Abstract
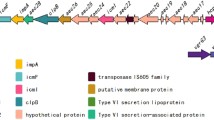
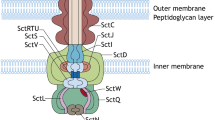
The type VI secretion system (T6SS) of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi (S. typhi) is associated with Salmonella pathogenicity island 6 (SPI-6). Though the T6SS gene cluster is intact in S. typhi, the protein complex is believed to be non-functional due to the presence of a pseudogene form of SciI (VipB homolog), a key component. We detected the SciK-his6 in the supernatant of the wild type strain of S. typhi containing the plasmid over-expressing SciK (hcp homolog) with a his6 epitope at the C-terminus, which suggested that the T6SS in S. typhi is functional. We also identified four genes that were essential to T6SS function: sciC (vasA homolog), sciS (vasK homolog), sciG (clpV homolog), and vrgS (vgrG homolog). Further analysis revealed that S. typhi T6SS is cytotoxic to human epithelial cells, but does not influence bacterial growth and mobility. RcsB, PmrA, and Hfq were identified as regulators of S. typhi T6SS gene expression; however, PhoP appears to not be involved. Taken together, the data demonstrate the functionality of S. typhi T6SS and confirm the important role of T6SS for S. typhi’s ability to invade and infect epithelial cells.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akeda Y, Galan JE (2005) Chaperone release and unfolding of substrates in type III secretion. Nature 437:911–915
Aschtgen MS, Bernard CS, De Bentzmann S et al (2008) SciN is an outer membrane lipoprotein required for Type VI secretion in enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 190:7523–7531
Aschtgen MS, Gavioli M, Dessen A et al (2010) The SciZ protein anchors the enteroaggregative Escherichia coli Type VI secretion system to the cell wall. Mol Microbiol 75:886–899
Bell BL, Mohapatra NP, Gunn JS (2010) Regulation of virulence gene transcripts by the Francisella orphan response regulator PmrA: role of phosphorylation and evidence of MglA/SspA interaction. Infect Immun 78:2189–2198
Bingle LE, Bailey CM, Pallen MJ (2008) Type VI secretion: a beginner’s guide. Curr Opin Microbiol 11:3–8
Blondel CJ, Jimenez JC, Contreras I et al (2009) Comparative genomic analysis uncovers 3 novel loci encoding type six secretion systems differentially distributed in Salmonella serotypes. BMC Genomics 10:354
Blondel CJ, Yang HJ, Castro B et al (2010) Contribution of the type VI secretion system encoded in SPI-19 to chicken colonization by Salmonella enterica serotypes Gallinarum and Enteritidis. PLOS One 5:e11724
Boyer F, Fichant G, Berthod J et al (2009) Dissecting the bacterial type VI secretion system by a genome wide in silico analysis: what can be learned from available microbial genomic resources? BMC Genomics 10:104
Bönemann G, Pietrosiuk A, Diemand A et al (2010) Remodelling of VipA/VipB tubules by ClpV-mediated threading is crucial for type VI protein secretion. EMBO J 28:315–325
Brill JA, Quinlan-Walshe C, Gottesman S (1998) Fine-structure mapping and identification of two regulators of capsule synthesis in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol 170:2599–2611
Connor BA, Schwartz E (2005) Typhoid and paratyphoid fever in travellers. Lancet Infect Dis 5:623–628
Das S, Chakrabortty A, Banerjee R et al (2002) Involvement of in vivo induced icmF gene of Vibrio cholerae in motility, adherence to epithelial cells, and conjugation frequency. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 295:922–928
Dudley E, Thomson N, Parkhill J et al (2006) Proteomic and microarray characterization of the AggR regulon identifies a pheU pathogenicity island in enteroaggregative Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 61:1267–1282
Enos-Berlage JL, Guvener ZT, Keenan CE et al (2005) Genetic determinants of biofilm development of opaque and translucent Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Mol Microbiol 55:1160–1182
Faucher SP, Forest C, Béland M et al (2009) A novel PhoP-regulated locus encoding the cytolysin ClyA and the secreted invasin TaiA of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi is involved in virulence. Microbiology 155:477–488
Filloux A (2009) The type VI secretion system: a tubular story. EMBO J 28:309–310
Filloux A, Hachani A, Bleves S (2008) The bacterial type VI secretion machine: yet another player for protein transport across membranes. Microbiology 154:1570–1583
Folkesson A, Lofdahl S, Normark S (2002) The Salmonella enterica subspecies I specific centisome 7 genomic island encodes novel protein families present in bacteria living in close contact with eukaryotic cells. Res Microbiol 153:537–545
Franze de Fernandez MT, Eoyang L et al (1968) Factor fraction required for the synthesis of bacteriophage Qbeta-RNA. Nature 219:588–590
Groisman EA (2001) The pleiotropic two-component regulatory system PhoP–PhoQ. J Bacteriol 183:1835–1842
Hsu F, Schwarz S, Mougous JD (2009) TagR promotes PpkA-catalysed type VI secretion activation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Microbiol 72:1111–1125
Huang X, Phung le V, Dejsirilert S et al (2004) Cloning and characterization of the gene encoding the z66 antigen of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi. FEMS Microbiol Lett 234:239–246
