Abstract
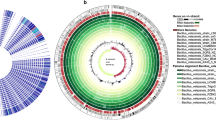
A plant growth-promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR) Pseudomonas aeruginosa (NG61) isolated from rhizosphere of Sunflower plant. The isolate was identified by 16S rRNA gene sequencing (Accession no. MK455763). NG61 showed various plant growth promotion and biocontrol activities like, Phosphate solubilisation, Nitrogen fixation, Ammonia production, IAA production, siderophore production, HCN production. The whole genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa (NG61) was reported and analysed. The estimated genome size was 6537180 bp with 66.18% of G+C content. The genome encoded 6186 protein-coding genes, 6252 genes were predicted, 66RNA genes. Phylogenetic tree showed that the P. aeruginosa( NG61) was closely related to P.aeruginosa strain DSM 50071. The annotated draft genome has been deposited at the NCBI database under the accession number PRJNA707114 BioProject and BioSample: SAMN18174979. The analysis of genome sequence of P. aeruginosa (NG61) showed various genes encoding plant growth promotion and biocontrol activities.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data of whole genome was saved as FASTQ files and deposited into National Center for Biotechnology Information under accession numbers of BioProject PRJNA707114 and BioSample: SAMN18174979.
References
Kloepper JW, Schroth MN (1978) Plant growth promoting rhizobacteria on radishes. In: 4th International Conference on Plant Pathogen Bacteria Angers France, vol 2, pp 879–882
Richardson AE, Barea JM, McNeill AM, Prigent-Combaret C (2009) Acquisition of phosphorus and nitrogen in the rhizosphere and plant growth promotion by microorganisms. Plant Soil 321:305–339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-9895-2
Whitelaw MA, Harden TJ, Helyar KR (1999) Phosphate solubilization in solution culture by the soil fungus Penicillium radicum. Soil Biol Biochem 32:655–665
Gupta A, Gopal M, Tilak KVBR (2000) Mechanism of plant growth promotion by rhizobacteria. Indian J Exp Biol 38:856–862
Spaepen S, Vanderleyden J, Remans R (2007) Indole-3-acetic acid in microbial and microorganism-plant signaling. FEMS Microbiol Rev 31:425–448. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6976.2007.00072.x
Hutchins SR, Davidson MS, Brierey JA, Brierley CL (1986) Microorganisms in reclamation of metals. Annu Rev Microbiol 40:311–336. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.mi.40.100186.001523
Glick BR (2012) Plant growth-promoting bacteria: mechanisms and applications. Scientifica (Cairo). https://doi.org/10.6064/2012/963401
Klockgether J, Cramer N, Wiehlmann L, Davenport CF, Tümmler B (2011) Pseudomonas aeruginosa genomic structure and diversity. Front Microbiol 2:150. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2011.00150
Stover CK, Pham XQ, Erwin AL, Mizoguchi SD, Warrener P, Hickey MJ, Brinkman FSL, Hufnagle WO, Kowallk DJ, Lagrou M, Garber RL, Goltry L, Tolentino E, Westbrock-Wadman S, Yuan Y, Brody LL, Coulter SN, Folger KR, Kas A, Larbig K, Lim R, Smith K, Spencer D, Wong GKS, Wu Z, Paulsen IT, Relzer J, Saler MH, Hancock REW, Lory S, Olson MV (2000) Complete genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, an opportunistic pathogen. Nature 406:959–964. https://doi.org/10.1038/35023079
Minas K, McEwan NR, Newbold CJ, Scott KP (2011) Optimization of a high-throughput CTAB-based protocol for the extraction of qPCR-grade DNA from rumen fluid, plant and bacterial pure cultures. FEMS Microbiol Lett 325(2):162–169. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6968.2011.02424.x
Pikovskaya RI (1948) Mobilization of phosphorus in soil in connection with the vital activity of some microbial species. Mikrobiol 17:362–370
Nguyen C, Yan W, Le TF (1992) Genetic variability phosphate solubilizing activity of the ectomycorrhizal fungus Laccaria bicolor (Maire) P.D. Plant Soil 143:193–199
Islam MT, Hossain MM (2012) Plant probiotics in phosphorous nutrition in crops, with special reference to rice. In: Maheshwari DK (ed) Bacteria in agrobiology: plant probiotics. Springer, Berlin, pp 325–363
Brick JM, Bostock RM, Silverstone SE (1991) Rapid in situ assay for indole acetic acid production by bacteria immobilized on nitrocellulose membrane. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:535–538. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.57.2.535-538.1991
