Abstract
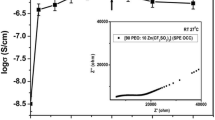
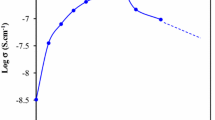
Synthesis and io n transport characterization of hot-pressed solid polymer electrolyte (SPE) membranes:(1 − x) poly (ethylene oxide) (PEO):x NaHCO3, where 0 < x < 50 wt.%, have been reported. SPE films have been synthesized using a hot-press technique in place of the traditional solution-cast method. A conductivity enhancement of the two orders of magnitude was achieved in SPE film:70PEO:30NaHCO3 and this composition has been referred to as optimum conducting composition (OCC). Materials characterization was done with the help of XRD, SEM, FTIR, DSC and TGA techniques. The ion transport behavior in SPE membranes has been discussed on the basis of experimental measurements on their ionic conductivity (σ), ionic mobility (μ) and some other important parameters. A solid-state polymer battery was fabricated using SPE OCC at room temperature, as a device application.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chandra S (1981) Superionic solids—principle and applications. North Holland, Amsterdam
Armand MB (1990) Polymers with ionic conductivity. Adv Mater 2:278–286
Fray FM (1991) Polymer electrolytes: fundamentals and technological applications. VCH, New York
Agrawal RC, Pandey GP (2008) Solid polymer electrolytes: materials designing and all-solid-state battery applications: an overview. J Phys D Appl Phys 41:223001–223018
Kumar JS, Kumar KV, Subrahmanyam AR, Reddy MJ (2007) Conductivity study of polyethylene oxide (PEO) complexed with sodium bicarbonate. Mater Sci 42:5752–5755
Chandrasekaran R, Mangani IR, Vasanthi RV, Selladurai S (2001) Ionic conductivity and battery characteristic studies on PEO–NaClO3 polymer electrolyte. Ionics 7:88–93
Hashmi SA, Chandra S (1995) Experimental investigations on a sodium ion conducting polymer electrolyte based on PEO complexed with NaPF6. J Mater Sci Engg B 34:18–26
Kumar JS, Reddy MJ, Rao UVS (2006) Ion transport and battery studies of a new (PVP + KIO3) polymer electrolyte system. Mater Sci Lett 41:6171–6173
Armand MP, Chabagno JM, Duclot M (1979) Polyethers as electrolytes. In: Vashistha P, Mundy M, Sheny GK (eds) Fast ion transport in solids. Elsevier, North Holland, pp 131–135
Bhide A, Kariharan K (2006) A new polymer electrolyte system (PEO)n: NaPO3. J Power Source 159:1450–1457
Balaji BP, Madhu MV, Sharma AK, Rao VVRN (2009) Investigations on electrical properties of (PVA:NaF) polymer electrolytes for electrochemical cell applications. Curr Appl Phys 9:165–171
Wang J, Hucheng Z, Honghe Z, Xiaopeng X (2006) Correlation of PEO conformations and solvation in PEO–NaSCN polymer electrolytes. Chem Phys 325:538–544
Poul AR, Kumar R, Kumar KV (2012) Ionic conductivity and electrochemical cell studies of a new Mg2+ ion conducting PVA/PEG based polymer blend electrolytes. Adv Mater Lett 3:406–409
Appetecchi GB, Croce F, Hassoun J, Scrosati B, Salomon M, Cassel F (2003) Hot-pressed, dry, composite, PEO-based electrolyte membranes I. Ionic conductivity characterization. J Power Sources 114:105–112
Agrawal RC, Chandra A (2007) Ion transport and electrochemical cell performance studies on hot-press-synthesized Ag+ ion conducting electroactive polymeric membranes:(1 − x) PEO:x [0.7(0.75AgI:0.25 AgCl):0.3 MI]. J Phys D Appl Phys 40:7024–7031
Chandra A, Agrawal RC, Mahipal YK (2009) Ion transport property studies on PEO-PVP blended solid polymer electrolyte membranes. J Phys D Appl Phys 42:135107–135110
Chandra A, Chandra A (2010) Hot-pressed polymer electrolytes: synthesis and characterization. Lambert Academic Pub, Germany
Chandra A (2010) Hot-pressed Na+ ion conducting solid polymer electrolytes:(1 − x) PEO:x NaPO3. Eur Phys J Appl Phys 50:21103–21106
Dey A, Karan S, De SK (2009) Effect of nanofillers on thermal and transport properties of potassium iodide–polyethylene oxide solid polymer electrolyte. Solid State Commun 149:1282–1287
Chandra A, Chandra A, Thakur K (2013) Synthesis, characterization and ion transport properties of hot-pressed solid polymer electrolytes:(1 − x) PEO:x KI. Chin J Polym Sci 31:302–308
Chandra A, Chandra A, Thakur K (2012) Synthesis and characterization on ion conducting superionic polymeric batteries. Int J Appl Phys 2:69–74
Chandra A, Chandra A, Thakur K (2013) Preparation and characterization of hot-pressed Na+ ion conducting nano-composite polymer electrolytes. Indian J Pure and Appl Phys 51:44–48
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandra, A., Chandra, A. & Thakur, K. Synthesis, characterization and device application of hot-pressed solid polymer electrolytes:(1 − x) PEO:x NaHCO3 . Polym. Bull. 71, 181–192 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-013-1053-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-013-1053-6