Abstract
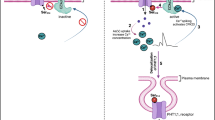
Three groups of fungicides (phenylpyrroles, dicarboximides, aromatic hydrocarbons) are effective against filamentous fungi. The target of these fungicides is the osmotic stress signal transduction pathway, which is dependent on the Os-1 family of two-component histidine kinases. These fungicides usually have no fungicidal effect on the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In this report, we found that expression of Hik1, an Os-1 orthologue from rice blast fungus, can confer fungicide-sensitivity to yeast. This requires both the histidine kinase and the response regulator domains of Hik1. Analysis of yeast mutants indicated that this sensitivity is Hog1- and Ssk1-dependent. In addition, our studies revealed an interaction between Hik1 and Ypd1. These observations suggest that Hik1 is a direct target of the fungicides or is a mediator of fungicide action and that the fungicidal effect is transmitted to the Hog1 pathway via Ypd1.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alex LA, Borkovich KA, Simon MI (1996) Hyphal development in Neurospora crassa: involvement of a two-component histidine kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:3416–3421
Alex LA, Korch C, Selitrennikoff CP, Simon MI (1998) COS1, a two-component histidine kinase that is involved in hyphal development in the opportunistic pathogen Candida albicans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:7069–7073
Catlett NL, Yoder OC, Turgeon BG (2003) Whole-genome analysis of two-component signal transduction genes in fungal pathogens. Eukaryot Cell 2:1151–1161
Cui W, Beever RE, Parkes SL, Weeds PL, Templeton MD (2002) An osmosensing histidine kinase mediates dicarboximide fungicide resistance in Botryotinia fuckeliana (Botrytis cinerea). Fungal Genet Biol 36:187–198
Davenport KR, Sohaskey M, Kamada Y, Levin DE, Gustin MC (1995) A second osmosensing signal transduction pathway in yeast. Hypotonic shock activates the PKC1 protein kinase-regulated cell integrity pathway. J Biol Chem 270:30157–30161
Dixon KP, Xu JR, Smirnoff N, Talbot NJ (1999) Independent signaling pathways regulate cellular turgor during hyperosmotic stress and appressorium-mediated plant infection by Magnaporthe grisea. Plant Cell 11:2045–2058
Dry IB, Yuan KH, Hutton DG (2004) Dicarboximide resistance in field isolates of Alternaria alternata is mediated by a mutation in a two-component histidine kinase gene. Fungal Genet Biol 41:102–108
Fujimura M, Ochiai N, Ichiishi A, Usami R, Horikoshi K, Yamaguchi I (2000) Sensitivity to phenylpyrrole fungicides and abnormal glycerol accumulation in os and cut mutant strains of Neurospora crassa. J Pestic Sci 25:31–36
Fujimura M, Ochiai N, Oshima M, Motoyama T, Ichiishi A, Usami R, Horikoshi K, Yamaguchi I (2003) Putative homologs of SSK22 MAPKK kinase and PBS2 MAPK kinase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encoded by os-4 and os-5 genes for osmotic sensitivity and fungicide resistance in Neurospora crassa. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 67:186–191
Furukawa K, Katsuno Y, Urao T, Yabe T, Yamada-Okabe T, Yamada-Okabe H, Yamagata Y, Abe K, Nakajima T (2002) Isolation and functional analysis of a gene, tcsB, encoding a transmembrane hybrid-type histidine kinase from Aspergillus nidulans. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:5304–5310
Inoue T, Higuchi M, Hashimoto Y, Seki M, Kobayashi M, Kato T, Tabata S, Shinozaki K, Kakimoto T (2001) Identification of CRE1 as a cytokinin receptor from Arabidopsis. Nature 409:1060–1063
Ito H, Fukuda Y, Murata K, Kimura K (1983) Transformation of intact yeast cells with alkali cations. J Bacteriol 96:163–168
Maeda T, Takekawa M, Saito H (1995) Activation of yeast PBS2 MAPKK by MAPKKKs or by binding of an SH3-containing osmosensor. Science 269:554–558
Miller TK, Renault S, Selitrennikoff CP (2002) Molecular dissection of alleles of the osmotic-1 locus of Neurospora crassa. Fungal Genet Biol 35:147–155
