Abstract
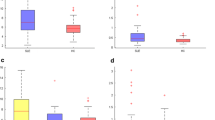
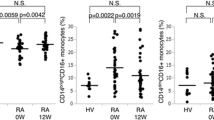
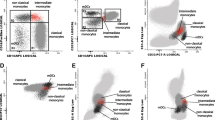
With the purpose of contributing to a better knowledge of the APCs functional activity in SLE, we evaluated the distribution and functional ability to produce pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-12) of peripheral blood (PB) monocytes and DC (tDC), particularly myeloid (mDC) and CD14−/lowCD16+ DC subpopulations comparing them with those obtained from healthy individuals. The study was performed in 34 SLE patients with diverse disease activity scores (SLEDAI) and 13 healthy age- and sex-matched controls (NC). Our results show an overall decrease in absolute number and relative frequency of tDC in SLE patients with active disease when compared to those with inactive disease and NC, although this decrease did not seem to have an effect on the distribution of PB DC subsets. The monocytes number in SLE patients was similar to those found in NC, whereas a higher frequency of monocytes producing cytokines as well as the amount of each cytokine per cell found without stimulation was particularly observed in those patients with active disease. After stimulation, we observed a higher frequency of IL-12-producing monocytes in active SLE patients. On the other hand, we found among DCs higher frequencies of cytokine-producing CD14−/lowCD16+ DCs and a higher amount of cytokines produced per cell, particularly in active disease. These findings support an increased production of inflammatory cytokines by APCs in active SLE, mostly associated with alterations in CD14−/lowCD16+ DC subset homeostasis that might contribute to explain the dynamic role of these cells in disease pathogenesis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mok CC, Lau CS (2003) Pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. J Clin Pathol 56:481–490. doi:10.1136/jcp.56.7.481
Tsubata T (2005) B cell abnormality and autoimmune disorders. Autoimmunity 38:331–337. doi:10.1080/08916930500123959
Foster MH (2007) T cells and B cells in lupus nephritis. Semin Nephrol 27:47–58. doi:10.1016/j.semnephrol.2006.09.007
Mozaffarian N, Wiedeman AE, Stevens AM (2008) Active systemic lupus erythematosus is associated with failure of antigen-presenting cells to express programmed death ligand-1. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47:1335–1341. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/ken256
Rutella S, De Cristofaro R, Ferraccioli G (2009) Function and dysfunction of dendritic cells in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Hum Immunol 70:360–373. doi:10.1016/j.humimm.2009.01.023
Pertovaara M, Hasan T, Raitala A, Oja SS, Yli-Kerttula U, Korpela M et al (2007) Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase activity is increased in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and predicts disease activation in the sunny season. Clin Exp Immunol 150:274–278. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2007.03480.x
Grage-Griebenow E, Flad HD, Ernst M (2001) Heterogeneity of human peripheral blood monocyte subsets. J Leukoc Biol 69:11–20
Ho CS, Lopez JA, Vuckovic S, Pyke CM, Hockey RL, Hart DN (2001) Surgical and physical stress increases circulating blood dendritic cell counts independently of monocyte counts. Blood 98(1):140–145. doi:10.1182/blood.V98.1.140
Fogg DK, Sibon C, Miled C, Jung S, Aucouturier P, Littman DR et al (2006) A clonogenic bone marrow progenitor specific for macrophages and dendritic cells. Science 311:83–87. doi:10.1126/science.1117729
Leon B, Lopez-Bravo M, Ardavin C (2005) Monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Semin Immunol 17:313–318
Almeida J, Bueno C, Alguero MC, Sanchez ML, de Santiago M, Escribano L et al (2001) Comparative analysis of the morphological, cytochemical, immunophenotypical, and functional characteristics of normal human peripheral blood lineage(−)/CD16(+)/HLA-DR(+)/CD14(-/lo) cells, CD14(+) monocytes, and CD16(−) dendritic cells. Clin Immunol 100:325–338. doi:10.1006/clim.2001.5072
Crespo I, Paiva A, Couceiro A, Pimentel P, Orfao A, Regateiro F (2004) Immunophenotypic and functional characterization of cord blood dendritic cells. Stem Cells Dev 13:63–70. doi:10.1089/154732804773099263
Ziegler-Heitbrock HW, Fingerle G, Strobel M, Schraut W, Stelter F, Schutt C et al (1993) The novel subset of CD14+/CD16+ blood monocytes exhibits features of tissue macrophages. Eur J Immunol 23:2053–2058. doi:10.1002/eji.1830230902
Thomas R, Lipsky PE (1994) Human peripheral blood dendritic cell subsets. Isolation and characterization of precursor and mature antigen-presenting cells. J Immunol 153:4016–4028
Ziegler-Heitbrock HW (1996) Heterogeneity of human blood monocytes: the CD14 + CD16+ subpopulation. Immunol Today 17:424–428. doi:10.1016/0167-5699(96)10029-3
Kubach J, Becker C, Schmitt E, Steinbrink K, Huter E, Tuettenberg A et al (2005) Dendritic cells: sentinels of immunity and tolerance. Int J Hematol 81:197–203. doi:10.1532/IJH97.04165
