Abstract
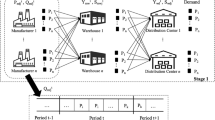
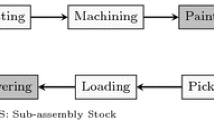
In the fast moving consumer goods industry there is an ongoing trend towards an increased product variety and shorter replenishment cycle times. Hence, manufacturers seek a better coordination of production and distribution activities. In this paper, a so-called block planning approach is presented which establishes cyclical production patterns based on the definition of setup families. For the delivery of final goods from the plants to distribution centres two transportation modes are considered, full truckload and less than truckload. The proposed mixed-integer linear optimization model minimizes total production and transportation costs. Numerical results demonstrate the practical applicability of the proposed block planning approach. In particular, a rigid and a flexible block planning approach are compared which differ by their degree of flexibility in the scheduling of the production lots.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahumada O, Villalobos JR (2009) Application of planning models in the agri-food supply chain: a review. Eur J Oper Res 196: 1–20
Akkerman R, van Donk DP (2007) Product prioritization in a two-stage food production system with intermediate storage. Int J Prod Econ 108: 43–53
Allahverdi A, Ng CT, Cheng TCE, Kovalyov MY (2008) A survey of scheduling problems with setup times and costs. Eur J Oper Res 187: 985–1032
Bilgen B, Ozkarahan I (2004) Strategic, tactical and operational production-distribution models: a review. Int J Technol Manag 28: 151–171
Bilgen B, Ozkarahan I (2007) A mixed-integer linear programming model for bulk grain blending and shipping. Int J Prod Econ 107:555–571
Blömer F, Günther HO (2000) LP-based heuristics for scheduling chemical batch processes. Int J Prod Res 38: 1029–1051
Boudia M, Louly MAO, Prins C (2008) Fast heuristics for a combined production planning and vehicle routing problem. Prod Plan Control 19: 85–96
Buschkühl L, Sahling F, Helber S, Tempelmeier H (2009) Dynamic capacitated lot-sizing problems: a classification and review of solution approaches. OR Spectr. doi:10.1007/s00291-008-0150-7 (in press)
Chandra P, Fisher ML (1994) Coordination of production and distribution planning. Eur J Oper Res 72: 503–517
Christou IT, Lagodimos AG, Lycopulou D (2007) Hierarchical production planning for multi-product lines in the beverage industry. Prod Plan Control 18: 367–376
Clark AR (2005) Rolling horizon heuristics for production planning and setup scheduling with backlogs and error-prone demand forecasts. Prod Plan Control 16: 81–97
Crainic TG (2000) Service network design in freight transportation. Eur J Oper Res 122: 272–288
de Matta R, Miller T (2004) Production and inter-facility transportation scheduling for a process industry. Eur J Oper Res 158: 72–88
Erengüç ŞS, Simpson NC, Vakharia AJ (1999) Integrated production/distribution planning in supply chains: An invited review. Eur J Oper Res 115: 219–236
Ferreira D, Morabito R, Rangel S (2009) Solution approaches for the soft drink integrated production lot sizing and scheduling problem. Eur J Oper Res 196: 697–706
Floudas CA, Lin X (2004) Continuous-time versus discrete-time approaches for scheduling of chemical processes: a review. Comput Chem Eng 28: 2109–2129
Floudas CA, Lin X (2005) Mixed integer linear programming in process scheduling: Modeling, algorithms, and applications. Ann Oper Res 139: 131–162
Fumero F, Vercellis C (1999) Synchronized development of production, inventory, and distribution schedules. Transp Sci 33: 330–340
Grunow M, Günther HO, Lehmann M (2002) Campaign planning for multi-stage batch processes in the chemical industry. OR Spectr 24: 281–314
Grunow M, Günther HO, Yang G (2003) Plant coordination in pharmaceutics supply networks. OR Spectr 25: 109–141
Grunow M, Günther HO, Westinner R (2007) Supply optimization for the production of raw sugar. Int J Prod Econ 110: 224–239
