Abstract
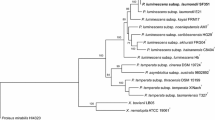
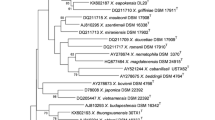
Association between bacteria Photorhabdus and their nematode hosts Heterorhabditis represents one of the emerging models in symbiosis studies. In this study, we isolated the bacterial symbionts of the nematode Heterorhabditis georgiana. Using gyrB sequences for phylogenetic analysis, these strains were shown to be part of the species of Photorhbdus luminescens but with clear separation from currently recognized subspecies. Physiological properties and DNA–DNA hybridization profiles also supported the phylogenetic relationship of these strains. Therefore, a new subspecies, Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. kleinii subsp. nov., is proposed with the type strain KMD37T (=DSM 23513 =ATCC =NRRL B-59419).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhurst RJ, Boemare NE, Janssen PH, Peel MM, Alfredson DA, Beard CE (2004) Taxonomy of Australian clinical isolates of the genus Photorhabdus and proposal of Photorhabdus asymbiotica subsp. asymbiotica subsp. nov. and P. asymbiotica subsp. australis subsp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1301–1310
Akhurst RJ, Mourant RG, Baud L, Boemare N (1996) Phenotypic and DNA relatedness between nematode symbionts and clinical strains of the genus Photorhabdus (Enterobacteriaceae). Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:1034–1041
An R, Grewal P (2010) Photorhabdus temperata subsp. stackebrandtii subsp. nov. (Enterobacteriales: Enterobacteriaceae). Curr Microbiol. doi:10.1007/s00284-010-9610-9
An R, Sreevatsan S, Grewal PS (2009) Comparative in vivo gene expression of the closely related bacteria Photorhabdus temperata and Xenorhabdus koppenhoeferi upon infection of the same insect host, Rhizotrogus majalis. BMC Genomics 10:433
Bowen D, Rocheleau TA, Blackburn M, Andreev O, Golubeva E, Bhartia R, ffrench-Constant RH (1998) Insecticidal toxins from the bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens. Science 280:2129–2132
Fischer-Le Saux M, Viallard V, Brunel B, Normand P, Boemare NE (1999) Polyphasic classification of the genus Photorhabdus and proposal of new taxa: P. luminescens subsp. luminescens subsp. nov., P. luminescens subsp. akhurstii subsp. nov., P. luminescens subsp. laumondii subsp. nov., P. temperata sp. nov., P. temperata subsp. temperata subsp. nov. and P. asymbiotica sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49:1645–1656
Grewal PS, Ehlers RU, Shapiro-Ilan DI (2005) Nematodes as biocontrol agents. CABI Publishing, CAB International, Oxon, UK
Hazir S, Stackebrandt E, Lang E, Schumann P, Ehlers RU, Keskin N (2004) Two new subspecies of Photorhabdus luminescens, isolated from Heterorhabditis bacteriophora (Nematoda: Heterorhabditidae): Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. kayaii subsp. nov. and Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. thracensis subsp. nov. Syst Appl Microbiol 27:36–42
Ruby EG (2008) Symbiotic conversations are revealed under genetic interrogation. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:752–762
Tailliez P, Laroui C, Ginibre N, Paule A, Pages S, Boemare N (2009) Phylogeny of Photorhabdus and Xenorhabdus based on universally conserved protein-coding sequences and implications for the taxonomy of these two genera. Proposal of new taxa: X. vietnamensis sp. nov., P. luminescens subsp. caribbeanensis subsp. nov., P. luminescens subsp. hainanensis subsp. nov., P. temperata subsp. khanii subsp. nov., P. temperata subsp. tasmaniensis subsp. nov., and the reclassification of P. luminescens subsp. thracensis as P. temperata subsp. thracensis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. doi:ijs.0.014308-014300
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tóth T, Lakatos T (2008) Photorhabdus temperata subsp. cinerea subsp. nov., isolated from Heterorhabditis nematodes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2579–2581
Yamamoto S, Harayama S (1995) PCR amplification and direct sequencing of gyrB genes with universal primers and their application to the detection and taxonomic analysis of Pseudomonas putida strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:1104–1109
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from the Ohio Agricultural Research and Development Center of The Ohio State University, Wooster, Ohio. The authors thank Drs. Byron J. Adams and Michael D. Klein for providing nematode strains.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00284-011-9907-3
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, R., Grewal, P.S. Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. kleinii subsp. nov. (Enterobacteriales: Enterobacteriaceae). Curr Microbiol 62, 539–543 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-010-9741-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-010-9741-z