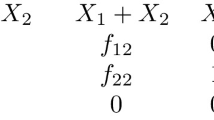Abstract
In this paper, we study a model for calcium buffering with bistable nonlinearity. We present some results on the stability of equilibrium states and show that there exists a threshold phenomenon in our model. In comparing with the model without buffers, we see that stationary buffers cannot destroy the asymptotic stability of the associated equilibrium states and the threshold phenomenon. Moreover, we also investigate the propagation property of solutions with initial data being a disturbance of one of the stable states which is confined to a half-line. We show that the more stable state will eventually dominate the whole dynamics and that the speed of this propagation (or invading process) is positive.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allbritton, N., Meyer, T., Stryer, L.: A Range of messenger action of calcium ion and inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Science (Washington, DC) 258, 1812–1815 (1992)
Aronson, D.G.: A comparison method for stability analysis of nonlinear parabolic problems. SIAM Review 20, 245–264 (1978)
Aronson, D.G., Weinberger, H.F.: Nonlinear diffusion in population genetics, combustion, and nerve pulse propagation. In: Goldstein, J.A. (ed.), Partial Differential Equations and Related Topics, Lecture notes in Mathematics 446, pp. 5–49. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1975
Atri, A., Amundson, J., Clapham, D., Sneyd, J.: A single pool model for intracellular calcium oscillations and waves in the Xenopus laevis oocyte. Biophys. J. 65, 1727–1739 (1993)
Berridge, M.J.: Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature (London) 361, 315–325 (1993)
Bezprozvanny, I., Watras, J., Ehrlich, B.E.: Bell-shaped calcium response curves of Ins(1,4,5) P3- and calcium-gated channels from endoplasmic reticulum of cerebellum. Nature 351, 751–754 (1991)
Britton, N.F.: Reaction-Diffusion Equations and their Applications to Biology. Academic Press, London, 1986
Falcke, M.: Buffers and oscillations in intracellular Ca2+ dynamics. Biophys. J. 84, 28–41 (2003)
Fontanilla, R.A., Nuccitelli, R.: Characterization of the sperm-induced calcium wave in Xenopus eggs using confocal microscopy. Biophys. J. 75, 2079–2087 (1998)
Fulton, B.P., Whitingham, D.G.: Activation of mammalian occytes by intracellular injection of calcium. Nature (London) 273, 149–151 (1978)
Dupont, G., Goldbeter, A.: Properties of intracellular Ca2+ waves generated by a model based on Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release. Biophys. J. 67, 2191–2204 (1994)
Evans, J., Shenk, N.: Solutions to axon equations. Biophys. J. 10, 1090–1101 (1970)
Fife, P.C., McLeod, J.B.: The approach of solutions of non-linear diffusion equations to traveling front solutions. Arch. Rat. Mech. Anal. 65, 335–361 (1977)
Finch, E.A., Turner, T.J., Goldin, S.M.: Calcium as a coagonist of inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced calcium release. Science (Washington, DC) 252, 443–446 (1991)
Friedman, A.: Partial Differential Equations of Parabolic Type. Prentice-Hall, 1964
Girard, S., Luckhoff, A., Lechleiter, J., Sneyd, J., Clapham, D.: Two-dimensional model of calcium waves reproduces the patterns observed in Xenopus laevis oocyte. Biophys. J. 61, 509–517 (1992)
Hastings, S.P.: On traveling wave solutions of the Hodgkin-Huxley equations. Arch. Rational Mech. Anal. 60, 229–257 (1976)
Igusa, Y., Miyazaki, S.-I.: Effects of altered extracellular and intracellular calcium concentration on hyperpolarizing responses of the hamster egg. J. Physiol. (London) 340, 611–632 (1983)
Iino, M.: Biphasic Ca2+-dependence of inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate-induced Ca2+ release in smooth muscle cells of the guinea pig Taenia caeci. J. Gen. Physiol. 95, 1103–1122 (1990)
Jaffe, L.F.: Classes and mechanisms of calcium waves. Cell Calcium 14, 736–745 (1993)