Günther HO (2005) Supply chain management and advanced planning systems. In: Günther HO, Mattfeld D, Suhl L (eds) Supply Chain Management und Logistik: Optimierung, Simulation, Decision Support. Physica, Heidelberg, pp 3–40
Günther HO, Seiler T (2008) Transportation planning in consumer goods supply chains. In: Lo HP, Leung SCH, Tam SML (eds) Transportation and management science. Hong Kong Society for Transportation Studies, Hong Kong, pp 17–26
Günther HO, Grunow M, Neuhaus U (2006) Realizing block planning concepts in make-and-pack production using MILP modelling and SAP APO©. Int J Prod Res 44: 3711–3726
Jans R, Degraeve Z (2008) Modeling industrial lot sizing problems: a review. Int J Prod Res 46: 1619–1643
Jordan C, Drexl A (1998) Discrete lotsizing and scheduling by batch sequencing. Manag Sci 44: 698–713
Karabuk S (2007) Modeling and optimizing transportation decisions in a manufacturing supply chain. Transp Res E 43: 321–337
Karimi B, Fatemi Ghomi SMT, Wilson JM (2003) The capacitated lot sizing problem: a review of models and algorithms. Omega 31: 365–378
Kreipl S, Pinedo M (2004) Planning and scheduling in supply chains: an overview of issues in practice. Prod Oper Manag 13: 77–92
Lei L, Liu S, Ruszczynski A, Park S (2006) On the integrated production, inventory, and distribution routing problem. IIE Trans 38: 955–970
Lütke Entrup M (2005) Advanced Planning in Fresh Food Industries: Integrating Shelf Life into Production Planning. Physica, Heidelberg
Lütke Entrup M, Günther HO, Van Beek P, Grunow M, Seiler T (2005) Mixed integer linear programming approaches to shelf-life-integrated planning and scheduling in yoghurt production. Int J Prod Res 43: 5071–5100
Mendéz CA, Cerdá J (2002) An MILP-based approach to the short term scheduling of make-and-pack continuous production plants. OR Spectr 24: 403–429
Özdamar L, Yazgaç T (1999) A hierarchical planning approach for a production-distribution system. Int J Prod Res 37: 3759–3772
Park YB (2005) An integrated approach for production and distribution planning in supply chain management. Int J Prod Res 43: 1205–1224
Quadt D, Kuhn H (2008) Capacitated lot-sizing with extensions: a review. 4OR 6:61–83
Rizk N, Martel A, d’Amours S (2006) Multi-item dynamic production-distribution planning in process industries with divergent finishing stages. Comput Oper Res 33: 3600–3623
Robinson P, Narayanan A, Sahin F (2009) Coordinated deterministic dynamic demand lot-sizing problem: A review of models and algorithms. Omega 37: 3–15
Sarmiento AM, Nagi R (1999) A review of integrated analysis of production-distribution systems. IIE Trans 31: 1061–1074
Soman CA, van Donk DP, Gaalman GJC (2007) Capacitated planning and scheduling for combined make-to-order and make-to-stock production in the food industry: An illustrative case study. Int J Prod Econ 108: 191–199
Stadtler H, Kilger C (2008) Supply chain management and advanced planning, 4th edn. Springer, Berlin
Van der Vorst JGAJ, Beulens ADM, van Beek P (2000) Modelling and simulating multi-echelon food systems. Eur J Oper Res 122: 354–366
Wagner M, Meyr H (2008) Food and beverages. In: Stadtler H, Kilger C (eds) Supply chain management and advanced planning, 4th edn. Springer, Berlin, pp 445–462
Wang X, Li D, Brien CO (2009) Optimisation of traceability and operations planning: an integrated model for perishable food production. Int J Prod Res 47: 2865–2886
Wieberneit N (2008) Service network design for freight transportation: a review. OR Spectr 30: 77–112
Zhu X, Wilhelm WE (2006) Scheduling and lot sizing with sequence-dependent setup: a literature review. IIE Trans 38: 987–1007
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bilgen, B., Günther, HO. Integrated production and distribution planning in the fast moving consumer goods industry: a block planning application. OR Spectrum 32, 927–955 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00291-009-0177-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00291-009-0177-4