Abstract
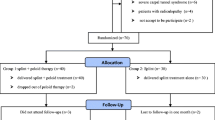
The objective of this study was to compare the short- and long-term efficacies of splinting (S), splinting plus local steroid injection (SLSI), and open carpal tunnel release (OCTR) in mild or moderate idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). Patients with mild or moderate idiopathic CTS who experienced symptoms for over 6 months were included in the study. The patients were evaluated for the baseline and the third and sixth month scores after treatment. Follow-up criteria were ENMG parameters, Boston Questionnaire, and patient satisfaction. Fifty-seven hands completed the study. Twenty-three hands had been splinted for 3 months. Twenty-three hands were given a single steroid injection and splinted for 3 months, and 11 hands were operated. In the first 3 months, all treatment methods provided significant improvements in both clinical and EMG parameters in which OCTR had better outcomes on median sensorial nerve velocity at palm wrist segment. In the second 3 months, while the clinical and EMG parameters began to deteriorate in S and SLSI group, OCTR group continued to improve, and BQ functional capacity score of OCTR group was statistically better than that in conservative methods (P = 0.03). S and SLSI treatments improved clinical and EMG parameters comparable to OCTR in short term. However, these beneficial effects were transient in the sixth month follow-up and OCTR was superior to conservative treatments.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stevens JC, Sun S, Beard CM, O’Fallon WM, Kurland LT (1988) Carpal tunnel syndrome in Rochester Minnesota, 1961 to 1980. Neurology 38:134–138
de Krom MC, Knipschild PG, Kester AD, Thijs CT, Spaans F (1992) Carpal tunnel syndrome: prevalence in the general population. J Clin Epidemiol 45:373–376
Brown RA, Gelberman RH, Seiler JG 3rd, Abrahamsson SO, Weiland AJ, Urbaniak JR, Schoenfeld DA, Furcolo D (1993) Carpal tunnel release. A prospective, randomized assessment of open and endoscopic methods. J Bone Joint Surg Am 75(9):1265–1275
Holmgren-Larsson H, Leszniewski W, Linden U, Rabow L, Thorling J (1985) Internal neurolysis or ligament division only in carpal tunnel syndrome—results of a randomized study. Acta Neurochir 74(3–4):118–121
Kruger VL, Kraft GH, Deitz JC, Ameis A, Polissar L (1991) Carpal tunnel syndrome: objective measures and splint use. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 72(7):517–520
Manente G, Torrieri F, Di Balassio F, Staniscia T, Romano F, Uncini A (2001) An innovative hand brace for carpal tunnel syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Muscle Nerve 24:1020–1025
Ayhan-Ardic FF, Erdem HR (2000) Long-term clinical and electrophysiological results of local steroid injection in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome. Funct Neurol 15(3):157–165
Giannini F, Passero S, Cioni R, Paradiso C, Battistini N, Giordano N, Vaccai D, Marcolongo R (1991) Electrophysiologic evaluation of local steroid injection in carpal tunnel syndrome. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 72(10):738–742
Dammers JW, Veering MM, Vermeulen M (1999) Injection with methylprednisolone proximal to the carpal tunnel: randomised double blind trial. BMJ. 319(7214):884–886
Ozdogan H, Yazici H (1984) The efficacy of local steroid injections in idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome: a double-blind study. Br J Rheumatol 23(4):272–275
O’Gradaigh D, Merry P (2000) Corticosteroid injection for the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 59(11):918–919
Stevens JC (1997) AAEM mimimonograph # 26: the electrodiagnosis of carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle Nerve 20(12):1477–1486
Levine DW, Simmons BP, Koris MJ, Daltroy LH, Hohl GG, Fossel AH, Katz JN (1993) A self-administered questionnaire for the assessment of severity of symptoms and functional status in carpal tunnel syndrome. J Bone Joint Surg 75(11):1585–1592
Heybeli N, Özerdemoğlu RA, Aksoy OG, Mumcu EF (2001) Karpal Tünel Sendromu: Cerrahi tedavi izleminde fonksiyonel ve semptomatik skorlama. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 35:147–151
Heybeli N, Kutluhan S, Demirci S, Kerman M, Mumcu EF (2002) Assessment of outcome of carpal tunnel syndrome: a comparison of electrophysiological findings and a self-administered Boston questionnaire. J Hand Surg (Br) 27(3):259–264
Mondelli M, Reale F, Sicurelli F, Padua L (2000) Relationship between the self-administered Boston questionnaire and electrophysiological findings in follow-up of surgically-treated carpal tunnel syndrome. J Hand Surg (Br) 25(2):128–134
Gonzalez MH, Bylak J (2001) Steroid injection and splinting in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome. Orthopedics 24(5):479–481
Wood MR (1980) Hydrocortisone injections for carpal tunnel syndrome. Hand 12(1):62–64
Girlanda P, Dattola R, Venuto C, Mangiapane R, Nicolosi C, Messina C (1993) Local steroid treatment in idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome: short- and long-term efficacy. J Neurol 240(3):187–190
Burke DT, Burke MM, Stewart GW, Cambre A (1994) Splinting for carpal tunnel syndrome: in search of the optimal angle. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 75(11):1241–1244
Demirci S, Kutluhan S, Koyuncuoglu HR, Kerman M, Heybeli N, Akkus S, Akhan G (2002) Comparison of open carpal tunnel release and local steroid treatment outcomes in idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome. Rheumatol Int 22(1):33–37
Gerritsen AA, de Vet HC, Scholten RJ, Bertelsmann FW, de Krom MC, Bouter LM (2002) Splinting vs surgery in the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 288(10):1245–1251
Ly-Pen D, Andre’u JL, de Blas G, Sa’nchez-Olaso A, Milla’n I (2005) Surgical decompression versus local steroid injection in carpal tunnel syndrome. Arthritis Rheum 52(2):612–619
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ucan, H., Yagci, I., Yilmaz, L. et al. Comparison of splinting, splinting plus local steroid injection and open carpal tunnel release outcomes in idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome. Rheumatol Int 27, 45–51 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-006-0163-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-006-0163-y