Abstract
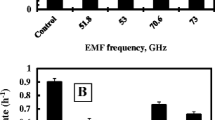
Antibacterial effects of the electromagnetic irradiation (EMI) of 51.8 and 53 GHz frequencies with low intensity (the flux capacity of 0.06 mW/cm2) and non-thermal action were investigated upon direct irradiation of E. coli K12. Significant decrease in bacterial growth rate and in the number of viable cells, marked change in H+ and K+ transport across membrane were shown. Subsequent addition of kanamycin or ceftriaxone (15 or 0.4 μM, respectively) enhanced the effects of irradiation. This was maximally achieved at the frequency of 53 GHz. These all might reveal membrane as probable target for antibacterial effects. Apparently, the action of EMI on bacteria might lead to changed membrane properties and to antibiotic resistance. The results should improve using extremely high frequency EMI in combination with antibiotics in biotechnology, therapeutic practice, and food industry.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akopyan K, Trchounian A (2006) Escherichia coli membrane proton conductance and proton efflux depend on growth pH and are sensitive to osmotic stress. Cell Biochem Biophys 46:201–208
Belyaev I, Shcheglov V, Alipov Y et al (1996) Current state and implications of research on biological effects of millimeter waves. Bioelectromagnetics 17:312–321
Betskii O, Devyatkov N, Kislov V (2000) Low intensity millimeter waves in medicine and biology. Crit Rev Biomed Eng 28:247–268
Bulgakova V, Grushina V, Orlova T et al (1996) The effect of millimeter-band radiation of non-thermal intensity on sensitivity of Staphylococcus to various antibiotics. Biophysics 41:1289–1293
Fesenko E, Geletyuk V, Kazachenko V et al (1995) Preliminary microwave irradiation of water solutions changes their channel-modifying activity. FEBS Lett 366:49–52
Golant M (1989) Resonance effect of coherent millimeter-band electromagnetic waves on living organisms. Biophysics 34:1004–1014 (in Russian)
Isakhanyan V, Trchounian A (2005) Indirect and repeated electromagnetic irradiation with extremely high frequency of bacteria Escherichia coli. Biophysics 50:604–606
Kirakosyan G, Bagramyan K, Trchounian A (2004) Redox sensing by Escherichia coli: effects of dithiothreitol, a redox reagent reducing disulphides, on bacterial growth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 325:803–806
Kirakosyan G, Trchounian K, Vardanyan Z et al (2008) Copper (II) Ions affect Escherichia coli membrane vesicles’ SH-groups and a disulfide-dithiol interchange between membrane proteins. Cell Biochem Biophys 51:45–50
Kohansky M, Dwyer D, Hayete B et al (2007) A common mechanism of cellular death induced by bactericidal antibiotics. Cell 130:797–810
Lee S, Hinz A, Bauerle E et al (2009) Targeting a bacterial stress response to enhance antibiotic action. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:14570–14575
Lukashevsky K, Belyaev I (1990) Switching of prophage λ genes in E. coli by millimeter waves. Med Sci Res 18:955–957
Markarian S, Poladyan A, Kirakosyan G et al (2002) Effect of diethylsulphoxide on growth, survival and ion exchange of Escherichia coli. Lett Appl Microbiol 34:417–421
McMurry L, Hendricks M, Levy S (1986) Effects of toluene permeabilization and cell deenergization on tetracycline resistance in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 29:681–686
Mirzoyan N, Pepoyan A, Trchounian A (2006) Modification of the biophysical characteristics of membranes in commensal Escherichia coli strains from breast cancer patients. FEMS Microbiol Lett 254:81–86
Nelson M, Levy S (1999) Reversal of tetracycline resistance mediated by different bacterial tetracycline resistance determinants by an inhibitor of the Tet(B) antiport protein. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 43:1719–1724
Novoselova E, Glushkova O, Sinotova O et al (2005) Stress response of the cell to exposure to ultraweak electromagnetic radiation. Dokl Russ Acad Sci 401:117–119 (in Russian)
Pakhomov A, Yahya A, Pakhomova O et al (1998) Current state and implications of research on biological effects of millimeter waves. Bioelectromagnetics 19:393–413
Poladyan A, Trchounian A (1999) Stoichiometry of the proton-potassium exchange in Enterococcus hirae grown at high pH values. Biophysics 44:472–474
Tadevosyan H, Kalantaryan V, Trchounian A (2007) The effects of electromagnetic radiation of extremely high frequency and low intensity on the growth rate of Escherichia coli and the role of medium pH. Biophysics 52:893–898
Tadevosyan H, Kalantaryan V, Trchounian A (2008) Extremely high frequency electromagnetic radiation enforces bacterial effects of inhibitors and antibiotics. Cell Biochem Biophys 51:97–103
Tadevosyan H, Trchounian A (2009) Effect of coherent extremely high-frequency and low-intensity electromagnetic radiation on the activity of membrane systems of Escherichia coli bacteria. Biophysics 54:1055–1059 (in Russian)
Trchounian A, Ohandjanyan E, Bagramyan K et al (1998) Relationship of the Escherichia coli TrkA system of potassium ion uptake with the F0F1-ATPase under growth conditions without anaerobic or aerobic respiration. Biosci Rep 18:143–154
Trchounian A, Ogandzhanyan E, Sarkisyan E et al (2001) Membranotropic effects of electromagnetic radiation of extremely high frequency in Escherichia coli. Biophysics 46:69–76
Trchounian A (2004) Escherichia coli proton-translocating F0F1-ATP synthase and its association with solute secondary transporters and/or enzymes of anaerobic oxidation-reduction under fermentation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 315:1051–1057
Trchounian A (2009) Potassium transport by bacteria: electrochemical approach, energetic and mechanisms. In: Trchounian A (ed) Bacterial membranes. Ultrastructure, bioelectrochemistry, bioenergetics and biophysics. Research Signpost, Trivandrum (India), pp 65–111
Trushin M (2003) The possible role of electromagnetic fields in bacterial communication. J Microbiol Immunol Infect 36:153–160
Zakharyan E, Trchounian A (2001) K+ influx by Kup in Escherichia coli is accompanied by a decrease in H+ efflux. FEMS Microbiol Lett 204:61–64
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. V. Kalantaryan for generous supply of generator G-141 and valuable advices as well for help in undertaking some experiments. This study was supported by Ministry of Education and Science of the Republic of Armenia (Grant # 1012-2008) and by Armenian National Science and Education Fund (ANSEF) project (Grant # NS-Microbiol-1635).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Torgomyan, H., Tadevosyan, H. & Trchounian, A. Extremely High Frequency Electromagnetic Irradiation in Combination with Antibiotics Enhances Antibacterial Effects on Escherichia coli . Curr Microbiol 62, 962–967 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-010-9811-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-010-9811-2