Abstract
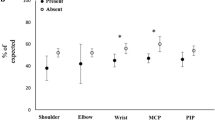
In 90% of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), the joints of the hand are affected. Studies of grip strength training have not indicated a negative effect on disease activity after training. Introduction of ultrasound Doppler (USD) to measure increased blood flow induced by inflammation has made it possible to investigate the direct effect on blood supply in the synovium after training. In this case–control study, 24 patients with RA with USD activity in the wrist joint participated. The USD activity was measured by the color fraction (CF) (CF = colored pixels/total number of pixels in ROI). Twenty-four patients were assigned to an 8-week grip strength training program. At baseline and after 8 weeks of training, an USD examination of the wrist joint was performed. In the training group, we measured grip strength and pain in the wrist joint. Six patients withdrew from the training because of pain or change in medication. Eighteen patients served as control group. There was a modest, not significant, decrease in the CF in response to training (1.86%; P = 0.08). Grip strength increased 8.8% after training (P = 0.055). Pain in motion deceased after training (P = 0.04). No difference in the CF was seen between the training and control groups, neither at baseline nor at follow-up (P = 0.82 and P = 0.48). Patients withdrawing from training had a significantly higher CF than the other patients (P > 0.001). The results in this study might indicate that the flow in the synovium assessed by USD is not affected by grip strength training.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Szkudlarek M, Narvestad E, Klarlund M, Court-Payen M, Thomsen HS, Ostergaard M (2004) Ultrasonography of the metatarsophalangeal joints in rheumatoid arthritis: comparison with magnetic resonance imaging, conventional radiography, and clinical examination. Arthritis Rheum 50:2103–2112
Terslev L, Torp-Pedersen S, Qvistgaard E, Kristoffersen H, Rogind H, Danneskiold-Samsoe B et al (2003) Effects of treatment with etanercept (Enbrel, TNRF:Fc) on rheumatoid arthritis evaluated by Doppler ultrasonography. Ann Rheum Dis 62:178–181
Ronningen A, Kjeken I (2008) Effect of an intensive hand exercise programme in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Occup Ther 7:1–11
Stenstrom CH, Minor MA (2003) Evidence for the benefit of aerobic and strengthening exercise in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 49:428–434
Speed CA, Campbell R (2010) Mechanisms of strength gain in a handgrip exercise programme in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. doi:10.1007/s00296-010-1596-x
Nordenskiold UM, Grimby G (1993) Grip force in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and fibromyalgia and in healthy subjects. A study with the Grippit instrument. Scand J Rheumatol 22:14–19
Dellhag B, Hosseini N, Bremell T, Ingvarsson PE (2001) Disturbed grip function in women with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 28:2624–2633
van den Ende CH, Vliet Vlieland TP, Munneke M, Hazes JM (1998) Dynamic exercise therapy in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review. Br J Rheumatol 37:677–687
Rall LC, Roubenoff R, Cannon JG, Abad LW, Dinarello CA, Meydani SN (1996) Effects of progressive resistance training on immune response in aging and chronic inflammation. Med Sci Sports Exerc 28:1356–1365
Wessel J (2004) The effectiveness of hand exercises for persons with rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review. J Hand Ther 17:174–180
Wakefield RJ, Brown AK, O’connor PJ, Emery P (2003) Power Doppler sonography: improving disease activity assessment in inflammatory musculoskeletal disease. Arthritis Rheum 48:285–288
Joshua F, de Carle R, Rayment M, Bryant C, Shnier R, Edmonds J et al (2005) Power Doppler ‘blanching’ after the application of transducer pressure. Australas Radiol 49:218–221
Ellegaard K, Torp-Pedersen S, Terslev L, Danneskiold-Samsøe B, Henriksen M, Bliddal H (2009) Ultrasound colour Doppler measurements in a single joint as measure of disease activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis—assessment of concurrent validity. Rheumatology (Oxford) 48:254–257
Naredo E, Gamero F, Bonilla G, Uson J, Carmona L, Laffon A (2005) Ultrasonographic assessment of inflammatory activity in rheumatoid arthritis: comparison of extended versus reduced joint evaluation. Clin Exp Rheumatol 23:881–884
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS et al (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:315–324
Brown AK, Conaghan PG, Karim Z, Quinn MA, Ikeda K, Peterfy CG et al (2008) An explanation for the apparent dissociation between clinical remission and continued structural deterioration in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 58:2958–2967
Brown AK, Quinn MA, Karim Z, Conaghan PG, Peterfy CG, Hensor E et al (2006) Presence of significant synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis patients with disease-modifying antirheumatic drug-induced clinical remission: Evidence from an imaging study may explain structural progression. Arthritis Rheum 54:3761–3773
O’Brien AV, Jones P, Mullis R, Mulherin D, Dziedzic K (2006) Conservative hand therapy treatments in rheumatoid arthritis–a randomized controlled trial. Rheumatology (Oxford) 45:577–583
Hoenig H, Groff G, Pratt K, Goldberg E, Franck W (1993) A randomized controlled trial of home exercise on the rheumatoid hand. J Rheumatol 20:785–789
Brighton SW, Lubbe JE, van der Merwe CA (1993) The effect of a long-term exercise programme on the rheumatoid hand. Br J Rheumatol 32:392–395
Fleck SJ, Kraemer WJ (1997) Resistance training for seniors. Designing resistance training programs, 2nd edn. Human Kinetics, Champaige, pp 217–229
Ellegaard K, Torp-Pedersen S, Lund H, Henriksen M, Terslev L, Jensen PS et al (2008) Quantification of colour Doppler activity in the wrist in patients with rheumatoid arthritis—the reliability of different methods for image selection and evaluation. Ultraschall Med 29:393–398
Ellegaard K, Torp-Pedersen S, Jensen PS, Lund H, Danneskiod-Samsoe B, Bliddal H (2007) The influence of physical activity, skin temperature and daily variation on the colour-Doppler measurements in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 66:651 Ref Type: Abstract
Qvistgaard E, Rogind H, Torp-Pedersen S, Terslev L, Danneskiold-Samsoe B, Bliddal H (2001) Quantitative ultrasonography in rheumatoid arthritis: evaluation of inflammation by Doppler technique. Ann Rheum Dis 60:690–693
Buljina AI, Taljanovic MS, Avdic DM, Hunter TB (2001) Physical and exercise therapy for treatment of the rheumatoid hand. Arthritis Rheum 45:392–397
Brorsson S, Hilliges M, Sollerman C, Nilsdotter A (2009) A six-week hand exercise programme improves strength and hand function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rehabil Med 41:338–342
Bodur H, Yilmaz O, Keskin D (2006) Hand disability and related variables in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 26(6):541–544
Acknowledgments
The study received financial support from the following foundations: The Oak Foundation, the Danish Physiotherapy Foundation, Praksisfonden and Aase and Ejnar Danielsens Fond.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ellegaard, K., Torp-Pedersen, S., Lund, H. et al. The effect of isometric exercise of the hand on the synovial blood flow in patients with rheumatoid arthritis measured by color Doppler ultrasound. Rheumatol Int 33, 65–70 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-011-2314-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-011-2314-z