Abstract
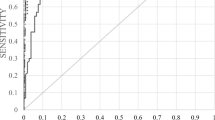
To use meta-analysis to determine the accuracy of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (CCP) antibody in diagnosis of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in a Chinese population, we searched MEDLINE and CNKI databases for studies published in English or Chinese between January 2000 and June 2010. Two investigators independently evaluated studies for inclusion, data extraction, and quality assessment. We used a random-effects model to combine estimates of sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio (LR+), negative likelihood ratio (LR−), and diagnostic odds ratio (DOR). One hundred and eighteen studies met our inclusion criteria. All studies were of high quality. The summary estimates for anti-CCP antibody in the diagnosis of RA in a Chinese population were as follows: sensitivity 0.65 (95% confidence interval (CI) 0.65–0.66), specificity 0.95 (95% CI 0.95–0.96), positive likelihood ratio (LR+) 15.84 (95% CI 13.55–18.54), negative likelihood ratio (LR−) 0.33 (95% CI 0.31–0.35), and diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) 51.60 (95% CI 43.64–61.01). With high specificity and moderate sensitivity, anti-CCP antibody tests play an important role in conforming the diagnosis of RA in a Chinese population.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee DM, Weinblatt ME (2001) Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 358:903–911
Zang JW (2005) Recent advance in autoimmune diseases study. Accompl Appl 20(3):208–210
Bosello S, Youinou P, Daridon C, Tolusso B, Bendaoud B, Pietrapertosa D et al (2008) Concentrations of BAFF correlate with autoantibody levels, clinical disease activity, and response to treatment in early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 35(7):1256–1264
Kiely PD, Brown AK, Edwards CJ, O’Reilly DT, OstÖr AJ, Quinn M et al (2009) Contemporary treatment principles for early rheumatoid arthritis: a consensus statement. Rheumatology(Oxford) 48(7):765–772
Zendman AJ, van Venrooij WJ, Pruijn GJ (2006) Use and significance of anti-CCP autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology(Oxford) 45(1):20–25
Nell VP, Machold KP, Stamm TA, Eberl G, Heinzl H, Uffmann M et al (2005) Autoantibody profiling as early diagnostic and prognostic tool for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 64(12):1731–1736
EI-Gabalawy HS, Wilkins JA (2004) Anti-Sa antibodies: prognostic and pathogenetic significance to rheumatoid arthritis. Arthr Res Ther 6(2):86–89
Bläss S, Meier C, Vohr HW, Schwochau M, Specker C, Burmester GR (1998) The p68 autoantigen characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis is reactive with carbohydrate epitope specific autoantibodies. Ann Rheum Dis 57(4):220–225
Lackner KJ, Schlosser U, Lang B, Schmitz G (1998) Autoantibodies against human calpastatin in rheumatoid arthritis: epitope mapping and analysis of patient sera. Br J Rheumatol 37(11):1164–1171
Matsumoto I, Lee DM, Goldbach-Mansky R, Sumida T, Hitchon CA, Schur PH et al (2003) Low prevalence of antibodies to glucose-6-phosphate isomerase in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and a spectrum of other chronic autoimmune disorders. Arthr Rheum 48(4):944–954
Nienhuis RL, Mandema E (1964) A new serum factor in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: the antiperinuclear factor. Ann Rheum Dis 23:302–305
Young BJ, Mallya RK, Leslie RD, Clark CJ, Hamblin TJ (1979) Anti-keratin antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Br Med J 2(6182):97–99
Schellekens GA, Visser H, de Jong BA, van den Hoogen FH, Hazes JM, Breedveld FC et al (2000) The diagnostic properties of rheumatoid arthritis antibodies recognizing a cyclic citrullinated peptide. Arthr Rheum 43(1):155–163
Irwig L, Tosteson AN, Gatsonis C, Lau J, Colditz G, Chalmers TC et al (1994) Guidelines for meta-analyses evaluating diagnostic tests. Ann Intern Med 120(8):667–676
Devillé WL, Buntinx F, Bouter LM, Montori VM, de Vet HC, van der Windt DA et al (2002) Conducting systematic reviews of diagnostic studies: didactic guidelines. BMC Med Res Methodol 2:9
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, McShane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS et al (1988) The American rheumatism association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthr Rheum 31(3):315–324
Whiting P, Rutjes AW, Reitsma JB, Bossuyt PM, Kleijnen J (2003) The development of QUADAS: a tool for the quality assessment of studies of diagnostic accuracy included in systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol 3:25
Lantz CA, Nebenzahl E (1996) Behavior and interpretation of the kappa statistic: resolution of the two paradoxes. J Clin Epidemiol 49(4):431–434