Jafri, M.S., Keizer, J.: On the roles of Ca2+ diffusion, Ca2+ buffers and the endoplasmic reticulum in IP3-induced Ca2+ waves. Biophys. J. 69, 2139–2153 (1995)
Kaftan, E.J., Ehrlich, B.E., Watras, J.: Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate (InsP3) and calcium interact to increase the dynamic range of InsP3 receptor-dependent calcium signaling. J. Gen. Physiol. 110, 529–538 (1997)
Keener, J., Sneyd, J.: Mathematical Physiology. Springer-Verlag, New York, 1998
Klaasen, G.A., Troy, W.C.: The Stability of traveling wave front solutions of a reaction-diffusion system. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 41, 145–167 (1981)
Klaasen, G.A., Troy, W.C.: The asymptotic behaviour of solutions of a system of reaction-diffusion equations which models the Belousov-Zhabotinskii chemical. J. Diff. Equations 40, 253–278 (1981)
Kline, J.T., Kline, D.: Regulation of intracellular calcium in the mouse egg: evidence for inositol trisphosphate-induced calcium release, but not calcium-induced calcium release. Biol. Reprod. 50, 193–203 (1994)
Lechleiter, J.D., Clapham, D.E.: Molecular mechanisms of intracellular calcium excitability in Xenopus laevis oocyte. Cell 69, 283–294 (1992)
Lieberman, G.M.: Second Order Parabolic Differential Equations. World Scientific, Singapore, 1996
Li, Y.-X., Rinzel, J.: Equations for InsP3 receptor-mediated [ Ca2+] i oscillations derived from a detailed kinetic model: a Hodgkin-Huxley like formalism. J. Theor. Biol. 166, 461–473 (1994)
Li, Y.-X.: Tango waves in a bidomain model of fertilization calcium waves. Physica D 186, 27–49 (2003)
Marshall, I.C.B., Taylor, C.W.: Regulation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors. J. Exp. Biol. 184, 161–182 (1993)
Miyazaki, S.-I., Yuzaki, M., Nakada, K., Shirakawa, H., Nakanishi, S., Nakade, S., Mikoshiba, K.: Block of Ca2+ wave and Ca2+ oscillation by antibody to the inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor in fertilized hamster eggs. Science (Washington, DC) 257, 251–255 (1992)
Murray, J.D.: Mathematical Biology. Springer, Berlin, 1989
Naraghi, M., Neher, E.: Linearized buffered Ca2+ diffusion in microdomains and its implications for calculation of [ Ca2+] at the mouth of a calcium channel. J. Neurosci. 17, 6961–6973 (1997)
Naraghi, M., Muller, T.H., Neher, E.: Two-dimensional determination of the cellular Ca2+ binding in bovine chromaffin cells. Biophys. J. 75, 1635–1647 (1998)
Neher, E., Augustine, G.J.: Calcium gradients and buffers in bovine chromaffin cells. J. Physiol. (London) 450, 273–301 (1992)
Neher, E.: Usefulness and limitations of linear approximations to the understanding of Ca2+ signals. Cell Calcium 24, 345–357 (1998)
Nowycky, M.C., Pinter, M.J.: Time courses of calcium and calcium-bound buffers following calcium influx in a model cell. Biophys. J. 64, 77–91 (1993)
Nuccitelli, R.: How do sperm activate eggs? Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 25, 1–16 (1991)
Nuccitelli, R., Yim, D.L., Smart, T.: The sperm-induced Ca2+ wave following fertilization of the Xenopus egg requires the production of Ins(1,4,5)P3. Dev. Biol. 158, 200–212 (1993)
Nuccitelli, R. (ed.) A Pratical Guide to the Study of Calcium in Living Cells. Methods in Cell Biology 40, Academic Press, San Diego, 1994
Othmer, H., Tang, T.: Oscillations and waves in a model of InsP3-controlled calcium dynamics. In: Othmer, H., Maini, P.K., Murray, J.D. (eds.), Experimental and Theoretical Advances in Biological Pattern Formation, pp. 277–299. Plenum Press, New Tork, 1993
Parker, I., Ivorra, I.: Inhibition by Ca2+ of inositol trisphosphate-mediated Ca2+ liberation: a possible mechanism for oscillatory release of Ca2+. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 260–264 (1990)
Peres, A.: InsP3- and Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release in single mouse oocytes. FEBS Lett. 275, 213–216 (1990)