Bakker AW, Schippers B (1987) Microbial cyanide production in the rhizosphere in relation to potato yield reduction and Pseudomonas SPP-mediated plant growth-stimulation. Soil Biol Biochem 19:451–457
Kumar P, Suseelendra G, Desai E, Leo DA, Reddy G (2015) Isolation of Fluorescent Pseudomonas spp. from Diverse Agro-Ecosystems of India and Characterization of their PGPR Traits. Bacteriology Journal 5:13–24. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/195946
Cappuccino JC, Sherman N (1992) Microbiology: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Benjamin/ Cummings Pub.co, New York, pp 125–179
Schwyn B, Neilands JB (1987) Universal chemical assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem 160:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(87)90612-9
Bunt JS, Rovira AD (1955) Microbiological studies of some subantarctic soils. J Soil Sci 6:119–128
Vazquez P, Holguin G, Puente ME, Lopez-Cortes A, Bashan Y (2000) Phosphate solubilizing microorganisms associated with the rhizosphere of of mangroves in a semiarid coastal lagoon. Biol Fertil Soils 30:460–468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003740050024
Aziz RK, Bartels D, Best AA, DeJongh M, Disz T, Edwards RA, Formsma K, Gerdes S, Glass EM, Kubal M, Meyer F, Olsen GJ, Olson R, Osterman AL, Overbeek RA, McNeil LK, Paarmann D, Paczian T, Parrello B, Pusch GD, Reich C, Stevens R, Vassieva O, Vonstein V, Wilke A, Zagnitko O (2008) The RAST server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genom 9:75. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-9-75
Arndt D, Grant JR, Marcu A, Sajed T, Pon A, Liang Y, Wishart DS (2016) PHASTER: a better, faster version of the PHAST phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res 8:44(1):16–21. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw387
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32(5):1792–1797. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh340
Tamura K, Nei M (1993) Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol Biol Evol 10(3):512–526. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040023
Crovadore J, Grizard D, Chablais R, Cochard B, Blanc P, Lefort F (2018) Wholegenome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain 4014, isolated from soil in France. Microbiol Resour Announc 7:01089–01118. https://doi.org/10.1128/MRA.01089-18
Lee I, Kim YO, Park SC, Chun J (2016) OrthoANI: an improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:1100–1103. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.000760
Liu H, Liang R, Tao F, Ma C, Liu Y, Liu X, Liu J (2012) Genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain SJTD-1, a bacterium capable of degrading long-chain alkanes and crude oil. J Bacteriol 194:4783–4784. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.01061-12
Norman A, Ciofu O, Amador CI, Høiby N, Jelsbak L (2016) Genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain DK1-NH57388A, a stable mucoid cystic fibrosis isolate. Genome Announc 4:00008–00016. https://doi.org/10.1128/genomeA.00008-16
Alori ET, Babalola OO (2018) Microbial inoculants for improving crop quality and human health in Africa. J Front Micro 9:2213. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02213
Keswani C, Prakash O, Bharti N, Vílchez JI, Sansinenea E, Lally RD, Borriss R, Singh SP, Gupta VK, Fraceto LF (2019) Re-addressing the biosafety issues of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria. Sci Total Environ 690:841–852. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.07.046
Olanrewaju OS, Glick BR, Babalola OO (2017) Mechanisms of action of plant growth promoting bacteria. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 33:197. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-017-2364-9
Behera BC, Singdevsachan SK, Mishra RR, Dutta SK, Thatoi HN (2014) Diversity, mechanism and biotechnology of phosphate solubilising microorganism in mangrove—a review. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol 3:97–110. ISSN-1878-8181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcab.2013.09.008
Suleman M, Yasmin S, Rasul M, Yahya M, Atta BM, Mirza MS (2018) Phosphate solubilizing bacteria with glucose dehydrogenase gene for phosphorus uptake and beneficial effects on wheat. PLoS ONE 13:1–28. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0204408
de Werra P, Péchy-Tarr M, Keel C, Maurhofer M (2009) Role of gluconic acid production in the regulation of biocontrol traits of Pseudomonas fluorescens CHA0. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:4162–4174. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00295-09