Palucka K, Banchereau J (1999) Dendritic cells: a link between innate and adaptive immunity. J Clin Immunol 19:12–25. doi:10.1023/A:1020558317162
Hawiger D, Inaba K, Dorsett Y, Guo M, Mahnke K, Rivera M et al (2001) Dendritic cells induce peripheral T cell unresponsiveness under steady state conditions in vivo. J Exp Med 194:769–779. doi:10.1084/jem.194.6.769
Curti A, Trabanelli S, Salvestrini V, Baccarani M, Lemoli RM (2009) The role of indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase in the induction of immune tolerance: focus on hematology. Blood 113:2394–2401. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-07-144485
Theofilopoulos AN, Koundouris S, Kono DH, Lawson BR (2001) The role of IFN-gamma in systemic lupus erythematosus: a challenge to the Th1/Th2 paradigm in autoimmunity. Arthritis Res 3:136–141. doi:10.1186/ar290
Ding D, Mehta H, McCune WJ, Kaplan MJ (2006) Aberrant phenotype and function of myeloid dendritic cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Immunol 177:5878–5889
Crispin JC, Alcocer-Varela J (2007) The role myeloid dendritic cells play in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev 6:450–456. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2007.01.014
Robak E, Smolewski P, Wozniacka A, Sysa-Jedrzejowska A, Stepien H, Robak T (2004) Relationship between peripheral blood dendritic cells and cytokines involved in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Eur Cytokine Netw 15:222–230
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40:1725
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, Masi AT, McShane DJ, Rothfield NF et al (1982) The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 25:1271–1277
Bombardier C, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Caron D, Chang CH (1992) Derivation of the SLEDAI. A disease activity index for lupus patients. The Committee on Prognosis Studies in SLE. Arthritis Rheum 35:630–640. doi:10.1002/art.1780350606
Gladman DD, Ibanez D, Urowitz MB (2002) Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index 2000. J Rheumatol 29:288–291
Griffiths B, Mosca M, Gordon C (2005) Assessment of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and the use of lupus disease activity indices. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 19:685–708. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2005.03.010
Ronnblom L, Alm GV, Eloranta ML (2009) Type I interferon and lupus. Curr Opin Rheumatol 21(5):471–477. doi:10.1097/BOR.0b013e32832e089e
Gigante A, Amoroso D, Ferri F, Gianni C, Coppolino G, Papa A et al (2006) Systemic lupus erythematosus and renal involvement: which role of citokines expression? Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 10:223–228
Kulkarni O, Anders HJ (2008) Chemokines in lupus nephritis. Front Biosci 13:3312–3320
Cederblad B, Blomberg S, Vallin H, Perers A, Alm GV, Ronnblom L (1998) Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus have reduced numbers of circulating natural interferon-alpha—producing cells. J Autoimmun 11:465–470. doi:10.1006/jaut.1998.0215
Vallin H, Blomberg S, Alm GV, Cederblad B, Ronnblom L (1999) Patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) have a circulating inducer of interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) production acting on leucocytes resembling immature dendritic cells. Clin Exp Immunol 115:196–202. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2249.1999.00772.x
Scheinecker C, Zwolfer B, Koller M, Manner G, Smolen JS (2001) Alterations of dendritic cells in systemic lupus erythematosus: phenotypic and functional deficiencies. Arthritis Rheum 44:856–865. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(200104)44:4<856:AID-ANR142>3.0.CO;2-A
Jin O, Kavikondala S, Sun L, Fu R, Mok MY, Chan A et al (2008) Systemic lupus erythematosus patients have increased number of circulating plasmacytoid dendritic cells, but decreased myeloid dendritic cells with deficient CD83 expression. Lupus 17:654–662. doi:10.1177/0961203308089410
Li Y, Lee PY, Sobel ES, Narain S, Satoh M, Segal MS et al (2009) Increased expression of FcgammaRI/CD64 on circulating monocytes parallels ongoing inflammation and nephritis in lupus. Arthritis Res 11:R6. doi:10.1186/ar2590
Means TK, Latz E, Hayashi F, Murali MR, Golenbock DT, Luster AD (2005) Human lupus autoantibody-DNA complexes activate DCs through cooperation of CD32 and TLR9. J Clin Invest 115:407–417. doi:10.1172/JCI200523025
Stanilova SA, Slavov ES (2001) Comparative study of circulating immune complexes quantity detection by three assays–CIF-ELISA, C1q-ELISA and anti-C3 ELISA. J Immunol Methods 253:13–21. doi:10.1016/S0022-1759(01)00370-2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
A. Henriques, L. Inês and T. Carvalheiro are contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Henriques, A., Inês, L., Carvalheiro, T. et al. Functional characterization of peripheral blood dendritic cells and monocytes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Int 32, 863–869 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-010-1709-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-010-1709-6