Abstract
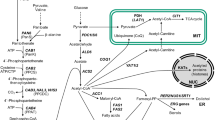
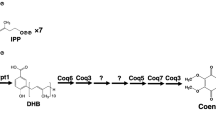
Coenzyme A (CoA) is a ubiquitous cofactor required for numerous enzymatic carbon group transfer reactions. CoA biosynthesis requires contributions from various amino acids with pantothenate as an important intermediate which can be imported from the medium or synthesized de novo. Investigating function and expression of structural genes involved in CoA biosynthesis of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, we show that deletion of ECM31 and PAN6 results in mutants requiring pantothenate while loss of PAN5 (related to panE from E. coli) still allows prototrophic growth. A temperature-sensitive mutant defective for fatty acid synthase activity could be functionally complemented by a gene significantly similar to eukaryotic pantothenate kinases (YDR531W). Enzymatic studies and heterologous complementation of this mutation by bacterial and mammalian genes showed that YDR531W encodes a genuine pantothenate kinase (new gene designation: CAB1, “coenzyme A biosynthesis”). A G351S missense mutation within CAB1 was identified to cause the conditional phenotype of the mutant initially studied. Similar to CAB1, genes YIL083C, YKL088W, YGR277C and YDR106C responsible for late CoA biosynthesis turned out as essential. Null mutants could be complemented by their bacterial counterparts coaBC, coaD and coaE, respectively. Comparative expression analyses showed that some CoA biosynthetic genes are weakly de-repressed with ethanol as a carbon source compared with glucose.




Similar content being viewed by others

References
Ben-Aroya S, Coombes C, Kwok T, O’Donnell KA, Boeke JD, Hieter P (2008) Toward a comprehensive temperature-sensitive mutant repository of the essential genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell 30:248–258
Bucovaz ET, Tarnowski SJ, Morrison WC, Macleod RM, Morrison JC, Sobhy CM, Rhoades JL, Fryer JE, Wakim JM, Whybrew WD (1980) Coenzyme A-synthesizing protein complex of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biochem 30:7–26
Bucovaz ET, Macleod RM, Morrison JC, Whybrew WD (1997) The coenzyme A-synthesizing protein complex and its proposed role in CoA biosynthesis in bakers’ yeast. Biochimie 79:787–798
Calder RB, Williams RS, Ramaswamy G, Rock CO, Campbell E, Unkles SE, Kinghorn JR, Jackowski S (1999) Cloning and characterization of a eukaryotic pantothenate kinase gene (panK) from Aspergillus nidulans. J Biol Chem 274:2014–2020
Chen M, Hancock LC, Lopes JM (2007) Transcriptional regulation of yeast phospholipid biosynthetic genes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1771:310–321
Cronan JE Jr, Littel KJ, Jackowski S (1982) Genetic and biochemical analyses of pantothenate biosynthesis in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol 149:916–922
Daugherty M, Polanuyer B, Farrell M, Scholle M, Lykidis A, de Crécy-Lagard V, Osterman A (2002) Complete reconstitution of the human coenzyme A biosynthetic pathway via comparative genomics. J Biol Chem 277:21431–21439
de La Sierra-Gallay IL, Collinet B, Graille M, Quevillon-Cheruel S, Liger D, Minard P, Blondeau K, Henckes G, Aufrere R, Leulliot N, Zhou CZ, Sorel I, Ferrer JL, Poupon A, Janin J, van Tilbeurgh H (2004) Crystal structure of the YGR205w protein from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: close structural resemblance to E. coli pantothenate kinase. Proteins 54:776–783
DeRisi JL, Iyer VR, Brown PO (1997) Exploring the metabolic and genetic control of gene expression on a genomic scale. Science 278:680–686
Fichtlscherer F, Wellein C, Mittag M, Schweizer E (2000) A novel function of yeast fatty acid synthase. Subunit α is capable of self-pantetheinylation. Eur J Biochem 267:2666–2671
Gasch AP, Spellman PT, Kao CM, Carmel-Harel O, Eisen MB, Storz G, Botstein D, Brown PO (2000) Genomic expression programs in the response of yeast cells to environmental changes. Mol Biol Cell 11:4241–4257
Giaever G, Chu AM, Ni L, Connelly C, Riles L, Véronneau S, Dow S, Lucau-Danila A, Anderson K, André B, Arkin AP, Astromoff A, El-Bakkoury M, Bangham R, Benito R, Brachat S, Campanaro S, Curtiss M, Davis K, Deutschbauer A, Entian KD, Flaherty P, Foury F, Garfinkel DJ, Gerstein M, Gotte D, Güldener U, Hegemann JH, Hempel S, Herman Z, Jaramillo DF, Kelly DE, Kelly SL, Kötter P, LaBonte D, Lamb DC, Lan N, Liang H, Liao H, Liu L, Luo C, Lussier M, Mao R, Menard P, Ooi SL, Revuelta JL, Roberts CJ, Rose M, Ross-Macdonald P, Scherens B, Schimmack G, Shafer B, Shoemaker DD, Sookhai-Mahadeo S, Storms RK, Strathern JN, Valle G, Voet M, Volckaert G, Wang CY, Ward TR, Wilhelmy J, Winzeler EA, Yang Y, Yen G, Youngman E, Yu K, Bussey H, Boeke JD, Snyder M, Philippsen P, Davis RW, Johnston M (2002) Functional profiling of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome. Nature 418:387–391
Gietz RD, Sugino A (1988) New yeast-Escherichia coli shuttle vectors constructed with in vitro mutagenized yeast genes lacking six-base pair restriction sites. Gene 74:527–534
