Abstract
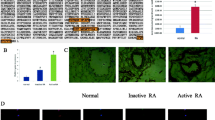
PADI4 that catalyzes the conversion of peptidylarginine to citrulline is associated with rheumatoid arthritis in some populations. The current study investigated the expressions of PADI4 in synovial fluid of RA (n = 73), osteoarthritis (OA, n = 96) and ankylosing spondylitis (AS, n = 32) using ELISA and western blotting following immuno-precipitation (n = 6 for each diseases). The study also compared the mRNA level of PADI4 in the synovial membrane of RA with the levels in the samples of OA and AS (n = 6 for each diseases) using real time PCR. ELISA detected a higher level of PADI4 in SF of RA than in samples of OA and AS (P = 0.0001). The level of PADI4 was significantly correlated with the level of rheumatic factor (P = 0.015), but not with anti cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody (anti-CCP) in the RA fluids. Western blotting confirmed the expression of PADI4 in SF of RA. Quantitative PCR measured higher transcription of PADI4 in the synovial membrane of RA than in the samples of OA and AS. The results confirmed increased expression of PADI4 in synovium of RA.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tarcsa E et al (1996) Protein unfolding by peptidylarginine deiminase substrate specificity and structural relationships of the natural substrates. J Biol Chem 271:30709–30716. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.48.30709
Utz PJ, Genovese MC, Robinson WH (2004) Unlocking the “PAD” lock on rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 63:330–332. doi:10.1136/ard.2003.015990
Suzuki A et al (2003) Functional haplotypes of PADI4, encoding citrullinating enzyme peptidylarginine deiminase 4, are associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Genet 34:395–402. doi:10.1038/ng1206
Kang CP, Lee HS, Ju H, Cho H, Kang C, Bae SC (2006) A functional haplotype of the PADI4 gene associated with increased rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility in Koreans. Arthritis Rheum 54:90–96. doi:10.1002/art.21536
Hoppe B, Haupl T, Gruber R, Kiesewetter H, Burmester GR, Salama A, Dorner T (2006) Detailed analysis of the variability of peptidylarginine deiminase type 4 in German patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a case-control study. Arthritis Res Ther 8:R34. doi:10.1186/ar1889
Vossenaar ER, Nijenhuis S, Helsen MM, van der Heijden A, Senshu T, van den Berg WB, van Venrooij WJ, Joosten LA (2003) Citrullination of synovial proteins in murine models of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 48:2489–2500. doi:10.1002/art.11229
Lundberg K, Nijenhuis S, Vossenaar ER, Palmblad K, van Venrooij WJ, Klareskog L, Zendman AJ, Harris HE (2005) Citrullinated proteins have increased immunogenicity and arthritogenicity and their presence in arthritic joints correlates with disease severity. Arthritis Res Ther 7:R458. doi:10.1186/ar1697
Chang X, Yamada R, Suzuki A, Sawada T, Yoshino S, Tokuhiro S, Yamamoto K (2005) Localization of peptidylarginine deiminase 4 (PADI4) and citrullinated protein in synovial tissue of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 44:40–50. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh414
Arnett FC, Edworthys Bloch DA et al (1987) ARA diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 30:17–19
Van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A (1984) Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum 27:361–368. doi:10.1002/art.1780270401
Chang X, Yamada R, Sawada T, Suzuki A, Kochi Y, Yamamoto K (2005) The inhibition of antithrombin by peptidylarginine deiminase 4 may contribute to pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 44:293–298. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/keh473
Chang X, Yamada R, Suzuki A, Kochi Y, Sawada T, Yamamoto K (2005) Citrullination of fibronectin in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue. Rheumatology (Oxford) 44:1374–1382. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kei023
Vossenaar ER, Radstake TR, van der Heijden A, van Mansum MA, Dieteren C, de Rooij DJ, Barrera P, Zendman AJ, van Venrooij WJ (2004) Expression and activity of citrullinating peptidylarginine deiminase enzymes in monocytes and macrophages. Ann Rheum Dis 63:373–381. doi:10.1136/ard.2003.012211
Caspi D, Anouk M, Golan I et al (2006) Synovial fluid levels of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies and IgA rheumatoid factor in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 55:53–56. doi:10.1002/art.21691
Agrawal S, Misra R, Aggarwal A (2007) Autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis: association with severity of disease in established RA. Clin Rheumatol 26:201–204. doi:10.1007/s10067-006-0275-5
del Amo N, Ibanez Bosch R, Fito Manteca C, Gutierrez Polo R, Loza Cortina E (2006) Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in rheumatoid arthritis: relation with disease aggressiveness. Clin Exp Rheumatol 24:281–286
Arnason JA, Jónsson T, Brekkan A, Sigurjónsson K, Valdimarsson H (1987) Relation between bone erosions and rheumatoid factor isotypes. Ann Rheum Dis 46:380–384. doi:10.1136/ard.46.5.380
Greiner A, Plischke H, Kellner H, Gruber R (2005) Association of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies, anti-citrullin antibodies, and IgM and IgA rheumatoid factors with serological parameters of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1050:295–303. doi:10.1196/annals.1313.031
De Rycke L, Verhelst X, Kruithof E, Van den Bosch F, Hoffman IE, Veys EM, De Keyser F (2005) Rheumatoid factor, but not anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies, is modulated by infliximab treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 64:299–302. doi:10.1136/ard.2004.023523
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NTFC) (30671949), the Shandong Science and Technology Research Program (2007GG20002001, 2006GG2202050), the Shandong Scientific Instrument Equipment Promotion Transformation Project (2006GG1108097-41, 2007GG2TC02050) and the Leading Project of Medical Science of Shandong.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chang, X., Zhao, Y., Sun, S. et al. The expression of PADI4 in synovium of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 29, 1411–1416 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-009-0870-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-009-0870-2