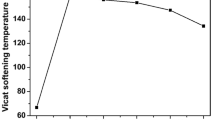
Abstract
Poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC)/acrylonitrile–butadiene rubber (NBR) blends with different types of partitioning agent were obtained through melt blending. The samples were characterized according to the viscosities properties, torque rheometry and mechanical resistance as tensile testing, tear strength, and hardness. The morphology and phase imaging were studied using an atomic force microscopy operating in tapping mode (TMAFM). It was observed that the PVC/NBR blends with PVC as partitioning agent showed an increase in the tensile stress and Young’s modulus compared to the PVC/NBR blends with calcium carbonate as partitioning agent. The morphology of the blends examined by TMAFM evidenced the effect of the partitioning agent as obtained with other techniques.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang Q, Zhang X, Liu S, Gui H, Lai J, Liu Y, Gao J, Huang F, Song Z, Tan BH, Qiao J (2005) Ultrafine full-vulcanized powdered rubbers/PVC compounds with higher toughness and higher heat resistance. Polymer 46(24):10614–10617
Passador FR, Rodolfo A Jr, Pessan LA (2008) Influência do Tipo de Agente de Partição da Borracha Nitrílica na Obtenção de Blendas PVC/NBR. Polímeros, Ciência e Tecnologia 18(3):193–200
Utracki LA, Favis BD (1989) Polymer alloys and blends. In: Cheremisinoff NP (ed) Handbook of polymers science and technology. Hanser, Munich, pp 125–132
Corradini E, Rubira AF, Muniz EC (1997) Miscibility of PVC/EVA hydrolysed blends by viscosimetric, microscopic and thermal analysis. Eur Polym J 33(10–12):1651–1658
Painter PC, Graf JF, Coleman MM (1991) Effect of hydrogen bonding on the enthalpy of mixing and the composition dependence of the glass transition temperature in polymer blends. Macromolecules 24(20):5630–5638
George KE, Rani J, Francis DJ (1986) Studies on NBR/PVC blends. J Appl Polym Sci 32(1):2867–2873
Ismail H, Tan S, Poh BT (2001) Curing and mechanical properties of nitrile and natural rubber blends. J Elastom Plast 33(4):251–262
Mousa A, Ishiaku US, Ishak ZAM (2005) Oil resistance of dynamically vulcanized poly(vinyl chloride)/nitrile butadiene rubber thermoplastic elastomers. Polym Bull 53(3):203–212
Shen F, Li H, Wu CF (2006) Crosslinking induced by in situ coordination in acrylonitrile butadiene rubber/poly(vinyl chloride) alloy, filled with anhydrous copper sulfate particles. J Polym Sci: Part B: Polym Phys 44:378–386
Passador FR, Rodolfo A Jr, Pessan LA (2006) Estado de mistura e dispersão da fase borrachosa em blendas PVC/NBR. Polímeros, Ciência e Tecnologia 16(3):174–181
Passador FR, Rodolfo A Jr, Pessan LA (2007) Blendas PVC/NBR por processamento reativo I: Desenvolvimento do processo de vulcanização dinâmica in situ. Polímeros, Ciência e Tecnologia 17(2):80–84
Liu ZH, Zhu X, Wu L, Li RY, Qi Z, Choy C, Wang F (2001) Effects of interfacial adhesion on the rubber toughening of poly(vinyl chloride) Part 1. Impact tests. Polymer 42(2):737–746
Liu ZH, Wu LX, Kwok KW, Zhu XG, Qi ZN, Choy CL, Wan FS (2001) Effects of interfacial adhesion on the rubber toughening of poly(vinyl chloride) Part 2. Low-speed tensile tests. Polymer 42(4):1719–1724
Liu ZH, Zhang XD, Zhu XG, Qi ZN, Wang FS (1997) Effect of morphology on the brittle-ductile transition of polymer blends.1. A new equation for correlating morphological parameters. Polymer 38(21):5267–5273
Liu ZH, Zhang XD, Zhu XG, Li RKY, Qi ZN, Wang FS, Choy CL (1998) Effect of morphology on the brittle ductile transition of polymer blends: 2. Analysis on poly(vinyl chloride) nitrile rubber blends. Polymer 39(21):5019–5025
Liu ZH, Zhang XD, Zhu XG, Li RKY, Qi ZN, Wang FS, Choy CL (1998) Effect of morphology on the brittle ductile transition of polymer blends: 3. The influence of rubber particle spatial distribution on the fracture behaviour of poly(vinyl chloride)/nitrile rubber blends. Polymer 39(21):5027–5033
Liu ZH, Zhang XD, Zhu XG, Li KY, Qi ZN, Wang FS, Choy CL (1998) Effect of morphology on the brittle ductile transition of polymer blends: 4. Influence of the rubber particle spatial distribution in poly(vinyl chloride)/nitrile rubber blends. Polymer 39(21):5035–5045
Sen AK, Mukherjee GS (1993) Studies on the thermodynamic compatibility of blends of poly(vinylchloride) and nitrile rubber. Polymer 34(11):2386–2391
Hafezi M, Nouri Khorasani S, Ziaei F, Azim HR (2007) Comparison of physicomechanical properties of NBR–PVC blend cured by sulfur and electron beam. J Elastom Plast 39(2):151–163
San Paulo A, García R (2000) High-resolution imaging of antibodies by tapping-mode atomic force microscopy: attractive and repulsive tip-sample interaction regimes. Biophys J 78(3):1599–1605
