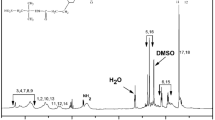
Abstract
A series of covalently and ionically crosslinked sulfonated poly(arylene ether ketone)s (SPAEKs) were prepared via the cyclocondensation reaction of crosslinkable SPAEKs with 3,3′-diaminobenzidine to form quinoxaline groups, where crosslinkable SPAEKs were synthesized by copolymerization of 4,4′-biphenol with 2,6-difluorobenzil, 4,4′-difluorobenzophenone, and 5,5′-carbonyl-bis(2-fluorobenzene sulfonate). The SPAEK membranes had high mechanical properties and the isotropic membrane swelling. The covalent and ionical crosslinking significantly improved the membrane performance, i.e., the crosslinked membranes showed the lower membrane dimensional change, lower methanol permeability, and higher oxidative stability than the corresponding uncrosslinked membranes, with keeping the reasonably high proton conductivity. The crosslinked membrane (CK3) with measured ion exchange capacity of 1.62 mequiv g−1 displayed a reasonably high proton conductivity of 110 mS/cm with water uptake of 33 wt% at 80 °C, and exhibited a low methanol permeability of 1.7 × 10−7 cm2 s−1 for 32 wt% methanol solution at 25 °C. The covalently and ionically crosslinked SPAEK membranes have potential for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells and direct methanol fuel cells.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kamarudin S, Achmad F, Daud W (2009) Overview on the application of direct methanol fuel cell (DMFC) for portable electronic devices. Int J Hydrogen Energy 34:6902–6916
Ahmad H, Kamarudin S, Hasran U, Daud W (2010) Overview of hybrid membranes for direct-methanol fuel-cell applications. Int J Hydrogen Energy 35:2160–2175
Mauritz K, Moore R (2004) State of understanding of Nafion. Chem Rev 104:4535–4585
Rikukawa M, Sanui K (2000) Proton-conducting polymer electrolyte membranes based on hydrocarbon polymers. Prog Polym Sci 25:1463–1502
Mehta V, Cooper J (2003) Review and analysis of PEM fuel cell design and manufacturing. J Power Sources 114:32–53
Jones D, Roziere J (2008) Advances in the development of inorganic-organic membranes for fuel cell applications. Adv Polym Sci 215:219–264
Higashihara T, Matsumoto K, Ueda M (2009) Sulfonated aromatic hydrocarbon polymers as proton exchange membranes for fuel cells. Polymer 50:5341–5357
Aslan A, Bozkurt A (2011) Proton conducting properties of ionically cross-linked poly(1-vinyl-1,2,4 triazole) and poly(2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid) electrolytes. Polym Bull 66:1099–1110
Hickner M, Ghassemi H, Kim Y, Einsla B, McGrath J (2004) Alternative polymer systems for proton exchange membranes (PEMs). Chem Rev 104:4587–4612
Yin Y, Yamada O, Tanaka K, Okamoto K (2006) On the development of naphthalene-based sulfonated polyimide membranes for fuel cell applications. Polym J 38:197–219
Chen X, Chen P, Okamoto K (2009) Synthesis and properties of novel side-chain-type sulfonated polyimides. Polym Bull 63:1–14
Marestin C, Gebel G, Diat O, Mercier R (2008) Sulfonated polyimides. Adv Polym Sci 216:185–258
Lee H, Roy A, Lane O, Lee M, McGrath J (2010) Synthesis and characterization of multiblock copolymers based on hydrophilic disulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone) and hydrophobic partially fluorinated poly(arylene ether ketone) for fuel cell applications. J Polym Sci A 48:214–222
Einsla M, Kim Y, Hawley M, Lee H, McGrath J, Liu B, Guiver M, Pivovar B (2008) Toward improved conductivity of sulfonated aromatic proton exchange membranes at low relative humidity. Chem Mater 20:5636–5642
Miyatake K, Chikashige Y, Higuchi E, Watanabe M (2007) Tuned polymer electrolyte membranes based on aromatic polyethers for fuel cell applications. J Am Chem Soc 129:3879–3887
Bae B, Yoda T, Miyatake K, Uchida H, Watanabe M (2010) Proton-conductive aromatic ionomers containing highly sulfonated blocks for high-temperature-operable fuel cells. Angew Chem Int Ed 49:317–320
Matsumoto K, Higashihara T, Ueda M (2009) Locally and densely sulfonated poly(ether sulfone)s as proton exchange membrane. Macromolecules 42:1161–1166
Kim D, Robertson G, Guiver M (2008) Comb-shaped poly(arylene ether sulfone)s as proton exchange membranes. Macromolecules 41:2126–2134
Kim D, Robertson G, Kim Y, Guiver M (2009) Copoly(arylene ether)s containing pendant sulfonic acid groups as proton exchange membranes. Macromolecules 42:957–963
Hu H, Xiao M, Wang S, Meng Y (2010) Poly (fluorenyl ether ketone) ionomers containing separated hydrophilic multiblocks used in fuel cells as proton exchange membranes. Int J Hydrogen Energy 35:682–689
Liu B, Robertson G, Kim D, Guiver M, Hu W, Jiang Z (2007) Aromatic poly(ether ketone)s with pendant sulfonic acid phenyl groups prepared by a mild sulfonation method for proton exchange membranes. Macromolecules 40:1934–1944
