Abstract
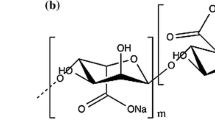
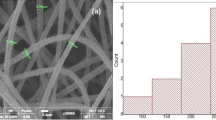
As a kind of novel hydrophobic drug carrier materials, the drug-loaded nanofibers were successfully fabricated using amphiphilic alginate derivative (AAD) and poly (vinyl alcohol) (PVA) by electrospinning method. The AAD was synthesized by amide linkage attachment of octylamine onto the carboxylic group of alginate, which was characterized by the means of elemental analysis, FT-IR spectrometer, 1H NMR spectrometer and fluorescence measurement. Experimental results showed the amidation of alginate was successful, in which the degree of modification was 0.27 and the critical aggregation concentration in 0.15 mol/L aqueous NaCl solution was 0.43 mg/mL. The octyl groups of AAD could effectively make alginate chains flexible and enhance chain entanglements through the hydrophobic interactions between octyl groups. In contrast to sodium alginate (SA)/PVA blend solutions, AAD/PVA blend solutions showed more excellent electrospinnability. Additionally, the different volume ratios of SA or AAD to PVA played an important role in the formation and morphology of the electrospun blend nanofibers. Although the amidation of alginate could not fundamentally alter the spinnability of alginate, the content of alginate in the blend nanofibers was appropriately increased. The new generated drug-loaded AAD/PVA (20/80) blend nanofibers exhibited relatively continuous and uniform nanofibers with the average diameter of 191.72 nm. Compared to the drug-loaded SA/PVA (20/80) blend nanofibers, the drug-loaded AAD/PVA (20/80) blend nanofibers presented a sustained release performance with the slow release of about 76 % λ-cyhalothrin during the initial period of 10 h.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu XL, Liu S, Zhou GY, Huang YB, Xie ZG, Jing XB (2014) Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers for drug delivery applications. J Control Release 185:12–21
Shalumon KT, Anulekha KH, Nair SV, Chennazhi KP, Jayakumar R (2011) Sodium alginate/poly (vinyl alcohol)/nano ZnO composite nanofibers for antibacterial wound dressings. Int J Biol Macromol 49:247–254
Han XJ, Huang ZM, He CL, Liu L, Wu QS (2006) Coaxial electrospinning of PC (shell)/PU (core) composite nanofibers for textile application. Polym Compos 27:381–387
Cui W, Li X, Zhou S, Weng JJ (2007) Investigation on process parameters of electrospinning systems through orthogonal experimental design. Appl Polym Sci 103:3105–3112
Li D, Xia Y (2004) Electrospinning of nanofibers: reinventing the whell. Adv Mater 16:1151–1170
Dersch R, Steinhart M, Boudrio U, Greiner A, Wendorf JH (2005) Nanoprocessing of polymers: applications in medicine, sensorics, catalysis, photonics. Polym Adv Technol 16:276–282
Jayaraman K, Kotaki M, Zhang Y, Mo X, Ramakrishna S (2004) Recent advance in polymer nanofibers. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 4:52–65
Neppalli R, Marega C, Marigo A, Bajgai MP, Kim HK, Causin V (2010) Poly(ε-caprolactone) filled with electrospun nylon fibers: a model for a facile composite fabrication. Eur Polym J 46:968–976
Huang ZM, Zhang YZ, Kotaki M, Ramakrishna S (2003) A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos Sci Technol 63:2223–2253
Ding B, Li C, Miyauchi Y, Kuwaki O, Shiratori S (2006) Formation of novel 2D polymer nanowebs. Nanotechnology 17:3685–3691
Fang DW, Liu Y, Jiang S, Nie J, Ma GP (2011) Effect of intermolecular interaction on electrospinning of sodium alginate. Carbohydr Polym 85:276–279
Bu H, Nguyen GTM, Kjøniksen AL (2006) Effects of the quantity and structure of hydrophobes on the properties of hydrophobically modified alginates in aqueous solutions. Polym Bull 57:563–574