Magonov SN, Elings V, Whangbo MH (1997) Phase imaging and stiffness in tapping-mode atomic-force microscopy. Surf Sci 375(2–3):L385–L391
Raghavan D, VanLandingham M, Gu X, Nguyen T (2000) Characterization of heterogeneous regions in polymer systems using tapping mode and force mode atomic force microscopy. Langmuir 16(24):9448–9459
Raghavan D, Gu X, Nguyen T, VanLandingham M, Karim A (2000) Mapping polymer heterogeneity by phase imaging and nanoindentation AFM. Macromolecules 33(7):2573–2583
Stark M, Möller C, Müller DJ, Guckenberger R (2001) From images to interactions: high-resolution phase imaging in tapping-mode atomic force microscopy. Biophys J 80(6):3009–3018
Garcia R, Calleja M, Pérez-Murano F (1998) Local oxidation of silicon surfaces by dynamic force microscopy: Nanofabrication and water bridge formation. Appl Phys Lett 72(18):2295–2297
Garcia R, San Paulo A (2000) Amplitude curves and operating regimes in dynamic atomic force microscopy. Ultramicroscopy 82:79–83
Tamayo J, Garcia R (1996) Deformation, contact time and phase contrast in tapping mode scanning force microscopy. Langmuir 12:4430–4435
Burham NA, Behrend OP, Ouveley F, Gremaud G, Gallo PJ, Gordon D, Dupas E, Kulik AJ, Pollock HM, Briggs GAD (1997) How does a tip tap? Nanotechnology 8:67
Garcia R, San Paulo A (1999) Attractive and repulsive tip-sample interaction regimes in tapping-mode atomic force microscopy. Phys Rev B 60(7):4961–4967
Garcia R, San Paulo A (2000) Dynamics of a vibrating tip near or in intermittent contact with a surface. Phys Rev B 61(20):13381–13384
Rodriguez TR, Garcia R (2002) Tip motion in amplitude modulation (tapping-mode) atomic-force microscopy: comparison between continuous and point-mass models. Appl Phys Lett 80(9):1646–1648
Garcia R, Perez R (2002) Dynamic atomic force microscopy methods. Surf Sci Report 47:197–301
Garcia R, San Paulo A (2002) Unifying theory of tapping-mode atomic-force microscopy. Phys Rev B 66:041406 (R)
Martinez NF, Garcia R (2006) Measuring phase shifts and energy dissipation with amplitude modulation atomic force microscopy. Nanotechnology 17:S167–S172
Martinez NF, Patil S, Lozano JR, Garcia R (2006) Enhanced compositional sensitivity in atomic force microscopy by the excitation of the first two flexural modes. Appl Phys Lett 89:153115b
Herruzo ET, Garcia R (2007) Frequency response of an atomic force microscope in liquids and air: magnetic versus acoustic excitation. Apll Phys Lett 91:143113
Efimov AE, Tonevitsky AG, Dittrich M, Matsko NB (2007) Atomic force microscope (AFM) combined with the ultramicrotome: a novel device for the serial section tomography and AFM/TEM complementary structural analysis of biological and polymer samples. J Microsc 226(3):207–217
Magonov SN, Reneker DH (1997) Characterization of polymer surfaces with atomic force microscopy. Annu Rev Mat Sci 27:175–222
Pickering JP, Vancso GJ (1998) Apparent contrast reversal in tapping mode atomic force microscope images on films of polystyrene-b-polyisoprene-b-polystyrene. Polym Bull 40:549–554
Liu J (2003) AFM applications in petrochemical polymers. Microsc Microanal 9(2):452–453
Zhong Q, Inniss D, Kjoller K, Elings V (1993) Fractured polymer/silica fiber surface studied by tapping mode atomic force microscopy. Surf Sci Lett 290:L688–L692
Schramn G (1994) A practical approach to rheology and rheometry, 2nd edn. Haake, Gebhard Schramm, Germany, pp 32–45
Utracki LA, Shi ZH (1992) Development of polymer blend morphology during compounding in a twin-screw extruder. I: Droplet dispersion and coalescence: a review. Polym Eng Sci 32(24):1824–1833
Passador FR, Rodolfo A Jr, Pessan LA (2008) Blendas PVC/NBR por processamento reativo II: Caracterização físico-mecânica e morfológica. Polímeros, Ciência e Tecnologia 18(2):87–91
Ehabe EE, Farid SA (2001) Chemical kinetics of vulcanisation and compression set. Euro Polym J 37(2):329–334
Rodolfo Jr. A, Nunes LR, Ormanji W (2006) Tecnologia do PVC. São Paulo: Proeditores/Braskem, p 365
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support provided by CAPES (Brazilian research supporting foundation), to Braskem S.A. for the donation of PVC, and to the technical support of the NEO-PVC Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gheno, S.M., Passador, F.R. & Pessan, L.A. Effect of NBR partitioning agent on the mechanical properties of PVC/NBR blends and investigation of phase morphology by atomic force microscopy. Polym. Bull. 63, 865–881 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-009-0130-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-009-0130-3