Abstract
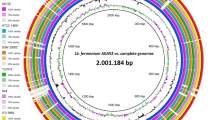
Using microbial culturomics, we were able to isolate strain Marseille-P3078 from a stool sample of a healthy 50-year-old Saudi Arabian woman. To this end, we used taxonogenomics that combines phenotypic, biochemical and genomic analyses, to describe this bacterium. Cells from strain Marseille-P3078 are anaerobic and Gram-negative rods that are motile and unable to sporulate. Its genome size is 3,377,914-bp-long with a 66.33 mol% G + C content. Based on its phenotypic and genomic features, including a 94.6% 16S rRNA similarity with Paraeggerthella hongkongensis strain JCM 14552, its closest phylogenetic neighbor withstanding in nomenclature, we propose that strain Marseille-P3078T (= CSUR P3078 = DSM 104007) is the representative strain of a new genus for which we propose the name Arabiibacter massiliensis gen. nov., sp. nov.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shreiner AB, Kao JY, Young VB (2015) The gut microbiome in health and in disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 31:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOG.0000000000000139
Martín R, Miquel S, Langella P, Bermúdez-Humarán LG (2014) The role of metagenomics in understanding the human microbiome in health and disease. Virulence 5:413–423. https://doi.org/10.4161/viru.27864
Million M, Diallo A, Raoult D (2017) Gut microbiota and malnutrition. Microb Pathog 106:127–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2016.02.003
Zapata HJ, Quagliarello VJ (2015) The microbiota and microbiome in aging: potential implications in health and age-related diseases. J Am Geriatr Soc 63:776–781. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.13310
Fonkou MD, Dufour J-C, Dubourg G, Raoult D (2018) Repertoire of bacterial species cultured from the human oral cavity and respiratory tract. Future Microbiol 13:1611–1624. https://doi.org/10.2217/fmb-2018-0181
Lagier J-C, Armougom F, Million M et al (2012) Microbial culturomics: paradigm shift in the human gut microbiome study. Clin Microbiol Infect 18:1185–1193. https://doi.org/10.1111/1469-0691.12023
Lagier J-C, Million M, Hugon P et al (2012) Human gut microbiota: repertoire and variations. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2012.00136
Lagier J-C, Dubourg G, Million M et al (2018) Culturing the human microbiota and culturomics. Nat Rev Microbiol 16:540–550. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-018-0041-0
Togo AH, Diop A, Bittar F et al (2018) Description of Mediterraneibacter massiliensis, gen. nov., sp. nov., a new genus isolated from the gut microbiota of an obese patient and reclassification of Ruminococcus faecis, Ruminococcus lactaris, Ruminococcus torques, Ruminococcus gnavus and Clostridium glycyrrhizinilyticum as Mediterraneibacter faecis comb. nov., Mediterraneibacter lactaris comb. nov., Mediterraneibacter torques comb. nov., Mediterraneibacter gnavus comb. nov. and Mediterraneibacter glycyrrhizinilyticus comb. nov. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 111:2107–2128. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-018-1104-y
Lo CI, Padhmanabhan R, Mediannikov O et al (2015) High-quality genome sequence and description of Bacillus ndiopicus strain FF3(T) sp. nov. New Microbes New Infect 8:154–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nmni.2015.10.009
Dione N, Lo CI, Raoult D et al (2020) Clostridium massiliamazoniense sp. nov., new bacterial species isolated from stool sample of a volunteer Brazilian. Curr Microbiol 77:2008–2015. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02099-9
Lagier J-C, Khelaifia S, Alou MT et al (2016) Culture of previously uncultured members of the human gut microbiota by culturomics. Nat Microbiol 1:16203. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.203
Bilen M, Mbogning Fonkou MD, Nguyen TT et al (2019) Miniphocibacter massiliensis gen. nov., sp. Nov., a new species isolated from the human gut and its taxono-genomics description. MicrobiologyOpen 8:e00735. https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.735
Morel A-S, Dubourg G, Prudent E et al (2015) Complementarity between targeted real-time specific PCR and conventional broad-range 16S rDNA PCR in the syndrome-driven diagnosis of infectious diseases. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 34:561–570. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-014-2263-z
