Abstract
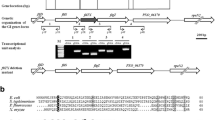
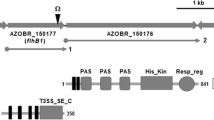
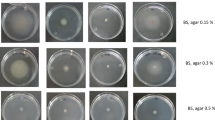
Bacterial motility is most likely a critical factor for rhizobium to chemotactically colonize on the root surface prior to infecting leguminous plant hosts. Several studies of the rhizobium flagellar filament have been reported, but little is known about the rhizobium flagellum hook. To investigate the roles of the hook protein in flagellum synthesis in Mesorhizobium tianshanense, the hook protein-encoding gene flgE of M. tianshanense was amplified by PCR and sequenced. Comparison of the deduced amino acid sequences revealed pronounced similarities in Domain 1 and lower similarities in Domain 2, which are supposed to be related to hook structure assembly and antigenic diversity, respectively. The level of transcription of flgE increased along with the cell growth and reached its maximum at the middle log phase. Disruption of the flgE gene caused a flagellar-less phenotype, thereby causing complete loss of swimming ability, modified nutrient-related swarming ability and biofilm formation. Moreover, the absence of flagellar caused decreased bacterial attachment on the root hair, suggesting that flagellar is involved in the early stage of symbiosis process.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ames P, Bergman K (1981) Competitive advantage provided by bacterial motility in the formation of nodules by Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol 148(2):728–729
Ballado T et al (2001) The hook gene (flgE) is expressed from the flgBCDEF operon in Rhodobacter sphaeroides: Study of an flgE mutant. J Bacteriol 183(5):1680–1687
Beringer JE (1974) R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol 84(1):188–198
Caetano-Anollés G, Wall LG, De Micheli AT, Macchi EM, Bauer WD, Favelukes G (1988) Role of motility and chemotaxis in efficiency of nodulation by Rhizobium meliloti. Plant Physiol 86(4):1228–1235
Chen W, Wang E, Wang S, Li Y, Chen X, Li Y (1995) Characteristics of Rhizobium tianshanense sp nov, a moderately and slowly growing root nodule bacterium isolated from an arid saline environment in Xinjiang, People’s Republic of China. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45(1):153–159
Cooper JE (2004) Multiple responses of rhizobia to flavonoids during legume root infection. Adv Bot Res 41:1–62
Covelli JM, Althabegoiti MJ, Lo´pez MF, Lodeiro AR (2013) Swarming motility in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Res Microbiol 164:136–144
Eggenhofer E, Rachel R, Haslbeck M, Scharf B (2006) MotD of Sinorhizobium meliloti and related α-proteobacteria is the flagellar-hook-length regulator and therefore reassigned as FliK. J Bacteriol 188(6):2144–2153
Fujishige NA, Kapadia NN, De Hoff PL, Hirsch AM (2006) Investigations of Rhizobium biofilm formation. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 56(2):195–206
Glenn-Calvo E, Bär W, Frosch M (1994) Isolation and characterization of the flagellar hook of Campylobacter jejuni. FEMS Microbiol Lett 123(3):209–304
Harshey RM (2003) Bacterial motility on a surface : many ways to a common goal. Annu Rev Microbiol 57(1):249–273
Hellweg C, Pühler A, Weidner S (2009) The time course of the transcriptomic response of Sinorhizobium meliloti 1021 following a shift to acidic pH. BMC Microbiol 9(1):37
Henrichsen J (1972) Bacterial surface translocation : a survey and a classification. Bacteriol Rev 36(4):478
Hirano T, Shibata S, Ohnishi K, Tani T, Aizawa SI (2005) N-terminal signal region of FliK is dispensable for length control of the flagellar hook. Mol Microbiol 56(2):346–360
Kinsella N, Guerry P, Cooney J (1997) The flgE gene of Campylobacter coli is under the control of the alternative sigma factor sigma54. J Bacteriol 179(15):4647–4653
Lüneberg E, Glenn-Calvo E, Hartmann M, Bär W, Frosch M (1998) The central, surface-exposed region of the flagellar hook protein FlgE of Campylobacter jejuni Shows hypervariability among strains. J Bacteriol 180(14):3711–3714
Le MT, Porcelli I, Weight CM, Gaskin DJ, Carding SR, Vliet AH (2012) Acid-shock of Campylobacter jejuni induces flagellar gene expression and host cell invasion. Eur J Microbiol Immunol 2(1):12–19
Li H, Ruby J, Charon N, Kuramitsu H (1996) Gene inactivation in the oral spirochete Treponema denticola: construction of an flgE mutant. J Bacteriol 178(12):3664–3667
Macnab RM (2003) How bacteria assemble flagella. Annu Rev Microbiol 57(1):77–100
Malek W (1992) The role of motility in the efficiency of nodulation by Rhizobium meliloti. Arch Microbiol 158(1):26–28
Mellor HY, Glenn AR, Arwas R, Dilworth MJ (1987) Symbiotic and competitive properties of motility mutants of Rhizobium trifolii TA1. Arch Microbiol 148(1):34–39
Merritt JH, Brothers KM, Kuchma SL, O’toole GA (2007) SadC reciprocally influences biofilm formation and swarming motility via modulation of exopolysaccharide production and flagellar function. J Bacteriol 189(22):8154–8164
