Abstract
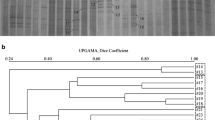
Human flora-associated (HFA) mice are frequently applied in studying the ecology and metabolism of human gut microbiota. However, the development and stability of the genus Bacteriodes, a prominent bacteria group of human gut microbiota, in HFA mice have not yet fully been examined. In this study, PCR-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) analysis was employed to monitor the Bacteriodes community in the fecal microbiota of six HFA Kunming mice during a period of 3 weeks. Based on the DGGE banding patterns, the majority of prominent bands in the HFA mice DGGE profile were also typical bands in the human DGGE profile, despite the absence of three bands (corresponding to two different B. thetaiotaomicron strains and one B. intestinalis strain) from the human DGGE profile. The Dice coefficient of similarity for the fecal microbiota of HFA mice in comparison to the human donor sample ranged between 74 ± 6% and 81 ± 7%. The phylogeny of bands in the DGGE profile showed that the dominant Bacteriodes species in the fecal microbiota of HFA mice were B. thetaiotaomicron, representing 66.7% of all bands. Our results indicate that the genus Bacteriodes in the fecal microbiota of HFA mice was selected from the human donor and could remain relatively stable over time.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpert C, Sczesny S, Gruhl B, Blaut M (2008) Long-term stability of the human gut microbiota in two different rat strains. Curr Issues Mol Biol 10:17–24
Backhed F, Ley RE, Sonnenburg JL, Peterson DA, Gordon JI (2005) Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science 307:1915–1920
Bernbom N, Norrung B, Saadbye P, Molbak L, Vogensen FK, Licht TR (2006) Comparison of methods and animal models commonly used for investigation of fecal microbiota: effects of time, host and gender. J Microbiol Methods 66:87–95
Eckburg PB, Bik EM, Bernstein CN, Purdom E, Dethlefsen L, Sargent M, Gill SR, Nelson KE, Relman DA (2005) Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science 308:1635–1638
Edwards CA, Rumney C, Davies M, Parrett AM, Dore J, Martin F, Schmitt J, Stahl B, Norin E, Midtvedt T, Rowland IR, Heavey P, Kohler H, Stocks B, Schroten H (2003) A human flora-associated rat model of the breast-fed infant gut. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 37:168–177
Franks AH, Harmsen HJ, Raangs GC, Jansen GJ, Schut F, Welling GW (1998) Variations of bacterial populations in human feces measured by fluorescent in situ hybridization with group-specific 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:3336–3345
Gerard P, Beguet F, Lepercq P, Rigottier-Gois L, Rochet V, Andrieux C, Juste C (2004) Gnotobiotic rats harboring human intestinal microbiota as a model for studying cholesterol-to-coprostanol conversion. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 47:337–343
Hayashi H, Sakamoto M, Benno Y (2002) Phylogenetic analysis of the human gut microbiota using 16S rDNA clone libraries and strictly anaerobic culture-based methods. Microbiol Immunol 46:535–548
Hazenberg MP, Bakker M, Verschoor-Burggraaf A (1981) Effects of the human intestinal flora on germ-free mice. J Appl Bacteriol 50:95–106
Hirayama K (1999) Ex-germfree mice harboring intestinal microbiota derived from other animal species as an experimental model for ecology and metabolism of intestinal bacteria. Exp Anim 48:219–227
Hirayama K, Kawamura S, Mitsuoka T (1991) Development and stability of human faecal flora in the intestine of ex-germ-free mice. Microbial Ecol Health Dis 4:95–99
Hirayama K, Itoh K, Takahashi E, Mitsuoka T (1995) Comparison of composition of faecal microbiota and metabolism of faecal bacteria among ‘human-flora-associated’ mice inoculated with faeces from six different human donors. Microbial Ecol Health Dis 8:199–211
Hong PY, Wu JH, Liu WT (2008) Relative abundance of Bacteroides spp. in stools and wastewaters as determined by hierarchical oligonucleotide primer extension. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:2882–2893
Imaoka A, Setoyama H, Takagi A, Matsumoto S, Umesaki Y (2004) Improvement of human faecal flora-associated mouse model for evaluation of the functional foods. J Appl Microbiol 96:656–663
Kibe R, Sakamoto M, Yokota H, Ishikawa H, Aiba Y, Koga Y, Benno Y (2005) Movement and fixation of intestinal microbiota after administration of human feces to germfree mice. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:3171–3178
Ley RE, Backhed F, Turnbaugh P, Lozupone CA, Knight RD, Gordon JI (2005) Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:11070–11075
Licht TR, Madsen B, Wilcks A (2007) Selection of bacteria originating from a human intestinal microbiota in the gut of previously germ-free rats. FEMS Microbiol Lett 277:205–209
Liu C, Song Y, McTeague M, Vu AW, Wexler H, Finegold SM (2003) Rapid identification of the species of the Bacteroides fragilis group by multiplex PCR assays using group- and species-specific primers. FEMS Microbiol Lett 222:9–16
Muyzer G, de Waal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes coding for 16S rRNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
Pang X, Ding D, Wei G, Zhang M, Wang L, Zhao L (2005) Molecular profiling of Bacteroides spp. in human feces by PCR-temperature gradient gel electrophoresis. J Microbiol Methods 61:413–417
Raibaud P, Ducluzeau R, Dubos F, Hudault S, Bewa H, Muller MC (1980) Implantation of bacteria from the digestive tract of man and various animals into gnotobiotic mice. Am J Clin Nutr 33:2440–2447
Sanguinetti CJ, Dias Neto E, Simpson AJ (1994) Rapid silver staining and recovery of PCR products separated on polyacrylamide gels. Biotechniques 17:914–921
Satokari RM, Vaughan EE, Akkermans AD, Saarela M, de Vos WM (2001) Bifidobacterial diversity in human feces detected by genus-specific PCR and denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Appl Environ Microbiol 67:504–513
Shen J, Zhang B, Wei G, Pang X, Wei H, Li M, Zhang Y, Jia W, Zhao L (2006) Molecular profiling of the Clostridium leptum subgroup in human fecal microflora by PCR-denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and clone library analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5232–5238
Turnbaugh PJ, Ley RE, Mahowald MA, Magrini V, Mardis ER, Gordon JI (2006) An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 444:1027–1031
Wilson KH, Ikeda JS, Blitchington RB (1997) Phylogenetic placement of community members of human colonic biota. Clin Infect Dis 25:S114–S116
Xu J, Bjursell MK, Himrod J, Deng S, Carmichael LK, Chiang HC, Hooper LV, Gordon JI (2003) A genomic view of the human-Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron symbiosis. Science 299:2074–2076
Zaneveld J, Turnbaugh PJ, Lozupone C, Ley RE, Hamady M, Gordon JI, Knight R (2008) Host-bacterial coevolution and the search for new drug targets. Curr Opin Chem Biol 12:109–114
Acknowledgments
This study was sponsored by National Key Technologies R&D Program of China during the 11th Five-Year Plan Period (2006BAK02A03-2), National Basic Research Program of China (2007CB513007) and National High-tech R&D Program of China (2007AA10Z356).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, J., Zeng, B., Niu, R. et al. The Development and Stability of the Genus Bacteriodes from Human Gut Microbiota in HFA Mice Model. Curr Microbiol 62, 1107–1112 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-010-9833-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-010-9833-9