Abstract
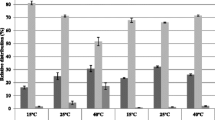
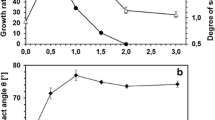
The adaptation of fatty acid composition of Chromohalobacter israelensis, a euryhalophilic bacterium, grown at different salt concentrations was studied. C. israelensis tolerated NaCl up to concentrations of 20% (w/v) and showed optimal growth at 7% (w/v). Major fatty acids of this bacterium were palmitic acid (16:0), stearic acid (18:0), palmetoleic acid (16:1cisΔ9), and cis-vaccenic acid (18:1Δ11). The salt concentration strongly influenced the fatty acid composition. In the presence of sub-optimal salt concentrations, the degree of saturation decreased, suggesting the importance of salt in maintaining the osmotic balance of the cell with its environment.


Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
SI Allakhverdiev Y Nishiyama I Osuzuki Y Tasaka N Murata (1999) ArticleTitleGenetic engineering of the unsaturation of fatty acids in membrane lipids alters the tolerance of Synechococcus to salt stress Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96 5862–5867 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.96.10.5862 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXjtFCnu7Y%3D Occurrence Handle10318975
SI Allakhverdiev A Sakamoto Y Nishiyama M Inaba N Murata (2000) ArticleTitleIonic and osmotic effects of NaCl induced inactivation of photosystem I and II in Synechococcus sp Plant Physiol 123 1047–1056 Occurrence Handle10.1104/pp.123.3.1047 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXlt1Slt74%3D Occurrence Handle10889254
DR Arahal MT Garcia W Ludwig KH Schleifer A Ventosa (2001) ArticleTitleTransfer of Halomonas canadensis and Halomonas israelensis to the genus Chromohalobacter as Chromohalobacter canadensis comb. nov and Chromohalobacter israelensis comb. nov Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51 1443–1448 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXmtVSmu7c%3D Occurrence Handle11491344
EG Bligh WJ Dyer (1959) ArticleTitleA rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification Can J Biochem Physiol 37 911–917 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaG1MXhtVSgt70%3D Occurrence Handle13671378
GR Brown IC Sutcliffe D Bendell SP Cummings (2000) ArticleTitleThe modification of the membrane of Oceanomonas baumanii when subjected to both osmotic and organic solvent stress FEMS Microbiol Lett 189 149–154 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-1097(00)00269-X Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXltlWhs74%3D Occurrence Handle10930729
LJ Halverson MK Firestone (2000) ArticleTitleDifferential effects of permeating and non-permeating solutes on the fatty acid composition of Pseudomonas putida Appl Environ Microbiol 66 2414–2421 Occurrence Handle10.1128/AEM.66.6.2414-2421.2000 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjvFWnsrw%3D Occurrence Handle10831419
HJ Heipieper R Diefenbach H Keweloh (1992) ArticleTitleConversion of cis unsaturated fatty acids to trans, a possible mechanism for the protection of phenol degrading Pseudomonas putida P8 from substrata toxicity Appl Environ Microbiol 58 1847–1852 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XksVCgsro%3D Occurrence Handle1622260
N Kabelitz PM Santos HJ Heipieper (2003) ArticleTitleEffect of aliphatic alcohols on growth and degree of saturation of membrane lipids in Acinetobacter calcoacetius FEMS Microbiol Lett 220 223–227 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-1097(03)00103-4 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXisV2mt7k%3D Occurrence Handle12670684
DJ Kushner (1985) The Halobacteriaceae CR Woese RS Wolfe (Eds) The bacteria, vol 8 Academic Press Orlando, FL 171–214
AG Marr JL Ingraham (1962) ArticleTitleEffect of temperature on the composition of fatty acids in Escherichia coli J Bacteriol 84 1260–1267 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF3sXit1Witg%3D%3D
KJ Miller (1986) ArticleTitleEffects of monovalent and divalent salts on the phospholipid and fatty acid compositions of a halotolerant Planococcus sp Appl Environ Microbiol 52 580–582 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28Xls1ymtL8%3D Occurrence Handle3801094
WR Morrison LM Smith (1964) ArticleTitlePreparation of fatty acid methyl esters and dimethylacetals from lipids with boron fluoride-methanol J Lipid Res 5 600–608 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF2MXhtVCqtw%3D%3D
S Mutnuri N Vasudevan M Kastner (2003) Biosurfactant production by an extremely halophilic bacterium R Devi N Ahsan (Eds) Water and wastewater: Perspectives of developing IWA UK 761–768
A Oren (1999) ArticleTitleBioenergetic aspects of halophilism Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63 334–348 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1M3os1eksw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10357854
M Potts (1994) ArticleTitleDesiccation tolerance of prokaryotes Microbiol Rev 58 755–805 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqC2MjjvFU%3D Occurrence Handle7854254
NJ Russell M Kogut M Kates (1985) ArticleTitlePhospholipid biosynthesis in the moderately halophilic bacterium Vibrio costicola during adaptation to changing salt concentrations J Gen Microbiol 131 781–789 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXkvVCktbg%3D
NJ Russell (1989) ArticleTitleAdaptive modifications in membranes of halotolerant and halophilic microorganisms J Bioenerg Biomembr 21 93–113 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00762214 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1MXhsFSqtb8%3D Occurrence Handle2651429
SC Singh RP Sinha DP Hader (2002) ArticleTitleRole of lipids and fatty acids in stress tolerance in cyanobacteria Acta Protozool 41 297–308 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XptV2ht7s%3D
MJ Valderrama M Monteoliva-Sanchez E Quesada A Ramos-Cormenzana (1998) ArticleTitleInfluence of salt concentration on the cellular fatty acid composition of the moderately halophilic bacterium Halomonas salina Res Microbiol 149 675–679 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0923-2508(99)80015-1 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXnsV2ju74%3D Occurrence Handle9826923
A Ventosa JJ Nieto A Oren (1998) ArticleTitleBiology of moderately halophilic aerobic bacteria Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62 504–544 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXkt1Oitb0%3D Occurrence Handle9618450
RH Vreeland (1987) ArticleTitleMechanisms of halotolerance in microorganisms Crit Rev Microbiol 14 311–356 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BieD3czlt1c%3D Occurrence Handle3308318
RH Vreeland EL Martin (1980) ArticleTitleGrowth characteristics, effects of temperature and ion specificity of the halotolerant bacterium Halomonas elongata Can J Microbiol 26 746–752 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3cXltFSgtbw%3D
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Marcell Nikolausz, UFZ for the identification of the bacterial strain and the German Academic Exchange Service (DAAD) for providing financial support to Mr. Mutnuri.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mutnuri, S., Vasudevan, N., Kastner, M. et al. Changes in Fatty Acid Composition of Chromohalobacter israelensis with Varying Salt Concentrations. Curr Microbiol 50, 151–154 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-004-4396-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-004-4396-2