Yang JS, Zhao JY, Fang Y (2008) Calorimetric studies of the interaction between sodium alginate and sodium dodecyl sulfate in dilute solutions at different pH values. Carbohydr Res 343:719–725
George M, Abraham TE (2006) Polyionic hydrocolloids for the intestinal delivery of protein drugs: alginate and chitosan-a review. J Control Release 114:1–14
Hua SB, Ma HZ, Li X, Yang HX, Wang AQ (2010) pH-sensitive sodium alginate/poly(vinyl alcohol) hydrogel beads prepared by combined Ca2+ crosslinking and freeze-thawing cycles for controlled release of diclofenac sodium. Int J Biol Macromol 46:517–523
Sangamesh GK, Kumaresh SS, Tejraj MA (2003) Synthesis and characterization of polyacrylamide-grafted chitosan hydrogel microspheres for the controlled release of indomethacin. J Appl Polym Sci 87:1525–1536
Silva CM, Ribeiro AJ, Figueiredo M, Ferreira D, Veiga F (2006) Microencapsulation of hemoglobin in chitosan-coated alginate microspheres prepared by emulsification/internal gelation. Aaps J 7:903–913
Connick WJ, Bradow JH, Wells W, Steward KK, Van TK (1984) Preparation and evaluation of controlled release formulations of 2,6-dichlorobenzonitrile. J Agric Food Chem 32:1199–1205
Pepperman AB, Kuan JW (1993) Slow release formulations of metribuzin based on alginate-kaolin-linseed oil. J Control Release 26:21–30
Fernández-Pérez M, Villafranca-Sánchez M, González-Pradas E, Martinez-López F, Flores-Céspedes F (2000) Controlled release of carbofuran from an alginate-bentonite formulation: water release kinetics and soil mobility. J Agric Food Chem 48:938–943
Cunha AG, Gandini A (2010) Turning polysaccharides into hydrophobic materials: a critical review. Part 2 hemicelluloses, chitin/chitosan, starch, pectin and alginates. Cellulose 17:1045–1065
Yang LQ, Zhang BF, Wen LQ, Liang QY, Zhang LM (2007) Amphiphilic cholesteryl grafted sodium alginate derivative: synthesis and self-assembly in aqueous solution. Carbohydr Polym 68:218–225
Yang JS, Ren HB, Xie YJ (2011) Synthesis of amidic alginate derivatives and their application in microencapsulation of λ-cyhalothrin. Biomacromolecules 12:2982–2987
Nie HR, He AH, Zheng JF, Xu SS, Li JX, Han CC (2008) Effects of chain conformation and entanglement on the electrospinning of pure alginate. Biomacromolecules 9:1362–1365
Bonino CA, Krebs MD, Saquing CD, Jeong SI, Shearer KL, Alsberg E, Khan SA (2011) Electrospinning alginate-based nanofibers: from blends to crosslinked low molecular weight alginate-only systems. Carbohydr Polym 85:111–119
Bhattarai N, Li Z, Edmondson D, Zhang M (2006) Alginate-based nanofibrous scaffolds: structural, mechanical, and biological properties. Adv Mater 18:1463–1467
Lu JW, Zhu YL, Guo ZX, Hu P, Yu J (2006) Electrospinning of sodium alginate with poly(ethylene oxide). Polymer 47:8026–8031
Lee YJ, Shin DS, Kwon OW, Park WH, Choi HG, Lee YR, Han SS, Noh SK, Lyoo WS (2007) Preparation of atactic poly(vinyl alcohol)/sodium alginate blend nanowebs by electrospinning. J Appl Polym Sci 106:1337–1342
SmidsrØd O (1970) Solution properties of alginate. Carbohydr Res 13:359–372
Mackie W, Perez S, Rizzo R, Taravel F, Vignon M (1983) Aspects of the conformation of polyguluronate in the solid state and in solution. Int J Biol Macromol 5:329–341
Barro R, Garcia-Jares C, Llompart M, Bollain MH, Cela R (2006) Rapid and sensitive determination of pyrethroids indoors using active sampling followed by ultrasound-assisted solvent extraction and gas chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1111:1–10
Tripathi S, Mehrotra GK, Dutta PK (2009) Physicochemical and bioactivity of cross-linked chitosan-PVA film for food packaging applications. Int J Biol Macromol 45:372–376
