreatitis. Clin Nephrol 71:173–178
Fervenza FC, Downer G, Beck LH Jr, Sethi S (2011) IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis with membranous nephrology. Am J Kidney Dis 58:320–324. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2011.05.006
Cravedi P, Abbate M, Gagliardini E et al (2011) Membranous nephropathy associated with IgG4-related disease. Am J Kidney Dis 58:272–275. doi:10.1053/j.ajkd.2011.05.002
Palmisano A, Corradi D, Carnevali ML et al (2010) Chronic periaortitis associated with membranous nephropathy: clues to common pathogenetic mechanisms. Clin Nephrol 74:485–490
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Diabetic Nephropathy and Nephrosclerosis Research and for Progressive Renal Diseases Research, Research on Intractable Disease, from the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare of Japan. This work was also supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Numbers, 23790967, 22590886, and 19590947 and by the Aichi Kidney Foundation.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Arai, H., Hayashi, H., Takahashi, K. et al. Tubulointerstitial fibrosis in patients with IgG4-related kidney disease: pathological findings on repeat renal biopsy. Rheumatol Int 35, 1093–1101 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-014-3153-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-014-3153-5