Abstract
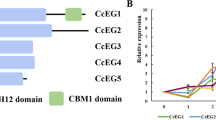
The plant cell cuticle is the first obstacle for penetration of the host by plant pathogens. To breach this barrier, most pathogenic fungi employ a complex assortment of cell wall-degrading enzymes including carbohydrate esterases, glycoside hydrolases, and polysaccharide lyases. We characterized the full complement of carbohydrate esterase-coding genes in three Phytophthora species and analyzed the expression of cutinase in vitro and in planta; we also determined the cutinase allele distribution in multiple isolates of P. infestans. Our investigations revealed that there are 49, 21, and 37 esterase homologs in the P. infestans, P. ramorum, and P. sojae genomes, respectively, with a considerable number predicted to be extracellular. Four cutinase gene copies were found in both the P. infestans and P. ramorum genomes, while 16 copies were found in P. sojae. Transcriptional analyses of cutinase in P. infestans revealed that its expression level during infection is significantly upregulated at all time points compared to that of the same gene in mycelium grown in vitro. Expression achieves maximum values at 15 hpi, declining at subsequent time points. These results may suggest, therefore, that cutinase most likely plays a role in P. infestans pathogenicity.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
References
Avrova AO, Boevink PC, Young V, Grenville-Briggs LJ, van West P, Birch PR, Whisson SC (2008) A novel Phytophthora infestans haustorium-specific membrane protein is required for infection of potato. Cell Microbiol 10:2271–2284
Belbahri L, Calmin G, Mauch F, Andersson JO (2008) Evolution of the cutinase gene family: evidence for lateral gene transfer of a candidate Phytophthora virulence factor. Gene 408:1–8
Blair JE, Coffey MD, Park SY, Geiser DM, Kang S (2008) A multi-locus phylogeny for Phytophthora utilizing markers derived from complete genome sequences. Fungal Genet Biol 45:266–277
Caten CE, Jinks JL (1968) Spontaneous variability of single isolates of P. infestans. I. Cultural variation. Can J Bot 46:329–348
Cooke DE, Drenth A, Duncan JM, Wagels G, Brasier CM (2000) A molecular phylogeny of Phytophthora and related oomycetes. Fungal Genet Biol 30:17–32
Coutinho PM, Henrissat B (1999) Carbohydrate-active enzymes: an integrated database approach. In: Gilbert HJ, Davies G, Henrissat B, Svensson B (eds) Recent advances in carbohydrate bioengineering. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge, pp 3–12
Crowhurst RN, Binnie SJ, Bowen JK, Hawthorne BT, Plummer KM, Rees-George J, Rikkerink EH, Templeton MD (1997) Effect of disruption of a cutinase gene (cutA) on virulence and tissue specificity of Fusarium solani f. sp. cucurbitae race 2 toward Cucurbita maxima and C. moschata. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 10:355–368
Davies KA, De Lorono I, Foster SJ, Li D, Johnstone K, Ashby AM (2000) Evidence for a role of cutinase in pathogenicity of Pyrenopeziza brassicae on brassicas. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 57:63–75
Deising H, Nicholson R, Haug M, Howard R, Mendgen K (1992) Adhesion pad formation and the involvement of cutinase and esterases in the attachement of uredospores to the host cuticle. Plant Cell 4:1101–1111
Dickman M, Podila G (1989) Insertion of cutinase gene into a wound pathogen enables it to infect intact host. Nature 342:446–448
Doss R (1999) Composition and enzymatic activity of the extracellular matrix secreted by germlings of Botrytis cinerea. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:404–408
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Francis S, Dewey F, Gurr S (1996) The role of cutinase in germling development and infection by Erysiphe graminis f.sp. hordei. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 49:201–211
Fry W (2008) Phytophthora infestans: the plant (and R gene) destroyer. Mol Plant Pathol 9:385–402
Grenville-Briggs LJ, Anderson VL, Fugelstad J, Avrova AO, Bouzenzana J, Williams A, Wawra S, Whisson SC, Birch PR, Bulone V, van West P (2008) Cellulose synthesis in Phytophthora infestans is required for normal appressorium formation and successful infection of potato. Plant Cell 20:720–738
Haas BJ, Kamoun S, Zody MC, Jiang RH, Handsaker RE, Cano LM, Grabherr M, Kodira CD, Raffaele S, Torto-Alalibo T, Bozkurt TO, Ah-Fong AM, Alvarado L, Anderson VL, Armstrong MR, Avrova A, Baxter L, Beynon J, Boevink PC, Bollmann SR, Bos JI, Bulone V, Cai G, Cakir C, Carrington JC, Chawner M, Conti L, Costanzo S, Ewan R, Fahlgren N, Fischbach MA, Fugelstad J, Gilroy EM, Gnerre S, Green PJ, Grenville-Briggs LJ, Griffith J, Grunwald NJ, Horn K, Horner NR, Hu CH, Huitema E, Jeong DH, Jones AM, Jones JD, Jones RW, Karlsson EK, Kunjeti SG, Lamour K, Liu Z, Ma L, Maclean D, Chibucos MC, McDonald H, McWalters J, Meijer HJ, Morgan W, Morris PF, Munro CA, O’Neill K, Ospina-Giraldo M, Pinzon A, Pritchard L, Ramsahoye B, Ren Q, Restrepo S, Roy S, Sadanandom A, Savidor A, Schornack S, Schwartz DC, Schumann UD, Schwessinger B, Seyer L, Sharpe T, Silvar C, Song J, Studholme DJ, Sykes S, Thines M, van de Vondervoort PJ, Phuntumart V, Wawra S, Weide R, Win J, Young C, Zhou S, Fry W, Meyers BC, van West P, Ristaino J, Govers F, Birch PR, Whisson SC, Judelson HS, Nusbaum C (2009) Genome sequence and analysis of the Irish potato famine pathogen Phytophthora infestans. Nature 461:393–398
