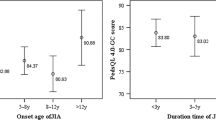
Abstract
The aim of this study was to identify the possible determinants of impaired health-related quality of life (HRQOL) in Egyptian children and adolescents with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA). Fifty-eight consecutive patients of JIA aged from 8 to 18 years underwent assessment of socio-economic and demographic characteristics; HRQOL using Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory 4.0 Generic Core Scale, disease activity using the Juvenile Arthritis Disease Activity Score based on 27 joints (JADAS-27), functional ability using the childhood health assessment questionnaire (CHAQ), pain score on visual analog scale and psychological symptoms using the Children’s Depression Inventory (CDI) score. Multivariate modeling was applied to determine the factors that associated with HRQOL impairment. A total of 55 % of the patients (32 of 58) had impaired HRQOL (<78.6). In multiple regression analyses, high CHAQ scores (OR 6.0, 95 % CI 2.0–17.5, P = 0.001), pain (OR 3.1, 95 % CI 1.9–6.3, P = 0.01), stop going to school (OR 3.9, 95 % CI 2.0–7.3, P = 0.01), low socioeconomic status (OR 2.3, 95 % CI 1.09–4.7, P = 0.04) and high psychological symptoms (OR 4.2, 95 % CI 2.0–12.6, P = 0.001) were determinants for HRQOL impairment. HRQOL impairment is a significant problem in Egyptian children and adolescents with JIA. These findings underscore the critical need for monitoring of HRQOL in these patients. More attention should be given to JIA patients who stop going to school and who has low socioeconomic status.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Olson JC (2003) Juvenile idiopathic arthritis: an update. WMJ 102:45–50
Abou El-Soud AM, EL-Naajjar AR, El-Shahawy EE et al. (2013) Prevalence of juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis in Sharkia Governorate, Egypt: epidemiological study. Rheumatol Int 33(9):2315–2322
Weiss JE, Llowite NT (2005) Juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Pediatr Clin North Am 52(2):413–442
Schanberg L, Anthony K, Gil K, Maurin E (2003) Daily pain and symptoms in children with polyarticular arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 48:1390–1397
Moorthy LN, Peterson MG, Hassett AL, Lehman TJ (2010) Burden of childhood-onset arthritis. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J 8:20
Amine B, Rostom S, Benbouazza K, Abouqal R, Hajjaj-Hassouni N (2009) Health related quality of life survey about children and adolescents with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Rheumatol Int 29(3):275–279
Shaw KL, Southwood TR, Duffy CM, McDonagh JE (2006) Health-related quality of life in adolescents with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 55(2):199–207
Norrby U, Nordholm L, Andersson-Gäre B, Fasth A (2006) Health-related quality of life in children diagnosed with asthma, diabetes, juvenile chronic arthritis or short stature. Acta Paediatr 95(4):450–456
Ringold S, Wallace CA, Rivara FP (2009) Health-related quality of life, physical function, fatigue, and disease activity in children with established polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis. J Rheumatol 36(6):1330–1336
Seid M, Opipari L, Huang B, Brunner HI, Lovell DJ (2009) Disease control and health-related quality of life in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 61(3):393–399
Gutierrez-Suarez R, Pistorio A, Cespedes CA, Norambuena X, Flato B, Rumba I et al (2007) Health-related quality of life of patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis coming from 3 different geographic areas: the PRINTO multinational quality of life cohort study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 46(2):314–320
Baars R, Atherton C, Koopman H, Bullinger M, Power M (2005) Group D. The European DISABKIDS project: development of seven condition-specific modules to measure health related quality of life in children and adolescents. Health Qual Life Outcome 3:70
Simeoni M, Schmidt S, Muehlan H, Debensason D, Bullinger M, Group D (2007) Field testing of a European quality of life instrument for children and adolescents with chronic conditions: the 37-item DISABKIDS Chronic Generic Module. Qual Life Res 16(5):881–893
Brunner HI, Klein-Gitelman MS, Miller MJ, Trombley M, Baldwin N, Kress A et al (2004) Health of children with chronic arthritis: relationship of different measures and the quality of parent proxy reporting. Arthritis Rheum 51:763–773
Varni JW, Burwinkle TM, Lane MM (2005) Health-related quality of life measurement in pediatric clinical practice: an appraisal and precept for future research and application. Health Qual Life Outcomes 3:34
Arkela-Kautiainen M, Haapasaari J, Kautiainen H, Vilkkumaa I, Malkia E, Leirisalo-Repo M (2005) Favourable social functioning and health related quality of life of patients with JIA in early adulthood. Ann Rheum Dis 64:875–880
Muller-Godeffroy E, Lehmann H, Kuster RM, Thyen U (2005) Quality of life and psychosocial adaptation in children and adolescents with juvenile idiopathic arthritis and reactive arthritis. Z Rheumatol 64(3):177–187
Sawyer MG, Whitham JN, Roberton DM, Taplin JE, Varni JW, Baghurst PA (2004) The relationship between health-related quality of life, pain and coping strategies in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43:325–330
Petty RE, South Wood TR, Manners P et al (2004) International league of associations for rheumatology. International league of associations for rheumatology classification of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: second revision, Edmonton, 2001. J Rheumatol 31:390–392