Stengel D, Bauwens K, Sehouli J, Ekkernkamp A, Porzsolt F (2003) A likelihood ratio approach to meta-analysis of diagnostic studies. J Med Screen 10(1):47–51
Glas AS, Lijmer JG, Prins MH, Bonsel GJ, Bossuyt PM (2003) The diagnostic odds ratio: a single indicator of test performance. J Clin Epidemiol 56(11):1129–1135
Gatsonis C, Paliwal P (2006) Meta-analysis of diagnostic and screening test accuracy evaluation: methodologic primer. AJR Am J Roentgenol 187(2):271–281
Pai M, Flores LL, Pai N, Hubbard A, Riley LW, Colford JM Jr (2003) Diagnostic accuracy of nucleic acid amplification tests for tuberculous meningitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis 3(10):633–643
Deeks JJ (2001) Systematic reviews in health care: systematic reviews of evaluations of diagnostic and screening tests. BMJ 323(7305):157–162
Petitti DB (2001) Approaches to heterogeneity in meta-analysis. Statist Med 20(23):3625–3633
Song F, Khan KS, Dinnes J, Sutton AJ (2002) Asymmetric funnel plots and publication bias in meta-analyses of diagnostic accuracy. Int J Epidemiol 31(1):88–95
Gu YL, Chen YM, Lv L, Xu ML (2004) Study on the anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies and the rheumatoid factors in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. J Diagn Concepts Pract 3(4):254–256
Wang YQ, Sun JH, Zhang T, Wang FD, Xu PR, Zhao YT (2005) Diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody detected by ELISA in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Univ Med Nanjing (Nat Sci) 25(3):215–216
Wang YL, Hu JF, Liu YM, Nie L (2006) Diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Pract Clin Med 7(6):36–39
Xu ZY, Zhao SP, Wu MH, Lin LR, Yu XR (2005) Diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Chin J Rheumatol 9(11):700–701
Wu SH, Chen G, Jin Q, Zhang WY (2005) Diagnostic value of combined detection of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and the rheumatoid factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Zhejiang Pract Med 10(6):381–405
Qin BR, Wang YQ (2007) Diagnostic value of serum anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Prev Med 34(2):346–348
Lu SJ, Shao J, Jiang QX (2005) Diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Shanxi Med J 34(7):585–586
Wang DT, Chen L, Wang YR (2007) The diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and anti-keratin antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Inner Mongolia Med J 39(7):797–798
Chen JW, Li XF, Ru JL, Hu XF (2007) Significance of anti-citrullinated peptide antibodies in patients with rheumatic diseases. Med Forums Basic 11(8):688–689
Wang Y, Shi J, Cheng W (2003) The diagnostic significance of anti-RA33 and anti-CCP in rheumatoid arthritis. Chongqing Med 32(8):1033–1034
Yang YQ, Zhang YM, Tang ZG (2008) Diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Lab Med Clin 5(6):343–344
Cui HD, Zhang N, Fu HX, Liu XK, Yang LL, Xue HX et al (2006) The detection value of anti- cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Chin J Pract Intern Med 26(24):1977–1978
Sun T, Zhu J, Ning F, Liu QJ (2008) Diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Anhui Health Voc Tech College 7(5):34–37
Zhu XH, Peng JH (2009) Diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and rheumatoid factor in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin J Med Off 37(6):1041–1042
Zhong LY, Li RY, Zeng ZH (2004) The diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and anti-RA33 antibody performed concomitantly with RF in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Clin Med 13(8):568–570
Dai CC, Dai L, Zheng DH (2005) Diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Guangdong Med J 26(6):796–797
Yan LW, Li J, Wu L, Zhang ML (2007) Diagnostic significance of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Jiangsu Univ (Med Ed) 17(2):165–166
Lei XM, Li SX (2005) Diagnosis value of anti-CCP, anti-RA33 and RF in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Intern Med 22(10):667–668
Pan XP, Xie W, Wu M, Zhang H (2006) Diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Jinagsu Med J 32(1):68–69
Bi XF, Zhu JH, Wang CH (2009) Evaluation of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptides in diagnosing rheumatoid Arthritis. J Diseasea Monit Control 3(4):207–208
Yuan Y, Qing YF, Qi J, Jiang H, Wang XR (2008) The clinical value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Sichuan J Anat 16(4):5–7
Wang CY, Hu XZ, Zhang HX (2008) Diagnosis value of anti-CCP and anti-RA33 in rheumatoid arthritis. Shangdong Med J 48(20):84–85
Yi MZ, Zhang J, Yu H (2009) Diagnostic value of anti-cyclic peptide citrullinated antiboby, anti-Sa antibody, and rheumatoid factor in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Pract Prev Med 16(4):1212–1214
Fan YY, Yu J (2009) Diagnostic significance of combined detection of serum anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and rheumatoid factor in rheumatoid arthritis. Lab Med Clin 6(18):1528–1529