Goldstein AH (1996) Involvement of the quinoprotein glucosedehydrogenase inthe solubilization of exogenous phosphates by Gram-negative bacteria. In: TorrianiGorini A, Yagil E, Silver S (eds) Phosphate in microorganisms: cellular and molecular biology. ASM Press, Washington, DC, pp 197–203
Nikata T, Sakai Y, Shibata K (1996) Molecular analysis of the phosphate-specific transport (pst) operon of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Gen Genet 250:692–698. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02172980
Anba J, Bidaud M, Vasil ML, Lazdunski A (1990) Nucleotide sequence of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa phoB gene, the regulatory gene for the phosphate regulon. J Bacteriol 172(8):4685–4689. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.172.8.4685-4689
Filloux A, Bally M, Soscia C, Murgier M, Lazdunski A (1988) Phosphate regulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: cloning of the alkaline phosphatase gene and identification of phoB- and phoR-like genes. Mol Gen Genet. 212(3):510–3. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00330857
Yu Z, Yang G, Liu X, Wang Y, Zhuang L, Zhou S (2018) Complete genome sequence of the nitrogen-fixing bacterium Azospirillum humicireducens type strain SgZ-5T. Stand Genomic Sci 13:28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40793-018-0322-2
Spaepen S, Vanderleyden J (2011) Auxin and plant-microbe interactions. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 3:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a001438
Thoma R, Hennig M, Sterner R, Kirschner K (2000) Structure and function of mutationally generated monomers of dimeric phosphoribosyl anthranilate isomerase from Thermotoga maritima. Structure 8:265–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00106-4
Gupta A, Gopal M, Thomas GV, Manikandan V, Gajewski J, Thomas G, Seshagiri S, Schuster SC, Rajesh P, Gupta R (2014) Whole genome sequencing and analysis of plant growth promoting bacteria isolated from the rhizosphere of plantation crops coconut, cocoa and arecanut. PLoS ONE 9:104259. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0104259
Laville J, Blumer C, Von Schroetter C, Gaia V, Defago G, Keel C, Haas D (1998) Characterization of the hcnABC gene cluster encoding hydrogen cyanide synthase and anaerobic regulation by ANR in the strictly aerobic biocontrol agent Pseudomonas fluorescens CHAO. J Bacteriol 180(12):3187–3196. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.180.12.3187-3196.1998
Hesse C, Schulz F, Bull CT, Shaffer BT, Yan Q, Shapiro N, Hassan KA, Varghese N, Elbourne LDH, Paulsen IT, Kyrpides N, Woyke T, Loper JE (2018) Genome-based evolutionary history of Pseudomonas spp. Environ Microbiol 20(6):2142–2159. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.14130
Llamas MA, Sparrius M, Kloet R, Jiménez CR, Vandenbroucke-Grauls C, Bitter W (2006) The heterologous siderophores ferrioxamine B and ferrichrome activate signaling pathways in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 188(5):1882–1891. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.188.5.1882-1891.2006
Dupont CL, Grass G, Rensing C (2011) Copper toxicity and the origin of bacterial resistance—new insights and applications. Metallomics 3:1109–1118. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1mt00107h
Chun J, Rainey FA (2014) Integrating genomics into the taxonomy and systematics of the Bacteria and Archaea. Int J Syst Evolut Microbiol 64:316–324. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.054171-0
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to DIC MHRD New Delhi for the financial Assistance.
Funding
The authors are thankful to DIC MHRD New Delhi for the financial Assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TR performed the In vitro plant growth-promoting activities. MB carried out genome analysis and written and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent for Publication
All authors approve to submit and publication to the journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rikame, T., Borde, M. Whole Genome, Functional Annotation and Comparative Genomics of Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa (NG61) with Potential Application in Agro-Industry. Curr Microbiol 79, 169 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-022-02845-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-022-02845-1