Abstract.
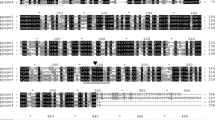
A gene, xyl5, was identified from the tomato vascular wilt fungus Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. lycopersici, whose predicted amino acid sequence shows significant homology with family 11 xylanases. Expression of xyl5 was detected during growth both on xylan and cellulose substrates as carbon sources and on tomato vascular tissue. RT-PCR analysis revealed the presence of two different transcript sizes, resulting from differential splicing of the third intron. The 3′-untranslated region of the xyl5 transcript contained a region of homology to cellulose-binding domains, suggesting that such a domain may have been part of an ancestral XYL5 version. As shown by RT-PCR, xyl5 is expressed by F. oxysporum exclusively during the initial stages of infection in tomato roots. Targeted inactivation of xyl5 had no detectable effect on virulence.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gómez-Gómez, E., Roncero, I.M., Di Pietro, A. et al. Molecular characterization of a novel endo-β-1,4-xylanase gene from the vascular wilt fungus Fusarium oxysporum. Curr Genet 40, 268–275 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-001-0260-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-001-0260-0