El-Gilany A, El-Wehady A, El-Wasify M (2012) Updating and validation of the socioeconomic status scale for health research in Egypt. East mediterr Health J 18(9):962–968
Varni JW, Seid M, Knight TS, Uzark K, Szer IS (2002) The PedsQL 4.0 generic core scales: sensitivity, responsiveness, and impact on clinical decision maker. J Behav Med 25:175–193
Varni JW, Burwinkle TM, Seid M, Skarr D (2003) The PedsQL™ 4.0 as a pediatric population health measure: feasibility, reliability, and validity. Ambul Pediatr 3:329–341
Arabiat D, Elliott B, Draper P, Al Jabery M (2011) Cross-cultural validation of the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory™ 4.0 (PedsQL™) generic core scale into Arabic language. Scand J Caring Sci 25(4):828–833
Varni JW, Limbers CA, Burwinkle TM (2007) How young can children reliably and validly self-report their health-related quality of life? An analysis of 8.591 children across age subgroups with the PedsQL 4.0 Generic Core Scales. Health Qual Life Outcomes 5:1
Consolaro A, Ruperto N, Bazso A et al (2009) Pediatric Rheumatology International Trials Organisation. Development and validation of a composite disease activity score for juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 61:658–666
Singh G, Athreya BH, Fries JF, Goldsmith DP (1994) Measurement of health status in children with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 37:1761–1769
Rostom S, Amine B, Bensabbah R, Chkirat B, Abouqal R, Hajjaj-Hassouni N (2010) Psychometric properties evaluation of the childhood health assessment questionnaire (CHAQ) in Moroccan juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Rheumatol Int 30(7):879–885
Kovacs M (1981) Rating scales to assess depression in school-age children. Acta Paedopsychiatr 46:305–315
Saylor C, Finch A, Spirito A, Bennett B (1984) The children’s Depression Inventory: a systematic evaluation psychometric properties. J Consult Clin Psychol 52:955–967
Gharib (1995) The Children Depression Inventory CDI. Dar El-Nahda: Cairo, Second
Logan DE, Simons LE, Kaczynski KJ (2009) School functioning in adolescents with chronic pain: the role of depressive symptoms in school impairment. J Pediatr Psychol 34(8):882–892
Cespedes-Cruz A, Gutierrez-Suarez R, Pistorio A, Ravelli A, Loy A, Murray KJ et al (2008) Methotrexate improves the health-related quality of life of children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 67:309–314
Lundberg V, Lindh V, Eriksson C, Petersen S, Eurenius E (2012) Health-related quality of life in girls and boys with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: self- and parental reports in a cross-sectional study. Pediatr Rheumatol 10(1):33
Hagerman L, Grootenhuis MA, van den Berg JM, van Veenendaal M, Dolman KM, Swart JF, Kujjpers Tw, van Rossum MA (2012) Predictors of health-related quality of life in children and adolescents with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: results from a Web-based survey. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 64(5):694–703. doi:10.1002/acr.21609.23
Oliveira S, Ravelli A, Pistorio A et al (2007) Proxy-reported health-related quality of life of patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: the Pediatric Rheumatology International Trials Organization multinational quality of life cohort study. Arthritis Rheum 57(1):35–43
Fuchs CE, Van Geelen SM, Hermans HJ, Van Putte EM, Van Geel R, Sinnema G, Kuis W (2013) Psychological intervention for adolescents with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: for whom and when? J Rheumatol 40(4):528–534
Van Brussel M, Lelieveld OT, van der Net J, Engelbert RH, Helders PJ, Takken T (2007) Aerobic and anaerobic exercise capacity in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 57:891–897
Lovell DJ, Passo MH, Beukelman T, Bowyer SL, Gottlieb BS, Henrickson M et al (2011) Measuring process of arthritis care: a proposed set of quality measures for the process of care in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 63:10–16
Stevanovic D, Susic G (2013) Health-related quality of life and emotional problems in juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Qual Life Res 22(3):607–612
Tahirovic E, Begic H, Sutovic A, Tahirovic H (2010) Impact of the family socioeconomic status on health related quality of life in children operated on for congenital heart defects. Acta Med Croatica 64(1):9–16
Toupin April K, Cavallo S, Eharmann Feldman D, Ni A (2012) The associations among economic hardship, caregiver psychological distress, disease activity, and health-related quality of life in children with juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Qual Life Res 21(7):1185–1191
Tahirovic E, Toromanovic A, Tahirovic E, Begic H (2013) Impact of socioeconomic status on health-related quality of life in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus in Bosnia and Herze-govina. Minervia Pediatr 65(2):207–212
Petersen C, Nordmeyer S, Muller-Godeffroy E, Foeldvari I, Kuster RM, Bullinger M (2008) Health-related quality of life in children and adolescents with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: which role do age sex and medical parameters play? Klin Padiatr 220(4):259–265
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdul-Sattar, A.B., Elewa, E.A., El-Shahawy, E.ED. et al. Determinants of health-related quality of life impairment in Egyptian children and adolescents with juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Sharkia Governorate. Rheumatol Int 34, 1095–1101 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-014-2950-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-014-2950-1