Abstract.
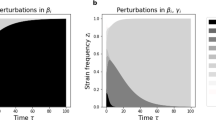
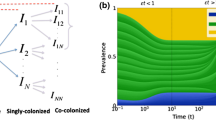
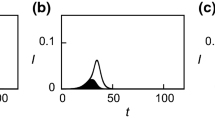
We investigate the population dynamics of host-pathogen systems in which the pathogen has a potentially arbitrary number of antigenically distinct strains interacting via cross-immunity. The interior equilibrium configuration of the symmetric multiple strain SIR model with cross-immunity is characterized. We develop an efficient iterative method for numerically solving the equilibrium equation together with a number of informative analytical approximations to the full solution. Equilibrium properties are studied as a function of the number of strains, reproduction number, infectious period, and cross immunity profile. We establish that the prevalence in the system increases monotonically with the number of strains and the reduction in cross immunity. Moreover, we demonstrate the existence of a phase transition separating high prevalence and low prevalence parameter regions, with the critical point being defined by σR0≅1, where σ is the level of cross-immunity and R0 is the reproduction number. Above the threshold, prevalence saturates with increasing numbers of strains as a result of the inclusion of prohibition of co-infection in the model. Below the threshold, prevalence saturates much more rapidly as the number of strains increases - indicating that when cross-protection is sufficiently intense, the selective advantage for a pathogen to increase its diversity is substantially less than in the threshold region. Similarly, there is limited benefit to increased transmissibility (or decreased cross-immunity) both for the high and low diversity pathogen systems compared with systems at the threshold σR0≅1 where small increase in transmissibility can result in significant increase in prevalence.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, R.M., May, R.M.: Infectious diseases of humans: dynamics and control. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1991
Andreasen, V., Levin, S.A., Lin, J.: Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 52 (76), 421 (1996)
Andreasen, V., Lin, J., Levin, S.A.: J. Math. Biol. 35 (7), 825 (1997)
Callen, H.B. Thermodynamics and an introduction to thermostatistics. Wiley Text Books, second edition, 1985
Castillo-Chavez, C., Hethcote, H.W., Andreasen, V., Levin, S.A., Liu, M.W.: J. Math. Biol. 27, 233 (1985)
Dawes, J.H., Gog, J.R.: J. Math. Biol. 45 (6), 471 (2002)
Delone, B.N.: In: A.D. Alexsandrov, A.N. Kolmogorov, M.A. Lavrent’ev (eds.), Mathematics, its content, methods, and meaning, vol. 1. Mineola, New York: Dover, second edition, 1999, pp. 356
Earn, D.J.D., Dushoff, J., Levin, S.A.: Trends in Ecol. Evol. 17 (7), 334 (2002)
Ferguson, N.M., Andreasen, V.: In: S.M. Blower, C. Castillo-Chavez (eds.), Mathematical approaches for emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases: models, methods and theory, vol. 125 of IMA columes on mathematics and its applications. New York: Springer, 2002, pp. 157–169
Ferguson, N.M., Donnelly, C.A., Anderson, R.M.: Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 354 (1384), 757 (1999)
Ferguson, N.M., Galvani, A.P., Bush, R.M.: Nature 422 (6930), 428 (2003)
Gog, J.R., Grenfell, B.T.: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 99 (26), 17209 (2002)
Gog, J.R., Swinton, J.: J. Math. Biol. 44 (2), 169 (2002)
Goldenfeld, N.: Lectures on phase transitions and the renormalization group, vol. 85 of Frontiers in Physics, Perseus Publishing, 1992
Gomes, M., Franco, A., Gomes, M., Medley, G.: Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 271, 617 (2004a)
Gomes, M., Medley, G.: In: S.M. Blower, C. Castillo-Chavez (eds.), Mathematical approaches for emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases: models, methods and theory, vol. 125 of IMA columes on mathematics and its applications. New York: Springer, 2002, pp. 171–191
Gomes, M., Medley, G., Nokes, D.: Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. B 269, 227 (2002)
Gomes, M., White, L.J., Medley, G.: J. Theor. Biol. (in press) (2004b)
Gupta, S., Anderson, R.M.: Parasitol Today 15 (12), 497 (1999)
Gupta, S., Ferguson, N., Anderson, R.: Science 280 (5365), 912 (1998)
Gupta, S., Maiden, M.C.J., Feavers, I.M., Nee, S., May, R.M., Anderson, R.M.: New Med. 2 (4), 437 (1996)
Gupta, S., Trenholme, K., Anderson, R.M., Day, K.P.: Science 263 (5149), 961 (1994)
Levin, S.A., Dushoff, J., Plotkin, J.B.: Math. Biosci. 188, 17 (2004)
Lin, J., Andreasen, V., Casagrandi, R., Levin, S.A.: J. Theor. Biol. 222 (4), 437 (2003)
Lin, J., Andreasen, V., Levin, S.A.: Math. Biosci. 162 (1–2), 33 (1999)
May, R.M.: Stability and complexity in model ecosystems. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1973
May, R.M., Nowak, M.: J. Theor. Biol. 170, 95 (1994)
May, R.M., Nowak, M.A.: Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 261, 209 (1995)
Nowak, M., May, R.M.: Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 255, 81 (1994)
Rohani, P., Earn, D.J., Finkenstadt, B., Grenfell, B.T.: Proc. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 265 (1410), 2033 (1998)
UNICEF, Malaria, UNICEF, 2003
WHO/UNICEF, Africa Malaria Report, 2003 WHO/UNICEF
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abu-Raddad, L., Ferguson, N. Characterizing the symmetric equilibrium of multi-strain host-pathogen systems in the presence of cross immunity. J. Math. Biol. 50, 531–558 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-004-0292-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00285-004-0292-4