Li X (2009) Diagnostic value of combined detection of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and the rheumatoid factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Guangxi Med J 31(4):515–516
Wei W, Qian YQ, Hou YQ (2007) The clinical value of combined detection antibodies in the early diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Guizhou Med J 31(5):401–403
Wang Y, Jian S (2008) Comparative analysis of three autoantibodies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. China Pract Med 3(15):130
Yang JJ, Gong Y, Zu H (2009) The clinical value of the combination of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody, anti-keratin and rheumatoid factor in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Ningxia Med Univ 31(1):43–46
Fan ZQ, Shi LH, Li YS (2007) Diagnostic value of anti-CCP in rheumatoid arthritis. Jilin Med J 28(17):1906–1907
Wang J, Li XM, Zhao HY (2009) Diagnostic value of combined detection of glucose phosphate isomerase, anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody, and rheumatoid factor in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Proc Clin Med J 18(8):581–583
Xiao Z, Bai LJ, Qin YQ (2005) The meaning of diagnosis and condition valuation of AFA, anti-CCP antibody and RF to rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Academiae Medicinae Mongolia 27(4):265–270
Bao QC (2008) Diagnostic value of level of anti-cyclic peptide citrullinated antibody, anti-keratin antibody, and rheumatoid factor in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Inner Mongolia Med J 40(3):323–325
Wang J, Wang Y, Guo XX (2010) Diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated Peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. China Foreign Med Treat 8:31
Dong W, Zhang JB, Hu X, Jun F, Zhou B (2005) Determination of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody for the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Pract J Clin Med 2(1):84–86
Zhang LF, Yan YG, Huang QC, Zhong Q (2004) Diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated Peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol J 20(1):52–57
Cui TP, Xie JL, Yu LK, Hu LH, Shen JL, Wu JM (2003) Diagnostic value of four autoantibodies in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Shanghai J Med Lab Sci 18(4):221–222
Liu XY, Xie MY, Huang J, Wang H (2010) Diagnostic value of combined detection of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and the rheumatoid factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Hubei Univ Chin Med 12(1):47–48
Wei H, Li XF, Hu XF, Xu K, Yang XY (2003) Diagnostic value of combined detection of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and anti-Sa antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Chin J Rheumatol 7(10):635–637
Zhang H, Ye ZX, Liu GX XUZH, Liu Q (2004) Diagnostic value of combined detection of rheumatoid factors, anti-RA33, and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Guizhou Med J 28(1):44–45
Gu FR, Zhang YD, Shi JJ (2007) Diagnosis value of anti-CCP antibody, anti-RA33 antibody, anti-Sa antibody, and RF in rheumatoid arthritis. Jiangxi J Med Lab Sci 25(1):24–34
Tao CH, Cai L, Ai Y, Cheng M (2009) Diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Youjiang Med Univ Nat 2:201–202
Zhang JM, Zhuo SX, Lin YP, Li Y (2009) Diagnostic value of combined detection of rheumatoid factors, anti-AKA, and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Guangdong Med College 27(2):151–153
Peng XD, Li LX, Bai YJ, Zhang RW, Liu GJ (2006) Diagnostic value of anti-CCP, anti-AKA, and RF in rheumatoid arthritis. J Sichuan Univ (Med Sci Ed) 37(2):317–318
Liu XD, Fu HX, Cui HD, Pan LL (2009) Detection value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in early diagnosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Pract Pharm Clin Rem 12(1):18–20
Huang Y, Wu YA, Ma XN, Wang SW (2004) Application and clinical value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Fujian Med Univ 38(3):337–338
Chen YJ, Wang X, Fan CL, Cao HJ, Chen J, Liu CL (2005) Application of measurements of serum anti-CCP and anti-RA33 in rheumatoid arthritis. J Postgrad Med 28(3):22–24
Wang H, Wu XH, Zhang ZY (2009) Diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and rheumatoid factor in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Chin J Trauma Disabil Med 17(5):15–16
Xie QB, Yin G (2009) Predictive values of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody, anti-keratin antibody and rheumatoid factor in diagnosing articular erosions in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Sichuan Univ (Med Sci Ed) 40(3):508–512