Haverkort AJ, Boonekamp PM, Hutten R, Jacobsen E, Lotz LAP, Kessel GJT, Visser RGF, van der Vossen EAG (2008) Societal costs of late blight in potato and prospects of durable resistance through cisgenic modification. Potato Res 51:47–57
Jiang RH, Tyler BM, Govers F (2006) Comparative analysis of Phytophthora genes encoding secreted proteins reveals conserved synteny and lineage-specific gene duplications and deletions. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 19:1311–1321
Kamoun S (2003) Molecular genetics of pathogenic oomycetes. Eukaryot Cell 2:191–199
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Li D, Ashby A, Johnstone K (2003) Molecular evidence that the extracellular cutinase Pbc1 is required for pathogenicity of Pyrenopeziza brassicae on oilseed rape. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 16:545–552
Money NP, Davis CM, Ravishankar JP (2004) Biomechanical evidence for convergent evolution of the invasive growth process among fungi and oomycete water molds. Fungal Genet Biol 41:872–876
Moreau RA, Seibles TS (1985) Production of extracellular enzymes by germinating cysts of Phytophthora infestans. Can J Bot 63:1811–1816
Muñoz C, Bailey A (1998) A cutinase-encoding gene from Phytophthora capsici isolated by differential-display RT-PCR. Curr Genet 33:225–230
Nawrath C (2002) The biopolymers cutin and suberin. Planta 174:127–138
Ospina-Giraldo MD, Jones RW (2003) Characterization of the glucose-6-phosphate isomerase gene in Phytophthora infestans reveals the presence of multiple alleles. Fungal Genet Biol 40:197–206
Rogers L, Flaishman M, Kolattukudy PE (1994) Cutinase gene disruption in Fusarium solani f. sp. pisi decreases its virulence on pea. Plant Cell 6:935–945
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sambrook JJ, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Soliday CL, Dickman MB, Kolattukudy PE (1989) Structure of the cutinase gene and detection of promoter activity in the 5′-flanking region by fungal transformation. J Bacteriol 171:1942–1951
Stahl D, Schafer W (1992) Cutinase is not required for fungal pathogenicity on pea. Plant Cell 4:621–629
Sweigard J, Chumley F, Valent B (1992) Disruption of a Magnaporthe grisea cutinase gene. Mol Gen Genet 232:183–190
Tang H, Bowers JE, Wang X, Ming R, Alam M, Paterson AH (2008) Synteny and collinearity in plant genomes. Science 320:486–488
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Tyler BM, Tripathy S, Zhang X, Dehal P, Jiang RH, Aerts A, Arredondo FD, Baxter L, Bensasson D, Beynon JL, Chapman J, Damasceno CM, Dorrance AE, Dou D, Dickerman AW, Dubchak IL, Garbelotto M, Gijzen M, Gordon SG, Govers F, Grunwald NJ, Huang W, Ivors KL, Jones RW, Kamoun S, Krampis K, Lamour KH, Lee MK, McDonald WH, Medina M, Meijer HJ, Nordberg EK, Maclean DJ, Ospina-Giraldo MD, Morris PF, Phuntumart V, Putnam NH, Rash S, Rose JK, Sakihama Y, Salamov AA, Savidor A, Scheuring CF, Smith BM, Sobral BW, Terry A, Torto-Alalibo TA, Win J, Xu Z, Zhang H, Grigoriev IV, Rokhsar DS, Boore JL (2006) Phytophthora genome sequences uncover evolutionary origins and mechanisms of pathogenesis. Science 313:1261–1266
van der Vlugt-Bergmans C, Wagemakers C, van Kan J (1997) Cloning and expression of the cutinase A gene of Botrytis cinerea. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 10:21–29
van Kan J, van’t Klooster J, Wagemakers C, Dees D, van der Vlugt-Bergmans C (1997) Cutinase A of Botrytis cinerea is expressed, but not essential, during penetration of gerbera and tomato. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 10:30–38
Yao C, Koller W (1995) Diversity of cutinases from plant pathogenic fungi: different cutinases are expressed during saprophytic and pathogenic stages of Alternaria brassicicola. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 8:122–130
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude for helpful comments and suggestions, and for allowing us the use of unpublished data and/or software, to Jeffrey Boore, Brian Hass, and Richard W. Jones. This research was funded by Lafayette’s EXCEL program and Lafayette’s Biology Department.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by B. Cormack.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ospina-Giraldo, M.D., McWalters, J. & Seyer, L. Structural and functional profile of the carbohydrate esterase gene complement in Phytophthora infestans . Curr Genet 56, 495–506 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-010-0317-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-010-0317-z