Hong BS, Senisterra G, Rabeh WM, Vedadi M, Leonardi R, Zhang YM, Rock CO, Jackowski S, Park HW (2007) Crystal structures of human pantothenate kinases Insights into allosteric regulation and mutations linked to a neurodegeneration disorder. J Biol Chem 282:27984–27993
Leonardi R, Zhang YM, Rock CO, Jackowski S (2005) Coenzyme A: back in action. Prog Lipid Res 44:125–153
Mumberg D, Müller R, Funk M (1994) Regulatable promoters of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: comparison of transcriptional activity and their use for heterologous expression. Nucleic Acids Res 22:5767–5768
Myers AM, Tzagoloff A, Kinney DM, Lusty CJ (1986) Yeast shuttle and integrative vectors with multiple cloning sites suitable for construction of lacZ fusions. Gene 45:299–310
Nosaka K, Onozuka M, Konno H, Kawasaki Y, Nishimura H, Sano M, Akaji K (2005) Genetic regulation mediated by thiamin pyrophosphate-binding motif in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Microbiol 58:467–479
Rock CO, Calder RB, Karim MA, Jackowski S (2000) Pantothenate kinase regulation of the intracellular concentration of coenzyme A. J Biol Chem 275:1377–1383
Roth S, Kumme J, Schüller HJ (2004) Transcriptional activators Cat8 and Sip4 discriminate between sequence variants of the carbon source-responsive promoter element in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet 45:121–128
Ruiz A, Muñoz I, Serrano R, González A, Simón E, Ariño J (2004) Functional characterization of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae VHS3 gene: a regulatory subunit of the Ppz1 protein phosphatase with novel, phosphatase-unrelated functions. J Biol Chem 279:34421–34430
Schüller HJ (2003) Transcriptional control of nonfermentative metabolism in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet 43:139–160
Schüller HJ, Hahn A, Tröster F, Schütz A, Schweizer E (1992) Coordinate genetic control of yeast fatty acid synthetase genes FAS1 and FAS2 by an upstream activation site common to genes involved in the membrane lipid biosynthesis. EMBO J 11:107–114
Schwank S, Ebbert R, Rautenstrauss K, Schweizer E, Schüller HJ (1995) Yeast transcriptional activator INO2 interacts as an Ino2p/Ino4p basic helix-loop-helix heteromeric complex with the inositol/choline-responsive element necessary for expression of phospholipid biosynthetic genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res 23:230–237
Schweizer E, Kniep B, Castorph H, Holzner U (1973) Pantetheine-free mutants of the yeast fatty-acid-synthetase complex. Eur J Biochem 39:353–362
Stolz J, Sauer N (1999) The fenpropimorph resistance gene FEN2 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a plasma membrane H+-pantothenate symporter. J Biol Chem 274:18747–18752
Stolz J, Caspari T, Carr AM, Sauer N (2004) Cell division defects of Schizosaccharomyces pombe liz1 - mutants are caused by defects in pantothenate uptake. Eukaryot Cell 3:406–412
Vallari DS, Rock CO (1985) Isolation and characterization of Escherichia coli pantothenate permease (panF) mutants. J Bacteriol 164:136–142
Vallari DS, Jackowski S, Rock CO (1987) Regulation of pantothenate kinase by coenzyme A and its thioesters. J Biol Chem 262:2468–2471
White WH, Gunyuzlu PL, Toyn JH (2001) Saccharomyces cerevisiae is capable of de novo pantothenic acid biosynthesis involving a novel pathway of β-alanine production from spermine. J Biol Chem 276:10794–10800
White WH, Skatrud PL, Xue Z, Toyn JH (2003) Specialization of function among aldehyde dehydrogenases: the ALD2 and ALD3 genes are required for β-alanine biosynthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 163:69–77
Winzeler EA, Shoemaker DD, Astromoff A, Liang H, Anderson K, Andre B, Bangham R, Benito R, Boeke JD, Bussey H, Chu AM, Connelly C, Davis K, Dietrich F, Dow SW, El Bakkoury M, Foury F, Friend SH, Gentalen E, Giaever G, Hegemann JH, Jones T, Laub M, Liao H, Liebundguth N, Lockhart DJ, Lucau-Danila A, Lussier M, M’Rabet N, Menard P, Mittmann M, Pai C, Rebischung C, Revuelta JL, Riles L, Roberts CJ, Ross-MacDonald P, Scherens B, Snyder M, Sookhai-Mahadeo S, Storms RK, Véronneau S, Voet M, Volckaert G, Ward TR, Wysocki R, Yen GS, Yu K, Zimmermann K, Philippsen P, Johnston M, Davis RW (1999) Functional characterization of the S cerevisiae genome by gene deletion and parallel analysis. Science 285:901–906
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Eckhart Schweizer (Erlangen) for kindly providing the cab1 ts mutant strain (initially designated ts6629) and Sonja Burghardt, Karola Hahn, Felix Kliewe, Kati Landsberg and Jan Witthöft for support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by K. Breunig.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olzhausen, J., Schübbe, S. & Schüller, HJ. Genetic analysis of coenzyme A biosynthesis in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae: identification of a conditional mutation in the pantothenate kinase gene CAB1 . Curr Genet 55, 163–173 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-009-0234-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-009-0234-1