Protter, M.H., Weinberger, H.F.: Maximum Principles in Differential Equations. Springer-Verlag, New York, 1999
Rauch, J., Smoller, J.: Qualitative theory of the FitzHugh-Nagumo equations. Advances in Math. 27, 12–44 (1978)
Ridgway, E.B., Gilkey, J.C., Jaffe, L.F.: Free calcium increases explosively in activating Medaka eggs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 74, 623–627 (1977)
Redheffer, R., Walter, W.: Invariant sets for systems of partial differential equations I: parabolic Equations. Arch. Rational Mech. Anal. 67, 41–52 (1978)
Sala, F., Hernández-Cruz, A.: Calcium diffusion modeling in a spherical neuron: relevance of buffering properties. Biophys. J. 57, 313–324 (1990)
Schonbek, M.E.: Boundary value problems for the Fitzhugh-Nagumo equations. J. Diff. Equations 30, 119–147 (1978)
Slepchenko, B.M., Schaff, J.C., Choi, Y.S.: Numerical approach to fast reactions in reaction-diffusion systems: application to buffered calcium waves in bistable model. J. Comput. Phys. 162, 186–218 (2000)
Sherman, A., Li, Y.-X., Keizer, J.: Whole cell models. In: Fall, C.P., Marland, E.S., Wagner, J.M., Tyson, J.J. (eds.), Computatiional Cell Biology, pp. 101–139. Springer-Verlag, New York, 2002
Smith, G.D.: Analytical steady-state solution to the rapid buffering approximation near an open Ca2+ channel. Biophys. J. 71, 3064–3072 (1996)
Smith, G.D., Dai, L., Miura, R.M., Sherman, A.: Asymptotic analysis of buffered calcium diffusion near a point source. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 61, 1816–1838 (2001)
Smith, G.: Modeling local and global Ca2+ signals using reaction-diffusion equations. In: Schutter, E.D. (ed.) Computational Neuroscience: Realistic Modeling for Experimentalists. CRC Press, 2001
Smith, G.D., Pearson, J.E., Keizer, J.: Modeling Intracellular Calcium Waves and Sparks. In: Fall, C.P., Marland, E.S., Wagner, J.M., Tyson, J.J. (eds.), Computatiional Cell Biology, pp. 198–229. Springer-Verlag, New York, 2002
Smoller, J.: Shock Waves and Reaction-Diffusion Equations. Springer-Verlag, New York, 1994
Sneyd, J., Keizer, J., Sanderson, M.J.: Mechanisms of calcium oscillations and waves: A quantitative analysis. FASEB J. 9, 1463–1472 (1995)
Sneyd, J., Dale, P.D., Duffy, A.: Traveling waves in buffered systems: applications to calcium waves. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 58, 1178–1192 (1998)
Tsai, J.-C., Sneyd, J.: Existence and stability of traveling waves in buffered systems. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 66, 237–265 (2005)
Terasaki, M., Slater, N.T., Fein, A., Schmidek, A., Reese, T.S.: A continuous cellular network of endoplasmic reticulum in cerebellar Purkinje neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 7510–7514 (1994)
Volpert, A.I., Volpert, V.A.: Applications of the rotation theory of vector fields to the study of wave solutions of parabolic equations. Trans. Moscow Math. Soc. 52, 59–108 (1990)
Wagner, J., Keizer, J.: Effects of rapid buffers on Ca2+ diffusion and Ca2+ oscillations. Biophys. J. 67, 447–456 (1994)
Wagner, J., Li, Y.-X., Pearson, J., Keizer, J.: Simulation of the Fertilization Ca2+ Wave in Xenopus laevis Eggs. Biophys. J. 75, 2088–2097 (1998)
Watras, J., Bezprozvanny, I., Ehrlich, B.E.: Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-gated channels in cerebellum: presence of multiple conductance states. J. Neurosci. 11, 3239–3245 (1991)
De Young, G., Keizer, J.: A single-pool inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate-receptor-based model for agonist-stimulated oscillations in Ca2+ concentration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 9895–9899 (1992)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, JS., Tsai, JC. The asymptotic behavior of solutions of the buffered bistable system. J. Math. Biol. 53, 179–213 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-006-0381-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-006-0381-7