Abstract
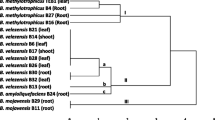
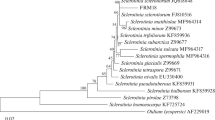
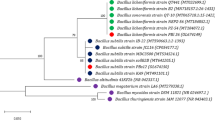
Endophytic bacteria play a key role in the biocontrol of phytopathogenic microorganisms. In this study, genotypic diversity was analyzed via repetitive element PCR (rep-PCR) of endophytic isolates of the phylum Actinobacteria that were previously collected from leaves of cultivars of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Considerable variability was observed, which has not been reported previously for this phylum of endophytic bacteria of the common bean. Furthermore, the ethanol extracts from cultures of various isolates inhibited the growth of pathogenic bacteria in vitro, especially Gram-positive pathogens. Extracts from cultures of Microbacterium testaceum BAC1065 and BAC1093, which were both isolated from the ‘Talismã’ cultivar, strongly inhibited most of the pathogenic bacteria tested. Bean endophytic bacteria were also demonstrated to have the potential to inhibit the quorum sensing of Gram-negative bacteria. This mechanism may regulate the production of virulence factors in pathogens. The ability to inhibit quorum sensing has also not been reported previously for endophytic microorganisms of P. vulgaris. Furthermore, M. testaceum with capacity to inhibit quorum sensing appears to be widespread in common bean. The genomic profiles of M. testaceum were also analyzed via pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, and greater differentiation was observed using this method than rep-PCR; in general, no groups were formed based on the cultivar of origin. This study showed for the first time that endophytic bacteria from common bean plants exhibit high variability and may be useful for the development of strategies for the biological control of diseases in this important legume plant.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Christina A, Christapher V, Bhore SJ (2013) Endophytic bacteria as a source of novel antibiotics: an overview. Pharmacol Rev 7:11–16
Costa LEO, Queiroz MV, Borges AC, Moraes CA, Araújo EF (2012) Isolation and characterization of endophytic bacteria isolated from the leaves of the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Braz J Microbiol 43:1562–1575
Dong YH, Xu JL, Li XZ, Zhang LH (2000) AiiA, an enzyme that inactivates the acylhomoserine lactone quorum sensing signal and attenuates the virulence of Erwinia carotovora. P Natl Acad Sci USA 497:4154–4158
Elasri M, Delorme S, Lemanceau P, Stewart G, Laue B, Glickmann E, Oger PM, Dessaux Y (2001) Acyl-homoserine lactone production is more common among plant-associated Pseudomonas spp. than among soilborne Pseudomonas spp. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:1198–1209
Hallmann J, Quadt-Hallmann A, Mahaffee WF, Kloepper JW (1997) Bacterial endophytes in agricultural crops. Can J Microbiol 43:895–914
López-López A, Rogel MA, Ormeño-Orrillo E, Martínez-Romero J, Martínez-Romero E (2010) Phaseolus vulgaris seed-borne endophytic community with novel bacterial species such as Rhizobium endophyticum sp. nov. Syst Appl Microbiol 33:322–327
Martins ML (2007) Caracterização de protease e lipase de Pseudomonas fluorescens e quorum sensing em bactérias psicrotróficas isoladas de leite. Thesis, Federal University of Viçosa
McClean KH, Winson MK, Fish L, Taylor A, Chhabra SR, Camara M, Daykin M, Lamb JH, Swift S, Bycroft BW, Stewart GS, Williams P (1997) Quorum sensing and Chromobacterium violaceum: exploitation of violacein production and inhibition for the detection of N-acylhomoserine lactones. Microbiology 143:3703–3711
Morohoshi T, Someya N, Ikeda T (2009) Novel N-acylhomoserine lactone-degrading bacteria isolated from the leaf surface of Solanum tuberosum and their quorum-quenching properties. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 73:2124–2127
Newman KL, Chatterjee S, Ho KA, Lindow SE (2008) Virulence of plant pathogenic bacteria attenuated by degradation of fatty acid cell-to-cell signaling factors. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 21:326–334
Ravn L, Christensen AB, Molin S, Givskov M, Gram L (2001) Methods for detecting acylated homoserine lactones produced by Gram-negative bacteria and their application in studies of AHL-production kinetics. J Microbiol Methods 44:239–251
Rosenblueth M, Martinez-Romero E (2006) Bacterial endophytes and their interactions with hosts. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 19:827–837
Uroz S, Oger P, Chapelle E, Adeline MT, Faure D, Dessaux Y (2008) A Rhodococcus qsdA-encoded enzyme defines a novel class of large-spectrum quorum-quenching lactonases. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:1357–1366
Versalovic J, Schneider M, Bruijn FJ, Lupski JR (1994) Genomic fingerprinting of bacteria using repetitive sequence-based polymerase chain reaction. Method Mol Cell Biol 5:25–40
Viana ES, Campos MEM, Ponce AR, Mantovani HC, Vanetti MCD (2009) Biofilm formation and acyl homoserine lactone production in Hafnia alvei isolated from raw milk. Biol Res 42:427–436
Winson MK, Swift S, Fish L, Throup JP, Jorgensen F, Chhabra SR, Bycroft BW, Williams P, Stewart GSAB (1998) Construction and analysis of luxCDABE-based plasmid sensors for investigating N-acyl homoserine lactone-mediated quorum sensing. FEMS Microbiol Lett 163:185–192
Yuan HM, Zhang XP, Zhao K, Zhong K, Gu YF, Lindstrom K (2008) Genetic characterisation of endophytic actinobacteria isolated from the medicinal plants in Sichuan. Ann Microbiol 58:597–604
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG) and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lopes, R.B.M., de Oliveira Costa, L.E., Vanetti, M.C.D. et al. Endophytic Bacteria Isolated from Common Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) Exhibiting High Variability Showed Antimicrobial Activity and Quorum Sensing Inhibition. Curr Microbiol 71, 509–516 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-015-0879-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-015-0879-6