Li X, Zhao C, Lu H, Wang Z, Na H (2005) Direct synthesis of sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone ketone)s (SPEEKKs) proton exchange membranes for fuel cell application. Polymer 46:5820–5827
Bi H, Chen S, Chen X, Chen K, Endo N, Higa M, Okamoto K, Wang L (2009) Poly(sulfonated phenylene)-block-polyimide copolymers for fuel cell applications. Macromol Rapid Commun 30:1852–1856
Asano N, Aoki M, Suzuki S, Miyatake K, Uchida H, Watanabe M (2006) Aliphatic/aromatic polyimide ionomers as a proton conductive membrane for fuel cell applications. J Am Chem Soc 128:1762–1770
Qiu Z, Wu S, Li Z, Zhang S, Xing W, Liu C (2006) Sulfonated poly(arylene-co-naphthalimide)s synthesized by copolymerization of primarily sulfonated monomer and fluorinated naphthalimide dichlorides as novel polymers for proton exchange membranes. Macromolecules 39:6425–6432
Kerres J, Zhang W, Haering T (2004) Covalently cross-linked ionomer (blend) membranes for fuel cells. J New Mater Electrochem Syst 7:299–309
Fang J, Zhai F, Guo X, Xu H, Okamoto K (2007) A facile approach for the preparation of cross-linked sulfonated polyimide membranes for fuel cell application. J Mater Chem 17:1102–1108
Mikhailenko S, Robertson G, Guiver M, Kaliaguine S (2006) Properties of PEMs based on cross-linked sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone). J Membr Sci 285:306–316
Gu S, He G, Wu X, Guo Y, Liu H, Peng L, Xiao G (2008) Preparation and characteristics of crosslinked sulfonated poly(phthalazinone ether sulfone ketone) with poly(vinyl alcohol) for proton exchange membrane. J Membr Sci 312:48–58
Zhong S, Cui X, Cai H, Fu T, Zhao C, Na H (2007) Crosslinked sulfonated poly(ether ether ketone) proton exchange membranes for direct methanol fuel cell applications. J Power Sources 164:65–72
Ding F, Wang S, Xiao M, Li X, Meng Y (2007) Fabrication and properties of cross-linked sulfonated fluorene-containing poly(arylene ether ketone) for proton exchange membrane. J Power Sources 170:20–27
Feng S, Shang Y, Xie X, Wang Y, Xu J (2009) Synthesis and characterization of crosslinked sulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone) membranes for DMFC applications. J Membr Sci 335:13–20
Kerres J, Ullrich A, Haring T, Baldauf M, Gebhardt U, Preidel W (2000) Preparation, characterization and fuel cell application of new acid-base blend membranes. J New Mater Electrochem Syst 3:229–239
Sen U, Bozkurt A, Ata A (2010) Nafion/poly(1-vinyl-1,2,4-triazole) blends as proton conducting membranes for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. J Power Sources 195:7720–7726
Li H, Zhang G, Ma W, Zhao C, Zhang Y, Han M, Zhu J, Liu Z, Wu J, Na H (2010) Composite membranes based on a novel benzimidazole grafted PEEK and SPEEK for fuel cells. Int J Hydrogen Energy 35:11172–11179
Lin H, Zhao C, Ma W, Li H, Na H (2009) Layer-by-layer self-assembly of in situ polymerized polypyrrole on sulfonated poly(arylene ether ketone) membrane with extremely low methanol crossover. Int J Hydrogen Energy 34:9795–9801
Yang M, Lu S, Lu J, Jiang S, Xiang Y (2010) Layer-by-layer self-assembly of PDDA/PWA-Nafion composite membranes for direct methanol fuel cells. Chem Commun 46:1434–1436
Kharlampieva E, Kozlovskaya V, Sukhishvili S (2009) Layer-bilayer hydrogen-bonded polymer films: from fundamentals to applications. Adv Mater 21:3053–3065
Taylor M, Sekol R, Podsiadlo P, Ho P, Kotov N, Thompson L (2007) High-performance nanostructured membrane electrode assemblies for fuel cells made by layer-by-layer assembly of carbon nanocolloids. Adv Mater 19:3859–3864
Chen X, Chen P, An Z, Chen K, Okamoto K (2011) Crosslinked sulfonated poly(arylene ether ketone) membranes bearing quinoxaline and acid-base complex cross-linkages for fuel cell applications. J Power Sources 196:1694–1703
Tripathi B, Chakrabarty T, Shahi V (2010) Highly charged and stable cross-linked 4, 4′-bis(4-aminophenoxy) biphenyl-3, 3′-disulfonic acid (BAPBDS)-sulfonated poly(ether sulfone) polymer electrolyte membranes impervious to methanol. J Mater Chem 20:8036–8044
Pang J, Zhang H, Li X, Jiang Z (2007) Novel wholly aromatic sulfonated poly(arylene ether) copolymers containing sulfonic acid groups on the pendants for proton exchange membrane materials. Macromolecules 40:9435–9442
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Key Technologies R&D Program of Shaanxi Province (No. 2009K06-08), Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (IRT1070), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. GK200902002, GK201002002), and the Scientific Research Foundation for Returned Scholars, Ministry of Education for financial support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, P., Chen, X. & An, Z. Covalently and ionically crosslinked sulfonated poly(arylene ether ketone)s as proton exchange membranes. Polym. Bull. 68, 1369–1386 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-011-0638-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-011-0638-1