Abstract
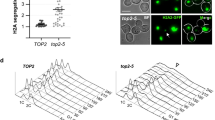
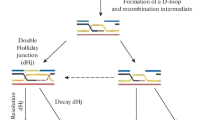
Meiotic DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) are associated with recombination hot spots in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae and are believed to initiate the process of recombination. Until now, meiosis-induced breaks have not been shown to occur regularly in other organisms. Here we show, by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of DNA, that meiotic DSBs occur transiently in all three chromosomes of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. In a repair defective mutant, carrying a mutation in the RecA homolog gene rhp51, meiotic DSBs accumulate. In contrast to expectation from the genetic map of S. pombe, however, many chromosomal DNA molecules remain unbroken during meiosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 27 February 2000 / 12 March 2000
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zenvirth, D., Simchen, G. Meiotic double-strand breaks in Schizosaccharomyces pombe . Curr Genet 38, 33–38 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002940000126
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002940000126