Yu W, Zhu MY, Shen HY, Zhang W (2006) Comparison of the value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptides, rheumatoid factor, and anti-keratin antibody in the diagnosis for rheumatoid arthritis. Lab Med 21(2):103–105
Wen AQ, Wang J, Yang YS, Chen W, Zhang ZC, Liu CY (2008) Application of anti-citrullinated peptides and related auto-antibodies in diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis. Chongqing Med 37(3):262–265
Mu CX (2007) The clinic value of combined test of RF, AKA, and anti-CCP antibody in diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis. J Med Theor Pract 20(5):517–518
Lu H, Xia Y, Zhou W, Chen YE (2009) Application of joint detection of four serum indicators in diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. China Trop Med 9(1):72–73
Liang JQ, Luo YF (2006) Evaluation of indicators of early rheumatoid arthritis. J Pract Med 22(15):1820–1821
Chen HL, Yong WD, Han JY (2007) Combination detection of serum anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and rheumatid factor: its diagnostic value of rheumatoid arthritis. Med J Qilu 22(6):508–511
Sun HY, Wang CY, Liu W, Wu B, Chen LY, Chen MQ (2008) Diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Fujian Med Univ 42(3):284–285
Lin L, Xiao ZY, Chen SB, Huang SB, Xie SH (2006) Diagnostic significance of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and its predictive value for radiological progression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Chin J Health Lab Technol 16(5):516–519
Chen HM, Sun MZ, Gu J (2007) Application of combined detection of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and the rheumatoid factors in diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. J Mod Lab Med 22(4):79–80
Liu ZH, Ge XJ, Zhu HL (2009) Diagnosis values of combined determination of serum rheumatoid factor, C reaction protein and anti-CCP antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod J Integrat Trad Chin West Med 18(27):3272–3283
Wang Y, Fang YF, Zhong B (2004) Significance of anti-cyclic citrullinase peptide antibody and rheumatoid factor in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Chin J Clin Rehabil 8(9):1616–1617
Fu KY, Chen R, Zhan F, Zhong L (2007) Value of detection of anti-CCP and rheumatoid factors AKA in diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. China Trop Med 7(11):2029–2030
Li FJ, Guo XJ, Zhao Y, Zhang J, Ding MR, Li QR (2005) Application of joint detection of four antibodies in diagnosis of early rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Focus 20(14):821–822
Cai F, Li L, Tang YP (2009) Clinical application of domestic anti-CCP antibody kit. J Radioimmunol 22(4):422–423
Chen XL, Pan SL, Gao ZF (2006) Application of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and the rheumatoid factors in diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Sichuan Med J 27(7):690–691
Li SS, Bao HY (2007) Clinical diagnosis value of citrullinated protein antibodies for rheumatoid arthritis. J Med Forum 28(2):42–43
Meng QS, Liu XX, Ye Y, Lin MQ (2006) Clinical value of APF, AKA, RF and anti-CCP antibody in diagnosis and differential diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Med Lab Sci Clin 17(6):35–37
Zeng ZH, Zhong LY, Li RY, Ding CP (2006) The diagnostic value of anticyclic citrullinated peptide antibody performed concomitantly with RF in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Guangzhou Med J 36(2):64–66
Gao LX, Liu FZ, Liu XL (2004) The clinical significance fo anti-cyclic citrullinated polypeptide antibody and the analysis of interference factors. Chin J Diffic Compl Cas 3(4):209–211
Qian L, Li XP, Li XM, Wang GS, Tao JH, Zhang H et al (2004) The diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Anhui Med J 25(3):171–173
Xu ZY, Dai Y, Zhang DY, Zhang J (2005) Diagnostic value of combined detection of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and the rheumatoid factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Academiae Medicinae Wannan 24(3):218–219
Xie W, Pan JP (2005) The clinical significance of anti-CCP antibody, AKA, RF in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Focus 20(5):287–289
Zhao LW, Wu J, Zhang BX (2007) To exam the anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody, anti-keratin antibody and antiperinuclear factor and to evaluate the diagnosis method of the early patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Med Lab Sci Clin 18(4):24–26
Lai ZF, Wu XN, Jiang JQ (2006) Diagnostic value of quantitative detection of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Guangxi Med Univ 23(6):985–986
Cai WH, Sun BD, Hong XP, Liu DZ, Tan YH, Xiao XL (2006) Evaluation of rheumatoid factor, anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and anti-keratin antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Exp Med 5(6):671–673