Motoyama T, Imanishi K, Yamaguchi I (1998) cDNA cloning, expression, and mutagenesis of scytalone dehydratase needed for pathogenicity of the rice blast fungus, Pyricularia oryzae. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 62:564–566
Motoyama T, Kadokura K, Ohira T, Ichiishi A, Fujimura M, Yamaguchi I, Kudo T (2005) A two-component histidine kinase of the rice blast fungus is involved in osmotic stress response and fungicide action. Fungal Genet Biol 42:200–212
Nagahashi S, Mio T, Ono N, Yamada-Okabe T, Arisawa M, Bussey H, Yamada-Okabe H (1998) Isolation of CaSLN1 and CaNIK1, the genes for osmosensing histidine kinase homologues, from the pathogenic fungus Candida albicans. Microbiology 144:425–432
Ochiai N, Fujimura M, Motoyama T, Ichiishi A, Usami R, Horikoshi K, Yamaguchi I (2001) Characterization of mutations in the two-component histidine kinase gene that confer fludioxonil resistance and osmotic sensitivity in the os-1 mutants of Neurospora crassa. Pestic Manage Sci 57:437–442
Ochiai N, Fujimura M, Oshima M, Motoyama T, Ichiishi A, Yamada-Okabe H, Yamaguchi I (2002) Effects of iprodione and fludioxonil on glycerol synthesis and hyphal development in Candida albicans. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 66:2209–2215
Oshima M, Fujimura M, Banno S, Hashimoto C, Motoyama T, Ichiishi A, Yamaguchi I (2002) A point mutation in the two-component histidine kinase BcOS-1 gene confers dicarboximide resistance in field isolates of Botrytis cinerea. Phytopathology 92:75–80
Ota IM, Varshavsky A (1993) A yeast protein similar to bacterial two-component regulators. Science 262:566–569
Pillonel C, Meyer T (1997) Effect of phenylpyrroles on glycerol accumulation and protein kinase activity of Neurospora crassa. Pestic Sci 49:229–236
Posas F, Wurgler-Murphy SM, Maeda T, Witten EA, Thai TC, Saito H (1996) Yeast HOG1 MAP kinase cascade is regulated by a multistep phosphorelay mechanism in the SLN1–YPD1–SSK1 “two-component” osmosensor. Cell 86:865–875
Pott GB, Miller TK, Bartlett JA, Palas JS, Selitrennikoff CP (2000) The isolation of FOS-1, a gene encoding a putative two-component histidine kinase from Aspergillus fumigatus. Fungal Genet Biol 31:55–67
Ramesh MA, Laidlaw RD, Durrenberger F, Orth AB, Kronstad JW (2001) The cAMP signal transduction pathway mediates resistance to dicarboximide and aromatic hydrocarbon fungicides in Ustilago maydis. Fungal Genet Biol 32:183–193
Reiser V, Raitt DC, Saito H (2003) Yeast osmosensor Sln1 and plant cytokinin receptor Cre1 respond to changes in turgor pressure. J Cell Biol 161:1035–1040
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Schumacher MM, Enderlin CS, Selitrennikoff CP (1997) The osmotic-1 locus of Neurospora crassa encodes a putative histidine kinase similar to osmosensors of bacteria and yeast. Curr Microbiol 34:340–347
Urao T, Yakubov B, Satoh R, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Seki M, Hirayama T, Shinozaki K (1999) A transmembrane hybrid-type histidine kinase in Arabidopsis functions as an osmosensor. Plant Cell 11:1743–1754
West AH, Stock AM (2001) Histidine kinases and response regulator proteins in two-component signaling systems. Trends Biochem Sci 26:369–376
Yoshimi A, Tsuda M, Tanaka C (2004) Cloning and characterization of the histidine kinase gene Dic1 from Cochliobolus heterostrophus that confers dicarboximide resistance and osmotic adaptation. Mol Genet Genomics 271:228–236
Zhang Y, Lamm R, Pillonel C, Lam S, Xu JR (2002) Osmoregulation and fungicide resistance: the Neurospora crassa os-2 gene encodes a HOG1 mitogen-activated protein kinase homologue. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:532–538
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants for the Bio-architect and the Ecomolecular Science Research Program of RIKEN. This work was also supported by MEXT.KAKENHI (15780063).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Motoyama, T., Ohira, T., Kadokura, K. et al. An Os-1 family histidine kinase from a filamentous fungus confers fungicide-sensitivity to yeast. Curr Genet 47, 298–306 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-005-0572-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-005-0572-6