Abstract
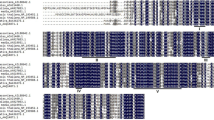
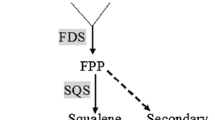
Farnesylpyrophosphate synthase (FPPS) is a key enzyme in isoprenoid biosynthesis. Several classes of essential metabolites, including sterols, quinones, carotenoids and gibberellins, are terpenoids with high biological activity. The structural gene for FPP synthase was isolated from two ascomycete fungi, Neurospora crassa and Gibberella fujikuroi. A comparative analysis of the nucleotide sequences of both FPPS genes revealed the presence of introns at the same positions at the 5′ end of the coding regions. Furthermore, the most conserved region of the gene was isolated from two other plant pathogenic fungi, Sphaceloma manihoticola and Claviceps purpurea, by PCR. Sequence analysis showed a high degree of similarity between the deduced proteins of all known FPP synthase genes. In contrast to animals, all analyzed fungi contain a single copy of the gene, although FPP is the precursor for essential sterol and quinone biosynthesis and secondary metabolites, such as gibberellins, as well. Transcription analysis in different light regimes has shown that the FPPS genes in G. fujikuroi and N. crassa are not regulated by light induction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 18 March / 21 May 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Homann, V., Mende, K., Arntz, C. et al. The isoprenoid pathway: cloning and characterization of fungal FPPS genes. Curr Genet 30, 232–239 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002940050126
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002940050126