Abstract
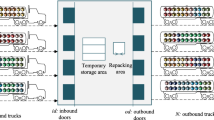
At cross docking terminals, shipments from inbound trucks are unloaded, sorted and moved to dispatch points where they are directly loaded onto outbound trucks for an immediate delivery elsewhere in the distribution system. This warehouse management concept aims at realizing economies in transportation cost by consolidating divergent shipments to full truckloads without requiring excessive inventory at the cross dock. The efficient operation of such a system requires an appropriate coordination of inbound and outbound trucks, e.g. by computerized scheduling procedures.This work introduces a base model for scheduling trucks at cross docking terminals, which relies on a set of simplifying assumptions in order to derive fundamental insights into the underlying problem’s structure, i.e. its complexity, and to develop a building block solution procedure, which might be employed to solve more complex real-world truck scheduling problems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apte UM, Viswanathan S (2000) Effective cross docking for improving distribution efficiencies. Int J Logist Res Appl 3: 291–302
Bartholdi JJ, Gue KR (2000) Reducing labor costs in an LTL crossdocking terminal. Oper Res 48: 823–832
Bartholdi JJ, Gue KR (2004) The best shape for acrossdock. Trans Sci 38: 235–244
Bautista J, Companys R, Corominas A (1996) Heuristics and exact algorithms for solving the Monden problem. Eur J Oper Res 88: 101–113
Bermudez R, Cole MH (2001) A genetic algorithm approach to door assignments in breakbulk terminals. Technical Report MBTC-1102, Mack Blackwell Transportation Center, University of Arkansas, Fayetteville, Arkansas
Boysen N, Fliedner M, Scholl A (2007) Sequencing mixed-model assembly lines to minimize part inventory cost. OR Spectrum, doi:10.1007/s00291-007-0095-2 (to appear)
Campbell JF (1994) A survey of network hub location. Stud Locat Anal 6: 31–49
Carraway RL, Schmidt RL (1991) An improved discrete dynamic programming algorithm for allocating resources among interdependent projects. Manage Sci 37: 1195–1200
Forger G (1995) UPS starts world’s premiere cross-docking operation. Mod Mater Handl 36–38
Garey MR, Johnson DS (1979) A guide to the theory of NP-completeness. Freeman, New York
Gue KR (1999) The effect of trailer scheduling on the layout of freight terminals. Trans Sci 33: 419–428
Johnson SM (1954) Optimal two- and three-stage production schedules with setup times included. Naval Res Logist Q 1: 61–68
Klose A, Drexl A (2005) Facility location models for distribution system design. Eur J Oper Res 162: 4–29
Li Y, Lim A, Rodrigues B (2004) Crossdocking—JIT scheduling with time windows. J Oper Res Soc 55: 1342–1351
McWilliams DL, Stanfield PM, Geiger CD (2005) The parcel hub scheduling problem: A simulation-based solution approach. Comput Ind Eng 49: 393–412
Marsten RE, Morin TL (1978) A hybrid approach to discrete mathematical programming. Math Program 14: 21–40
Morin TL, Marsten RE (1976) Branch-and-bound strategies for dynamic programming. Oper Res 24: 611–627
Oh Y, Hwang H, Cha CN, Lee S (2006) A dock-door assignment problem for the Korean mail distribution center. Comput Ind Eng 51: 288–296
Stalk G, Evans P, Shulman LE (1992) Competing on capabilities: the new role of corporate strategy. Harvard Bus Rev 70(2): 57–69
Tsui LY, Chang C-H (1990) A microcomputer based decision support tool for assigning dock doors in freight yards. Comput Ind Eng 19: 309–312
Tsui LY, Chang C-H (1992) An optimal solution to dock door assignment problem. Comput Ind Eng 23: 283–286
Witt CE (1998) Crossdocking: concepts demand choice. Mater Handl Eng 53(7): 44–49
Yu W, Egbelu PJ (2006) Scheduling of inbound and outbound trucks in cross docking systems with temporary storage. Eur J Oper Res, doi:10.1016/j.ejor.2006.10.047 (to appear)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boysen, N., Fliedner, M. & Scholl, A. Scheduling inbound and outbound trucks at cross docking terminals. OR Spectrum 32, 135–161 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00291-008-0139-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00291-008-0139-2