Xia QF, Qin X, Qian SJ, Wu XP (2003) The diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody for the patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Hainan Med College 9(6):331–333
Zhou B, Zhu J, Liu J, Long WB, Wu D, Chen J et al (2004) The diagnostic and prognostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Chin J Rheumatol 8(6):360–362
Zeng Y, Chen M, Cai MZ, Liu Q, Gu YL, Wang KZ (2006) The diagnostic value of combinate determination of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and rheumatoid factor for the rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Med J China 13(6):1022–1023
Yang CM, Wang HM, Cong H, Cao LH (2005) Diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody quantitative analysis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Jiangxi J Med Lab Sci 23(1):7–8
Wang J, Wen AQ, Yang YS, Zhuang SB (2007) Clinical evaluation of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptides in diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis. Chongqing Med 36(15):1513–1515
Ding ZM (2008) Examine the diagnostic significance by the detection anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and rheumatoid factor. Med Lab Sci Clin 19(1):38–39
Hu Y, Wang J, Wang QX (2008) The diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and rheumatoid factor for the rheumatoid arthritis. Central China Med J 32(1):31–32
Chen PF, Liu YR, Chen C, Chen Q, Ye QY (2005) Clinical evaluation of early marker in diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis. Med J Wuhan Univ 26(4):529–532
Yu F, Fei Y, Shi P (2005) An evaluation of the diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis disease. Guizhou Med J 29(5):409–411
Hu XT, Xia XJ, Wei H, Jin W (2007) Diagnostic value of combined detection of anti-CCP antibody and rheumatoid factor in RA. Acta Acad Weifang 29(1):57–58
Song JJ, Pan XJ, Yue XH (2007) Clinical value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Occup Health 23(22):2020–2021
Liu Y, Yong J (2005) Evaluation of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis. J North Sichuan Med College 20(3):327–329
Wu CY, Huang LY, Li YM, Lin J, Li YY, Pan ZX (2009) Application of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide in diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. China Trop Med 9(9):1907–1908
Ji CM (2008) Use of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide and anti-RA33 antibodies in diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis. Med Lab Sci Clin 19(3):84–85
Chen YH, Li SZ (2008) The diagnostic value of combined detection of anti-CCP antibody and rheumatoid factor in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Lab Med Clin 5(18):1093–1094
Zeng HQ, Zhang DX, Yu HG, Dong HJ, Zhang XS (2008) Clinical value of combined tests of three antibodies assaies in the diagnosis of early stage for rheumatoid arthritis. Chin Gen Pract 11(4B):650–651
Li XL, Tao HQ, Zhang WH, Zheng YB (2006) The clinical application of Mark2 anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide determination in rheumatoid arthritis. Lab Med 21(6):599–601
Liang RC, Li YJ (2003) The detection of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and the early diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. China J Mod Med 13(13):85–86
Chen BY, Deng HL, Yang WP (2008) Diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Lab Med Clin 5(18):1091–1093
Li XH, Zhang CJ (2009) Evaluation of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody, anti-keratin antibody and rheumatoid factor in diagnosis of early rheumatoid arthritis. China Med Herald 6(19):32–34
Zhou HQ, Xu XD, Zhang H, Dong M (2009) The comparison of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and rheumatoid factor in rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis. Shenzhen J Integrat Chin West 19(4):224–226
Zhang RF, Jiang M (2009) Clinical application of anti-CCP antibody and AFA detection in diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Qinghai Med J 39(4):1–3
Guo PE, Qin Q, Wu SM, Shen Q (2003) Clinical significance of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Jiangxi Med Lab Sci 21(5):331–332
Han YX, Shao FL, Liu FZ, Jin HT, Liu XL (2005) Diagnostic value of anti- cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody assay for rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Focus 20(22):1276–1278
Zhu HL (2006) Clinical value of the combined detection of anti-CCP antibody and RF in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Med Health 22(11):1593–1594
Li GF, Gao F, Wang L (2005) The diagnostic value anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Mod Lab Med 20(3):7–10
Zhao L, Ren SH, Hou AP (2009) Study on the anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies and the rheumatoid factors in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. China Pract Med 4(36):67–68