Miller JH (1972) Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Miller LD, Yost CK, Hynes MF, Alexandre G (2007) The major chemotaxis gene cluster of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv viciae is essential for competitive nodulation. Mol Microbiol 63(2):348–362
Murray TS, Kazmierczak BI (2008) Pseudomonas aeruginosa exhibits sliding motility in the absence of type IV pili and flagella. J Bacteriol 190(8):2700–2708
Platzer J, Sterr W, Hausmann M, Schmitt R (1997) Three genes of a motility operon and their role in flagellar rotary speed variation in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol 179(20):6391–6399
Rinaudi L, Fujishige NA, Hirsch AM, Banchio E, Zorreguieta A, Giordano W (2006) Effects of nutritional and environmental conditions on Sinorhizobium meliloti biofilm formation. Res Microbiol 157(9):867–875
Sal MS, Li C, Motalab M, Shibata S, Aizawa SI, Charon NW (2008) Borrelia burgdorferi uniquely regulates its motility genes and has an intricate flagellar hook-basal body structure. J Bacteriol 190(6):1912–1921
Samatey FA, Matsunami H, Imada K, Nagashima S, Shaikh TR, Thomas DR, Chen JZ, DeRosier DJ, Kitao A, Namba K (2004) Structure of the bacterial flagellar hook and implication for the molecular universal joint mechanism. Nature 431(7012):1062–1068
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Santaella C, Schue M, Berge O, Heulin T, Achouak W (2008) The exopolysaccharide of Rhizobium sp. YAS34 is not necessary for biofilm formation on Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica napus roots but contributes to root colonization. Environ Microbiol 10(8):2150–2163
Sauer K, Cullen M, Rickard A, Zeef L, Davies D, Gilbert P (2004) Characterization of nutrient-induced dispersion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 biofilm. J Bacteriol 186(21):7312–7326
Scharf B, Schuster-Wolff-Bühring H, Rachel R, Schmitt R (2001) Mutational analysis of the Rhizobium lupini H13-3 and Sinorhizobium meliloti flagellin genes: importance of flagellin A for flagellar filament structure and transcriptional regulation. J Bacteriol 183(18):5334–5342
Skorupska A, Deryło M, Lorkiewicz Z (1989) Siderophore production and utilization by Rhizobium trifolii. Biol Metals 2(1):45–49
Smit G, Logman T, Boerrigter M, Kijne J, Lugtenberg B (1989) Purification and partial characterization of the Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae Ca2+-dependent adhesin, which mediates the first step in attachment of cells of the family Rhizobiaceae to plant root hair tips. J Bacteriol 171(7):4054–4062
Soby S, Bergman K (1983) Motility and chemotaxis of Rhizobium meliloti in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 46(5):995–998
Sourjik V, Muschler P, Scharf B, Schmitt R (2000) VisN and VisR are global regulators of chemotaxis, flagellar, and motility genes in Sinorhizobium (Rhizobium) meliloti. J Bacteriol 182(3):782–788
Tambalo DD, Bustard DE, Del Bel KL, Koval SF, Khan MF, Hynes MF (2010) Characterization and functional analysis of seven flagellin genes in Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae. characterization of R. leguminosarum flagellins. BMC Microbiol 10(1):219
Tambalo DD, Del Bel KL, Bustard DE, Greenwood PR, Steedman AE, Hynes MF (2010) Regulation of flagellar, motility and chemotaxis genes in Rhizobium leguminosarum by the VisN/R-Rem cascade. Microbiology 156(6):1673–1685
Thomason MK, Fontaine F, De Lay N, Storz G (2012) A small RNA that regulates motility and biofilm formation in response to changes in nutrient availability in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 84(1):17–35
Van Houdt R, Michiels CW (2005) Role of bacterial cell surface structures in Escherichia coli biofilm formation. Res Microbiol 156(5):626–633
Vatanyoopaisarn S, Nazli A, Dodd CE, Rees CE, Waites WM (2000) Effect of flagella on initial attachment of Listeria monocytogenes to stainless steel. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(2):860–863
Walker TS, Bais HP, Grotewold E, Vivanco JM (2003) Root exudation and rhizosphere biology. Plant Physiol 132(1):44–51
Wang P, Zhong Z, Zhou J, Cai T, Zhu J (2008) Exopolysaccharide biosynthesis is important for Mesorhizobium tianshanense: plant host interaction. Arch Microbiol 189(5):525–530
Zheng H, Zhong Z, Lai X, Chen WX, Li S, Zhu J (2006) A LuxR/LuxI-type quorum-sensing system in a plant bacterium, Mesorhizobium tianshanense, controls symbiotic nodulation. J Bacteriol 188(5):1943–1949
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Jun Zhu for helpful discussion, and Dr. Yunduan Wang for the gene sequence determination. This study was supported by a 973 project (CB126502, to J.Z.), the Ph.D. programs foundation of the Ministry of Education (MOE) (20120097110016, to J.Z.), and an NSFC award (31170077, to Z.Z).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, H., Mao, Y., Teng, J. et al. Flagellar-Dependent Motility in Mesorhizobium tianshanense is Involved in the Early Stage of Plant Host Interaction: Study of an flgE Mutant. Curr Microbiol 70, 219–227 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-014-0701-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-014-0701-x