Ishikawa T, Rompikuntal PK, Lindmark B et al (2009) Quorum sensing regulation of the two hcp alleles in Vibrio cholerae O1 strains. PLoS One 4:e6734
Kevin BL, Henrik CS, Karina JK et al (2010) Salmonella enterica bacteraemia: a multi-national population-based cohort study. BMC Infect Dis 10:95
Leiman PG, Basler M, Ramagopal UA et al (2009) Type VI secretion apparatus and phage tail-associated protein complexes share a common evolutionary origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:4154–4159
Ma LS, Lin JS, Lai EM (2009) An IcmF family protein, ImpLM, is an integral inner membrane protein interacting with ImpKL, and its walker a motif is required for type VI secretion system-mediated SciK secretion in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol 191:4316–4329
Mougous JD, Gifford CA, Ramsdell TL et al (2007) Threonine phosphorylation post-translationally regulates protein secretion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nat Cell Biol 9:797–803
Mougous JD, Cuff ME, Raunser S et al (2006) A virulence locus of Pseudomonas aeruginosa encodes a protein secretion apparatus. Science 312:1526–1530
Mouslim C, Latifi T, Groisman EA (2003) Signal-dependent requirement for the co-activator protein RcsA in transcription of the RcsB-regulated ugd gene. J Biol Chem 278:50588–50595
Nassif X, Honoré N, Vasselon T et al (1998) Positive control of colanic acid synthesis in Escherichia coli by rmpA and rmpB, two virulence-plasmid genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Mol Microbiol 3:1349–1359
Neuwald AF, Aravind L, Spouge JL et al (1999) AAA+: a class of chaperone-like ATPases associated with the assembly, operation, and disassembly of protein complexes. Genome Res 9:27–43
Nielsen H, Gradel KO, Schonheyder HC (2006) High incidence of intravascular focus in nontyphoid Salmonella bacteremia in the age group above 50 years: a population-based study. Apmis 114:641–645
Parkhill J, Dougan G, James KD et al (2001) Complete genome sequence of a multiple drug resistant Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi CT18. Nature 413:848–852
Parry CM, Hien TT, Dougan G et al (2002) Typhoid fever. N Engl J Med 347:1770–1782
Parsons DA, Heffron F (2005) sciS, an icmF homolog in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, limits intracellular replication and decreases virulence. Infect Immun 73:4338–4345
Porwollik S, Boyd EF, Choy C et al (2004) Characterization of Salmonella enterica subspecies I genovars by use of microarrays. J Bacteriol 186:5883–5898
Pukatzki S, Ma AT, Sturtevant D et al (2006) Identification of a conserved bacterial protein secretion system in Vibrio cholerae using the Dictyostelium host model system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:1528–1533
Santos RL, Zhang S, Tsolis RM et al (2001) Animal models of Salmonella infections: enteritis versus typhoid fever. Microbes Infect 3:1335–1344
Schwan WR, Huang XZ, Hu L et al (2000) Differential bacterial survival, replication, and apoptosis-inducing ability of Salmonella serovars within human and murine macrophages. Infect Immun 68:1005–1013
Schlieker C, Zentgraf H, Dersch P et al (2005) ClpV, a unique Hsp100/Clp member of pathogenic proteobacteria. Biol Chem 386:1115–1127
Shrivastava S, Mande SS (2008) Identification and functional characterization of gene components of type VI secretion system in bacterial genomes. PLoS One 3:e2955
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:4350–4354
Virlogeux I, Waxin H, Ecobichon C et al (1996) Characterization of the rcsA and rcsB genes from Salmonella typhi: rcsB through tviA is involved in regulation of Vi antigen synthesis. J Bacteriol 178:1691–1698
Weber B, Hasic M, Chen C, Wai SN et al (2009) Type VI secretion modulates quorum sensing and stress response in Vibrio anguillarum. Environ Microbiol 11:3018–3028
Wösten MM, Kox LF, Chamnongpol S et al (2000) A signal transduction system that responds to extracellular iron. Cell 103:113–125
Wu HY, Chung PC, Shih HW et al (2008) Secretome analysis uncovers an SciK-family protein secreted via a type VI secretion system in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol 190:2841–2850
Xu S, Zhang H, Sheng X, Xu H et al (2008) Transcriptional expression of fljB:z66, a flagellin gene located on a novel linear plasmid of Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi under environmental stresses. New Microbiol 31:241–247
Zheng J, Leung K (2007) Dissection of a type VI secretion system in Edwardsiella tarda. Mol Microbiol 66:1192–1206
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30870095), National Special Scientific Program (2008ZX10004-009). We thank Jie Tian, Yan Liu, Dong Zheng, and Yinxia Zhao for technical assistance. We also appreciate International Science Editing for language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Luo, Z., Du, H. et al. Molecular Characterization of a Functional Type VI Secretion System in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi. Curr Microbiol 63, 22–31 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-011-9935-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-011-9935-z