Abstract
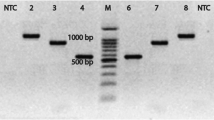
In this study we compared two routine PCR systems for the detection of Leptospira spp. and assessed their performance when directly applied to kidney samples from small mammals. Although the kappa value of 0.9 indicated a high level of agreement between the tests, the outer membrane lipoprotein gene lipl32 based PCR was more robust and showed a higher number of positive kidney samples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous. (28 July 1998) What is molecular epidemiology?. Molecular Epidemiology Homepage. University of Pittsburgh. http://www.pitt.edu/~kkr/molepi.html. Retrieved 15 Nov 2010
Bal AE, Gravekamp C, Hartskeerl RA et al (1994) Detection of leptospires in urine by PCR for early diagnosis of leptospirosis. J Clin Microbiol 32(8):1894–1898
Bär W, Kratzer A, Mächler M, Schmid W (1988) Postmortem stability of DNA. Forensic Sci Int 39(1):59–70
Cerqueira GM, Picardeau M (2009) A century of Leptospira strain typing. Infect Genet Evol 9(5):760–768 2009 Sep
Faine S (1999) Leptospira and Leptospirosis. MedSci, Melbourne
Gravekamp C, Van de Kemp H, Franzen M et al (1993) Detection of seven species of pathogenic leptospires by PCR using two sets of primers. J Gen Microbiol 139(8):1691–1700
Guerra MA (2009) Leptospirosis. J Am Vet Med Assoc 234(4):472–478
Haake DA, Chao G, Zuerner RL et al (2000) The leptospiral major outer membrane protein LipL32 is a lipoprotein expressed during mammalian infection. Infect Immun 68(4):2276–2285
Holland NT, Smith MT, Eskenazi B et al (2003) Biological sample collection and processing for molecular epidemiological studies. Mutat Res 543(3):217–234
Hoorfar J, Malorny B, Abdulmawjood A et al (2004) Practical considerations in design of internal amplification controls for diagnostic PCR assays. J Clin Microbiol 42(5):1863–1868
Karaseva EV, Chernukha YG, Piskunova LA (1973) Results of studying the time of survival of pathogenic leptospira under natural conditions. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol 17(3):339–345
Levett PN, Morey RE, Galloway RL et al (2005) Detection of pathogenic leptospires by real-time quantitative PCR. J Med Microbiol 54(Pt 1):45–49
Levett PN (2001) Leptospirosis. Clin Microbiol Rev 14(2):296–326
Petrie A, Watson P (2006) Additional techniques. In: statistics for veterinary and animal science, 2nd edn. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 200–201
Sasse D, Reuter G (1978) Survival ability of Leptospira pomona in kidney and muscle tissue of slaughtered pigs in freezing temperatures. Berl Munch Tierarztl Wochenschr 91(7):130–136
Ulrich RG, Schmidt-Chanasit J, Schlegel M et al (2008) Network “Rodent-borne pathogens” in Germany: longitudinal studies on the geographical distribution and prevalence of hantavirus infections. Parasitol Res 103(1):121–129
Vijayachari P, Sugunan AP, Shriram AN (2008) Leptospirosis: an emerging global public health problem. J Biosci 33(4):557–569
World Health Organization Human leptospirosis: guidance for diagnosis, surveillance and control http://whqlibdoc.who.int/hq/2003/WHO_CDS_CSR_EPH_2002.23.pdf accessed 19.02.2010
Acknowledgments
The assistance of Dörte Kaufmann and Mathias Schlegel in necropsy and sample collection is kindly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mayer-Scholl, A., Draeger, A., Luge, E. et al. Comparison of Two PCR Systems for the Rapid Detection of Leptospira spp. from Kidney Tissue. Curr Microbiol 62, 1104–1106 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-010-9829-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-010-9829-5