Sayers EW, Cavanaugh M, Clark K et al (2019) GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D94–D99. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky989
Kim M, Oh H-S, Park S-C, Chun J (2014) Towards a taxonomic coherence between average nucleotide identity and 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity for species demarcation of prokaryotes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:346–351. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.059774-0
Stackebrandt E, Ebers J (2006) Taxonomic parameters revisited : tarnished gold standards. Microbiol Today 33:152–155
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M et al (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547–1549. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy096
Elsawi Z, Togo AH, Beye M et al (2017) Hugonella massiliensis gen. nov., sp. Nov., genome sequence, and description of a new strictly anaerobic bacterium isolated from the human gut. Microbiologyopen 6:e00458. https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.458
Lo CI, Sankar SA, Fall B et al (2016) High-quality draft genome sequence and description of Haemophilus massiliensis sp. nov. Stand Genomic Sci 11:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40793-016-0150-1
Lo CI, Niang EHA, Sarr M et al (2020) Fenollaria timonensis sp. nov., a new bacterium isolated from healthy human fresh stool. Curr Microbiol 77:3780–3786. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02151-8
Su G, Morris JH, Demchak B, Bader GD (2014) Biological network exploration with cytoscape 3. Curr Protoc Bioinform 47:8.13.1-8.13.24. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471250953.bi0813s47
Lee I, Ouk Kim Y, Park S-C, Chun J (2016) OrthoANI: an improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:1100–1103. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijsem.0.000760
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk H-P, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform 14:60. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-14-60
McCarthy BJ, Bolton ET (1963) An approach to the measurement of genetic relatedness among organisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 50:156–164
Woese CR, Kandler O, Wheelis ML (1990) Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya. PNAS 87:4576–4579. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576
Würdemann D, Tindall BJ, Pukall R et al (2009) Gordonibacter pamelaeae gen. nov., sp. Nov., a new member of the Coriobacteriaceae isolated from a patient with Crohn’s disease, and reclassification of Eggerthella hongkongensis Lau et al. 2006 as Paraeggerthella hongkongensis gen. nov., comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1405–1415. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.005900-0
Wade WG, Downes J, Dymock D et al (1999) The family Coriobacteriaceae: reclassification of Eubacterium exiguum (Poco et al. 1996) and Peptostreptococcus heliotrinreducens (Lanigan 1976) as Slackia exigua gen. nov., comb. nov. and Slackia heliotrinireducens gen. nov., comb. nov., and Eubacterium lentum (Prevot 1938) as Eggerthella lenta gen. nov., comb. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49(Pt 2):595–600. https://doi.org/10.1099/00207713-49-2-595
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Enora Tomei for her technical assistance, Ludivine Brechard for sequencing the genome and Aurélia Caputo for depositing the genome sequence in Genbank.
Funding
The study was funded by the Mediterranee Infection foundation and the French Agence Nationale de la Recherche under reference Investissements d’Avenir Méditerranée Infection 10-IAHU-03.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, DR and PEF; methodology, PEF; software, AD and MB; validation, DR, JCL, FF and PEF; formal analysis, SIT, AD, MB, and CIL; investigation, SIT, and EIA; resources, EIA, FB, AJF, and MY; data curation, CIL and SIT; writing-original draft preparation, CIL and SIT writing-review and editing, CIL, FF, PEF; supervision, PEF and FF; project administration, PEF and DR; funding acquisition, DR All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lo, C.I., Traore, S.I., Diop, A. et al. Arabiibacter massiliensis gen. nov. sp. nov., New Anaerobic Bacterium Isolated from the Human Gut. Curr Microbiol 79, 47 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-021-02739-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-021-02739-8