Abstract
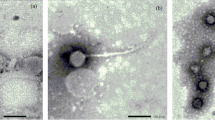
The bacteriophage BA3 multiplies in and lyses the coral pathogen Thalassomonas loyana. The complete genome of phage BA3 was sequenced; it contains 47 open reading frames with a 40.9% G + C content. Phage BA3 adsorbed to its starved host in seawater with a k = 1.0 × 10−6 phage ml−1 min−1. Phage therapy of coral disease in aquarium experiments was successful when the phage was added at the same time as the pathogen or 1 day later, but failed to protect the coral when added 2 days after bacterial infection. When the phages were added 1 day after coral infection, the phage titer increased about 100-fold and remained present in the aquarium water throughout the 37-day experiment. At the end of the experiment, the concentration of phages associated with the corals was 2.5 ± 0.5 × 104 per cm2 of coral surface. Corals that were infected with the pathogen and treated with phage did not transmit the disease to healthy corals.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MH (1959) Bacteriophage. Interscience, New York
Barash Y, Sulam R, Loya Y, Rosenberg E (2005) Bacterial Strain BA-3 and a filterable factor cause a white plague-like disease in corals from the Eilat coral reef. Aquat Microb Ecol 40:183–189
Ben-Haim Y, Rosenberg E (2002) A novel Vibrio sp pathogen of the coral Pocillopora damicornis. Mar Biol 141:47–55
Ben-Haim Y, Zicherman-Keren M, Rosenberg E (2003) Temperature-regulated bleaching and lysis of the coral Pocillopora damicornis by the novel pathogen Vibrio coralliilyticus. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4236–4242
Bruno JF, Petes LE, Harvell CD, Hettinger A (2003) Nutrient enrichment can increase the severity of coral diseases. Ecol Lett 6:1056–1061
Bryant D, Burke L, McManus JW, Spalding M (1998) Reefs at risk. A map-based indicator of threats to the world’s coral reefs. World Resources Institute, Washington, DC
Cervino J, Hayes R, Polson S, Goreau T, Martinez R, Smith G (2004) Relationship of Vibrio species infection and elevated temperatures to yellow blotch/band disease in Caribbean corals. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6855–6864
Efrony R, Loya Y, Bacharach E, Rosenberg E (2007) Phage therapy of coral disease Coral Reefs 26:7–13
Gardner T, Cote I, Gill J, Grant A, Watkinson A (2003) Long-term region-wide declines in Caribbean corals. Science 301:958–960
Green EP, Bruckner AW (2000) The significance of coral disease epizootiology for coral reef conservation. Biol Conserv 96:347–361
Harvell CD, Mitchell CE, Ward JR, Altizer S, Dobson AP, Ostfeld RS, Samuel MD (2002) Climate warming and disease risks for terrestrial and marine biota. Science 296:2158–2162
Kerri M, Mullen EC, Peters C, Harvell D (2004) Coral resistance to disease. In: Rosenberg E, Loya Y (eds) Coral health and disease. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg, pp 377–399
Kuntz NM, Kline DI, Sandin SA, Rowher FL (2005) Pathologies and mortality rates caused by organic carbon and nutrient stressors in three Caribbean coral species. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 294:173–180
Moran NA, Degnan PH, Santos SR, Dunbar HE, Ochman H (2005) The players in a mutualistic symbiosis: insects, bacteria, viruses and virulence genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:16919–16926
Nair SV, Del Valle H, Gross PS, Terwilliger DP, Smith LC (2005) Macroarray analysis of coelomocyte gene expression in response to LPS in the sea urchin. Identification of unexpected immune diversity in an invertebrate. Physiol Genomics 22:33–47
Paul JH, Sullivan MB (2005) Marine phage genomics: what have we learned? Curr Opin Biotech 16:299–307
Ritchie KB, Polson SW, Smith G (2001) Microbial disease causation in marine invertebrates: problems, practices, and future prospects. Hydrobiologia 460:131–139
Rosenberg E, Ben-Haim Y (2002) Microbial diseases of corals and global warming. Environ Microbiol 4:318–326
Rosenberg E, Koren O, Reshef L, Efrony R, Zilber-Rosenberg I (2007) The role of microorganisms in coral health, disease and evolution. Nature Rev Microbiol 5:355–362
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Stent SG (1963) Molecular biology of bacterial viruses. Freeman WH and company publishers, San Francisco
Thompson FL, Barash Y, Sawabe T, Sharon G, Swings J, Rosenberg E (2006) Thalassomonas loyana sp. nov., a causative agent of the white plague-like disease of corals on the Eilat coral reef. Int J Sys Evol Microbiol 56:365–368
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from the Israel Center for the Study of Emerging Diseases, the Israel Science Foundation, and the World Bank Coral Disease and Bleaching Groups.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Efrony, R., Atad, I. & Rosenberg, E. Phage Therapy of Coral White Plague Disease: Properties of Phage BA3. Curr Microbiol 58, 139–145 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-008-9290-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-008-9290-x