Abstract
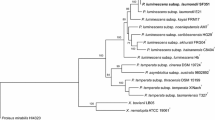
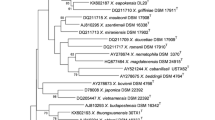
The bacterial symbiont of the entomopathogenic nematode Heterorhabditis bacteriophora strain GPS11 was characterized by 16S rRNA gene sequence and physiological traits. The phylogenetic tree built upon 16S rRNA gene sequences clustered the GPS11 bacterial isolate with Photorhabdus temperata strains which have been previously isolated from Heterorhabditis species. The phylogenetic tree further identified four subgroups in P. temperata, and the relationships among these subgroups were confirmed by gyrase subunit B (gyrB) gene sequence analysis. The subgroup containing the GPS11 bacterial isolate differs from other subgroups in sequences of 16S rRNA and gyrB gene, physiological traits, nematode host species, and geographic origin. Therefore, the subgroup comprising the GPS11 bacterial isolate is proposed here as a new subspecies: Photorhabdus temperata subsp. stackebrandtii subsp. nov. (type strain GPS11). The type strain has been deposited in ATCC and DSMZ collections.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhurst RJ, Mourant RG, Baud L, Boemare N (1996) Phenotypic and DNA relatedness between nematode symbionts and clinical strains of the genus Photorhabdus (Enterobacteriaceae). Int J Syst Bacteriol 46:1034–1041
Akhurst RJ, Boemare NE, Janssen PH, Peel MM, Alfredson DA, Beard CE (2004) Taxonomy of Australian clinical isolates of the genus Photorhabdus and proposal of Photorhabdus asymbiotica subsp. asymbiotica subsp. nov. and P. asymbiotica subsp. australis subsp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1301–1310
Boemare N (2002) Biology, taxonomy and systematics of Photorhabdus and Xenorhabdus. In: Gaugler R (ed) Entomopathogenic nematology. CABI Publishing, New York, pp 35–56
Burnell AM, Stock SP (2000) Heterorhabditis, Steinernema and their bacterial symbionts—lethal pathogens of insects. Nematology 2:31–42
Duchaud E, Rusniok C, Frangeul L, Buchrieser C, Givaudan A, Taourit S, Bocs S, Boursaux-Eude C, Chandler M, Charles JF, Dassa E, Derose R, Derzelle S, Freyssinet G, Gaudriault S, Médigue C, Lanois A, Powell K, Siguier P, Vincent R, Wingate V, Zouine M, Glaser P, Boemare N, Danchin A, Kunst F (2003) The genome sequence of the entomopathogenic bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens. Nat Biotechnol 21:1307–1313
Fischer-Le Saux M, Viallard V, Brunel B, Normand P, Boemare NE (1999) Polyphasic classification of the genus Photorhabdus and proposal of new taxa: P. luminescens subsp. luminescens subsp. nov., P. luminescens subsp. akhurstii subsp. nov., P. luminescens subsp. laumondii subsp. nov., P. temperata sp. nov., P. temperata subsp. temperata subsp. nov. and P. asymbiotica sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 49:1645–1656
Grewal PS, Lewis EE, Gaugler R (1997) Response of infective stage parasites (Nematoda: Steinernematidae) to volatile cues from infected hosts. J Chem Ecol 23:503–515
Grewal PS, Grewal SK, Malik VS, Klein MG (2002) Differences in susceptibility of introduced and native white grub species to entomopathogenic nematodes from various geographic localities. Biol Control 24:230–237
Hazir S, Kaya HK, Stock SP, Keskun N (2003) Entomopathogenic nematodes (Steinernematidae and Heterorhabditidae) for biological control of soil pests. Turk J Biol 27:181–202
Hazir S, Stackerbandt E, Lang E, Schumann P, Ehlers RU, Keskin N (2004) Two new subspecies of Photorhabdus luminescens, isolated from Heterorhabditis bacteriophora (Nematoda: Heterorhabditidae): Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. kayaii subsp. nov and Photorhabdus luminescens subsp. thracensis subsp. nov. Syst Appl Microbiol 27:36–42
Joyce SA, Watson RJ, Clarke DJ (2006) The regulation of pathogenicity and mutualism in Photorhabdus. Curr Opin Microbiol 9:1–6
Kalita M, Małek W, Kaznowski A (2004) Analysis of genetic relationship of Sarothamnus scoparius microsymbionts and Bradyrhizobium sp. by hybridization in microdilution wells. J Biosci Bioeng 97:158–161
Marokhazi J, Waterfield N, LeGoff G, Feil E, Stabler R, Hinds J, Fodor A, ffrench-Constant RH (2003) Using a DNA microarray to investigate the distribution of insect virulence factors in strains of Photorhabdus bacteria. J Bacteriol 185:4648–4656
Nielsen O, Lubeck PS (2002) Characterization of symbionts of entomopathogenic nematodes by universally primed-PCR (UP-PCR) and UP-PCR product cross-hybridization. FEMS Microbiol Lett 215:63–68
Poinar GO (1990) Biology and taxonomy of Steinernematidae and Heterorhabditidae. In: Gaugler R, Kaya HK (eds) Entomopathogenic nematodes in biological control. CRC press, Boca Raton, pp 23–62
Power DA (1988) Manual of BBL® products and laboratory procedures, 6th edn. Becton Dickinson Microbiology Systems, Cockeysville
Staley J, Krieg NR (1984) Bacterial classification I. Classification of prokaryotic organisms: an overview. In: Krieg NR, Holt JG (eds) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 1. The Williams & Wilkins Co, Baltimore, pp 1–4
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tarrand JJ, Groschel DH (1982) Rapid, modified oxidase test for oxidase-variable bacterial isolates. J Clin Microbiol 16:772–774
Tóth T, Lakatos T (2008) Photorhabdus temperata subsp. cinerea subsp. nov., isolated from Heterorhabditis nematodes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2579–2581
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by an interdisciplinary grant from the Ohio Agricultural Research and Development Center of The Ohio State University, Wooster, Ohio.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, R., Grewal, P.S. Photorhabdus temperata subsp. stackebrandtii subsp. nov. (Enterobacteriales: Enterobacteriaceae). Curr Microbiol 61, 291–297 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-010-9610-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-010-9610-9