Vallee F, Muller C, Durand A, Schimchowitsch S, Dellacherie E, Kelche C, Cassel JC, Leonard M (2009) Synthesis and rheological properties of hydrogels based on amphiphilic alginate-amide derivatives. Carbohydr Res 344:223–228
Galant C, Kjøniksen AL, Nguyen GTM, Knudsen KD, Nystrom B (2006) Altering associations in aqueous solutions of a hydrophobically modified alginate in the presence of β-cyclodextrin monomers. J Phys Chem B 110:190–195
Gomez CG, Chambat G, Heyraud A, Villar M, AuzelyVelty R (2006) Synthesis and characterization of a β-CD-alginate conjugate. Polymer 47:8509–8516
Liu CG, Desai KGH, Chen XG, Park HJ (2005) Linolenic acid-modified chitosan for formation of self assembled nanoparticles. J Agric Food Chem 53:437–441
Islam MS, Karim MR (2010) Fabrication and characterization of poly (vinyl alcohol)/alginate blend nanofibers by electrospinning method. Colloid Surf A 366:135–140
Yan HQ, Chen XQ, Wu TT, Feng YH, Wang CX, Li JC, Lin Q (2014) Mechanochemical modification of kaolin surfaces for immobilization and delivery of pesticides in alginate-chitosan composite beads. Polym Bull 71:2923–2944
Nouvel C, Frochot C, Sadtler V, Dubois P, Dellacherie E, Six JL (2004) Polylactide-grafted dextrans: synthesis and properties at interfaces and in solution. Macromolecules 37:4981–4988
Li W, Li XY, Chen Y, Li XX, Deng HB, Wang T, Huang R, Fan G (2013) Poly(vinyl alcohol)/sodium alginate/layered silicate based nanofibrous mats for bacterial inhibition. Carbohydr Polym 92:2232–2238
Deitzel JM, Kleinmeyer J, Harris D, Beck Tan NC (2001) The effect of processing variables on the morphology of electrospun nanofibers and textiles. Polymer 42:261–272
Bhattarai N, Zhang M (2007) Controlled synthesis and structural stability of alginate-based nanofibers. Nanotechnology 18:455601(10 pp)
He Y, Zhu B, Inoue Y (2004) Hydrogen bonds in polymer blends. Prog Polym Sci 29:1021–1051
Talwar S, Krishnan AS, Hinestroza JP, Pourdeyhimi B, Khan SA (2010) Electrospun nanofibers with associative polymer-surfactant systems. Macromolecules 43:7650–7656
Nie HR, He AH, Wu WL, Zheng JF, Xu SS, Li JX, Han CC (2009) Effect of poly(ethylene oxide) with different molecular weights on the electrospinnability of sodium alginate. Polymer 50:4926–4934
Deng HB, Li XY, Ding B, Du YM, Li GX, Yang JH, Hu XW (2011) Fabrication of polymer/layered silicate intercalated nanofibrous mats and their bacterial inhibition activity. Carbohydr Polym 83:973–978
Zhang Y, Huang X, Duan B, Wu L, Li S, Yuan X (2007) Preparation of electrospun chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol) membranes. Colloid Polym Sci 285:855–863
Yarin AL, Koombhongse S, Reneker DH (2001) Taylor cone and jetting from liquid droplets in electrospinning of nanofibers. J Appl Phys 90:4836–4846
Zeng J, Xu X, Chen X, Liang Q, Bian X, Yang L, Jing X (2003) Biodegradable electrospun fibers for drug delivery. J Control Release 92:227–231
Ritger PL, Peppas NA (1987) A simple equation for description solute release. J Control Release 5:23–36
Singh B, Sharma DK, Kumar R, Gupta A (2009) Controlled release of the fungicide thiram from starch–alginate–clay based formulation. Appl Clay Sci 45:76–82
Acknowledgments
We gratefully thank the financial support form the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21366010), Hainan Province Fund (213010), Key Projects in the National Science & Technology Pillar Program during the Twelfth Five-year Plan Period (2011BAE06B06-07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Yan, H., Sun, W. et al. Synthesis of amphiphilic alginate derivatives and electrospinning blend nanofibers: a novel hydrophobic drug carrier. Polym. Bull. 72, 3097–3117 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-015-1455-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-015-1455-8