Abstract
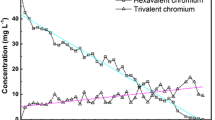
Arthrobacter species is of interest because of its high potential for bioremediation. Bacteria can detoxify chromium, by either reduction or accumulation inside the bacteria and/or absorption of chromium(VI) (CrVI) on their surface, and efflux pump. The possible pathway of Cr(VI) reduction by Arthrobacter oxydans isolated from Columbia basalt rocks at a US DOE highly contaminated site (USA) has been considered in the present study. FTIR absorption spectroscopy showed that these bacteria reduce Cr(VI). In the present study the threshold Cr(VI) nontoxic concentration (35 μg/mL) for A. oxydans growing in liquid medium was estimated. Complete uptake of this concentration was achieved in about 10 days after chromium addition into the medium. At this concentration an increase in the protein isolated from the cell wall of A. oxydans was observed. This increased protein predominated independently of the growth phase at which Cr(VI) was added. Thermal analysis was used to identify any influence of Cr(VI) on the DNP complex of A. oxydans. According to the data obtained it can be supposed that Cr(VI) reduction predominantly occurs on the bacterial surface and that cell wall represents a permeable barrier for these bacteria at the non-toxic chromium action.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asatiani, ., Abuladze, ., Kartvelishvili, . et al. Effect of Chromium(VI) Action on Arthrobacter oxydans. Curr Microbiol 49, 321–326 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-004-4351-2
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-004-4351-2