Zeng XF, Ai MX, Tian XP, Gan XD, Shi YP, Song QF et al (2003) Diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 30(7):1451–1455
Li H, Song WQ, Li Y, Liu YH, Bai J, Li X et al (2010) Diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in Northern Chinese Han patients with rheumatoid arthritis and its correlation with disease activity. Clin Rheumatol 29(4):413–417
Ge WL (2010) Clinical value of combined detection of serum anti-citrullinated peptide antibody (anti-CCP Ab) and rheumatoid factor (RF) in diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. J Radioimmumol 23(2):131–133
Zhang GQ, Chang LM, Fang XL (2010) Diagnostic value of the combined detection of anti-CCP antibody, anti-RA33 antibody and RF in rheumatoid arthritis. Chin J Clin Lab Sci 28(3):196–197
Guo DM, Zhang HW, Chen GQ (2009) The clinical value of anti- anti-citrullinated peptide antibody and rheumatoid factor combined detection in rheumatoid arthritis. PJCCPVD 17(12):1048–1049
He HJ, Qiu GB (2008) Clinical application of anti-CCP antibody in diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Chins Med Herald 5(5):76
Hu ZD, Lv JQ, Yan BY, Xing N, Fu L, Wei G et al (2007) The value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and vascular endothelial growth factor in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Lab Med 22(1):41–43
Xiao CH, Wu QF, Zhang LH, Yang SF, Li KQ (2006) Detection and significance of synovial fluid anti-CCP antibody in rheumatoid arthritis. Chin J Rheumatol 10(3):184–186
Wang JY, Li P, Wang WG (2006) Specific antibodies of the early diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Chin J Diagn 10(12):1446–1448
Sun SJ (2004) Diagnostic value of detecting anti-cyclic cirtrullinated peptide antibody in rheumatoid arthritis. Acta Academiae Medicinae Militaris Tertiae 26(19):1786–1787
Zhao HC, Xiang GJ (2005) Clinical diagnostic value of combined determiantion of serum RF, AKA, and anti-CCP antibody levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Radioimmunol 18(6):501–503
Shi HY (2007) Clinical value of combined detection of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and the rheumatoid factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. China Pract Med 2(2):116–117
Zhao X, Jiang H, Liu DJ (2006) Clinical diagnostic value of anti-CCP antibody levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Heilongjiang Med J 30(8):637–638
Zhao YX, Zhang TH, Zhang JJ (2006) Clinical significance of RF, AKA, and anti-CCP antibody levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Shaanxi Med J 35(3):335–336
Zhang JM, Mu Y, Jin M, Jin Y, Lv TH (2005) Detection and significance of the anti-CCP antibody, anti-RA54, anti-Sa antibody and rheumatoid factor in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Pract Diagn Therapy 19(2):81–83
Tan LM, Peng WH, Cao LP, Li H, Cai LL, Wang YY et al (2006) A study on anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Jiangxi J Med Lab Sci 24(4):312–314
Sui XF, Chi WQ, Yao YH, Zhang CM, Jiang YH (2010) The significance of detecting anti-cyclic citrullianted peptide and rheumatoid factor in the earlier diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Heilongjiang Med J 34(4):268–269
Kwok JSY, Hui KH, Lee TL, Wong W, Lau YL, Wong RWS et al (2005) Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide: diagnostic and prognostic values in juvenile idiopathic arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis in a Chinese population. Scand J Rheumatol 34:359–366
Mimori T (2005) Clinical significance of anti-CCP antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Intern Med 44(11):1122–1126
Huang QS, Wan LQ, Luo ZQ, Le AP, Wang WQ (2006) Diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody for rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis. Natl Med J China 86(31):2182–2187
Nishimura K, Sugiyama D, Kogata Y, Tsuji G, Nakazawa T, Kawano S et al (2007) Meta-analysis diagnostic accuracy of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody and rheumatoid factor for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Intern Med 146(11):816–817
Liao KP, Batra KL, Chibnik L, Schur PH, Costenbader KH (2008) Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 67(11):1557–1561
Acknowledgments
Thanks to M. M. Jiayong Liu for his assistance in statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors Fei Gao and Lei Ren equally contributed to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, F., Ren, L., Zhang, CQ. et al. Diagnostic value of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody for rheumatoid arthritis in a Chinese population: a meta-analysis. Rheumatol Int 32, 3201–3218 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-011-2153-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-011-2153-y